
- jaro education
- 12, March 2024
- 2:00 pm
Strategic human resource management (SHRM) refers to the alignment of human resource policies and practices with overall business goals. It ensures that the human resources of an organization are optimized to achieve its objectives. Unlike traditional HR roles focused on admin tasks, SHRM focuses on forward-thinking initiatives to develop talent, boost performance, and foster a positive work culture.
Alignment with Organisational Goals
Alignment with Organisational Goals requires:
1. Strategic Alignment
Strategic alignment is one of the key importance of strategic human resource management initiatives to drive business success. All aspects of human resource management, from talent acquisition to training and rewards, must ultimately serve the organization’s overarching strategy. For instance, if the goal is business expansion, HR strategies could focus on hiring people with the competencies needed for growth.
2. Long-Term Planning
One of the important functions of strategic human resource management is long-term workforce planning. Instead of addressing immediate HR concerns, SHRM takes a forward-looking approach to anticipate human capital needs. Such planning allows organizations to develop the talent pipelines required for future success. For example, succession planning ensuring leadership continuity in case of attrition at senior levels.
Table of Contents
Talent Acquisition and Retention
Talent Acquisition and Retention are critical features of strategic human resource management. For that, the managers need to apply recruitment strategies and employee retention abilities to keep the organization on par with competitors. Here are the short descriptions of what these two terms mean.
1. Recruitment Strategies
The ability to attract and recruit suitable talent is critical for organizational success. SHRM plays a key role through data-driven hiring practices tailored to business requirements. Strategic recruiting may involve extensive market research to identify channels that yield the best candidates. Organizations can strengthen their talent brand across these channels to draw top applicants. Recruitment strategies could also leverage technology like video interviewing to improve candidate screening.
2. Employee Retention
SHRM significantly impacts talent retention in organizations. Strategies like career development programs and skill-building incentives enhance employee satisfaction and commitment. SHRM also entails monitoring metrics like the turnover rate to identify problem areas that need improvement. For instance, exit interviews can provide insights into why employees leave, and suitable HR interventions can address those pain points through compensation reviews or culture change initiatives. By boosting retention, SHRM ensures business continuity and growth.
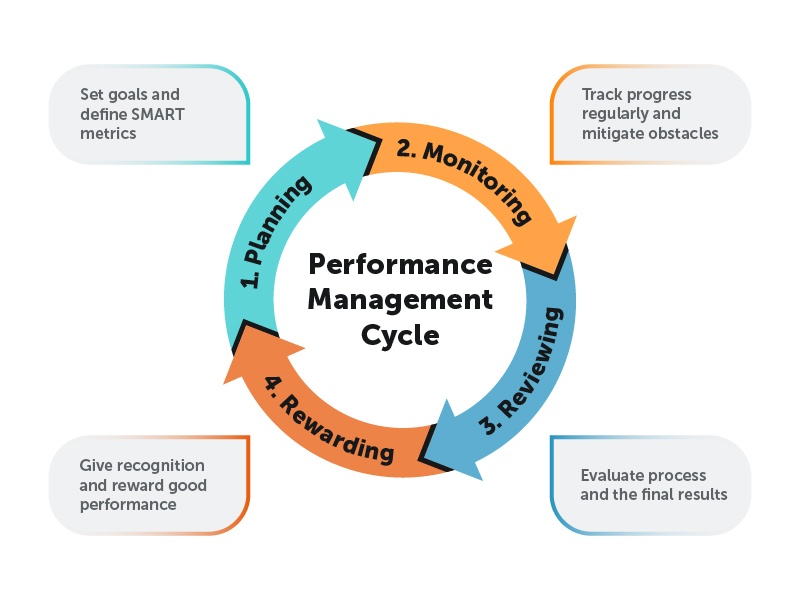
Performance Management
SHRM is key in developing performance management processes aligned with organizational objectives. This includes setting appropriate Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for employees based on their roles and monitoring performance vis-a-vis those KPIs. Regular feedback essential for improving performance is enabled through practices like biannual reviews.
*valamis.com
Training and Development
Training and Development focuses on:
1. Skills Enhancement
Ongoing training and workforce upskilling is a key SHRM priority to maintain organizational competitiveness. Training needs analyses help identify individual and collective skill gaps that must be addressed. Learning initiatives ranging from mentorship programs to e-learning modules can then be implemented to bridge those gaps.
2. Leadership Development
Strategic Human Resource Management facilitates leadership development across various organizational levels to build a robust talent pipeline. High-potential employees can be enrolled in fast-track programs to take on leadership responsibilities early on. Those in junior management roles may undergo external leadership development interventions.
Employee Engagement and Satisfaction
There is a proven correlation between SHRM and employee engagement levels in organizations. Initiatives like workplace flexibility and learning opportunities enhance engagement and satisfaction among employees. Employee surveys help identify areas of low engagement that require improvement. For instance, changes to performance evaluation processes could be undertaken if they emerge as a sore point. Higher employee engagement reduces turnover risks and fosters a collaborative organizational culture. This has a direct impact on productivity and strategic goal achievement.
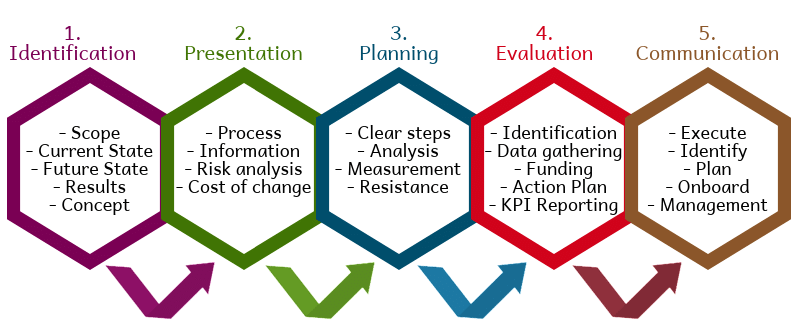
Change Management
In today’s evolving business landscape, managing change is a key priority for SHRM. HR has a significant role to play in organizational change management. For instance, when new technologies are introduced, SHRM ensures that employees are sufficiently trained and empowered to adopt them. Change communication is also critical to Secure employee buy-in and address concerns. SHRM analyzes adoption metrics to gauge the success of change initiatives. Any obstacles to change can be addressed through additional training or leadership intervention. Strong change management capabilities facilitated by SHRM confer strategic advantages to organizations.
*researchgate.net
Legal Compliance and Ethics
1. Legal Compliance
Compliance with all applicable laws and regulations is a fundamental SHRM responsibility in organizations. HR teams need to be well-versed in the nuances of labor law to ensure organizational practices are compliant. Violations can lead to expensive lawsuits and damages to the company’s reputation.
2. Ethical Considerations
In addition to legal requirements, organizations must make ethical HR decisions. SHRM promotes ethical integrity at the workplace through policies like anti-harassment guidelines and whistleblowing protections. Training on topics like unconscious bias also fosters sensitivity. SHRM measures aspects like pay equity to ensure compensation practices are fair.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Strategic HR decisions today are driven by workforce analytics and metrics. Employee surveys, retention data, performance scores and other HR metrics provide valuable insights that can inform strategy. For instance, productivity numbers may show that home-based employees deliver better results compared to those in the office – this could steer policies on remote work.
Conclusion
Strategic human resource management creates a powerful linkage between HR and broader business objectives in organizations. It takes a forward-looking approach to managing talent and fostering a high-performance work culture geared towards organizational success. SHRM initiatives like strategic recruitment, employee development programs, and change management ultimately impact the bottom line.
Thus, there is a bright scope for strategic human resource management and every HR professional must master it by taking up a valuable course. For instance, IIM Tiruchirappalli’s Post Graduate Certificate Programme in Strategic Human Resource Management. Learn to align talent and capabilities to business goals through forward-thinking SHRM. Explore areas like performance management, change leadership and more with IIM Trichy experts. So, elevate your career today with the prestige of an IIM Tiruchirappalli certification, symbolizing excellence and proficiency in Strategic Human Resource Management embark on a transformative journey towards becoming a strategic HR leader.









