
- jaro education
- 26, May 2024
- 6:19 pm
Big data analytics has changed the landscape of technology, and data is transforming at a rapid scale. With terabytes of data generated daily, companies are now taking further steps to handle it differently. So, what is this voluminous data called? It refers to big data; this cutting-edge approach empowers organizations to extract valuable insights from vast and complex datasets, paving the way for accurate decision-making and enhanced strategic planning. Learn more about big data analytics and how it’s helping businesses.
What is Big Data?
Big Data refers to a large volume of information collected or processed collectively. It encompasses vast datasets derived from various sources, such as user interactions, sensors, or transactions, typically measured in terabytes or more.
Managing and extracting valuable insights from this abundance of data pose significant challenges, prompting companies to adopt advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and scalable storage solutions to navigate the evolving landscape of technology and information.
Big Data Analytics has emerged as a game-changer for businesses and organizations seeking to extract valuable insights from the vast volumes of data generated daily.
Among the leading players in this field is Big Data Analytics, a robust and versatile platform that facilitates the processing, analysis, and interpretation of large datasets.
Table of Contents
What is Big Data Analytics?
Big Data Analytics is the process of examining large and complex datasets to uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and other useful information. It goes beyond traditional data analysis methods, as it deals with vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, streaming in from various sources such as social media, sensors, websites, and more. The primary goal is to extract meaningful insights that can drive business strategies, optimize processes, and enhance overall decision-making.
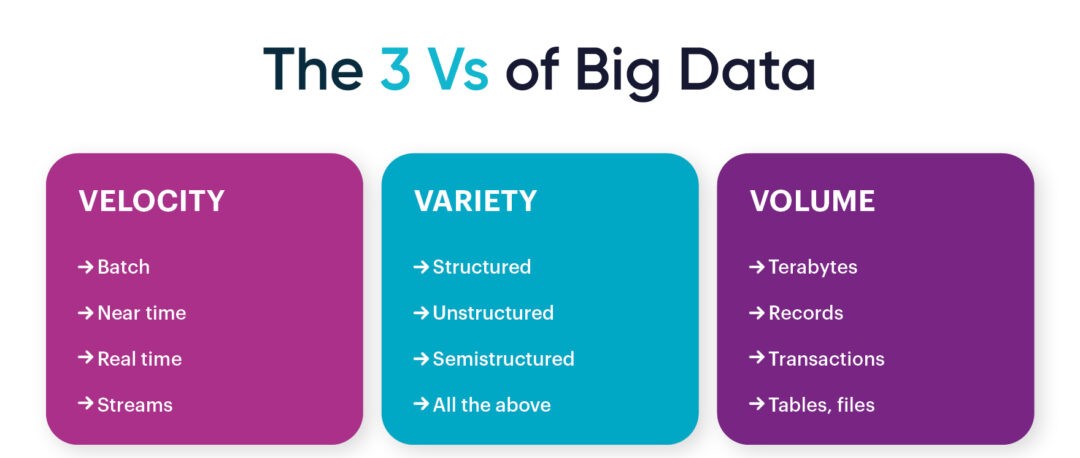
3 Vs of Big Data
To understand the essence of Big Data Analytics, one must delve into the three fundamental characteristics known as the “3 Vs”:
1. Volume
Big data refers to the immense volume of data generated daily. Traditional databases and analysis tools often struggle to handle these large datasets efficiently. Big Data Analytics solutions are designed to manage and process these massive volumes of information effectively.
2. Velocity
The speed at which data is generated and collected is another critical aspect. With the rise of real-time data streams from various sources, businesses need the ability to analyze and respond to information swiftly. Big Data Analytics enables the processing of data in real-time or near real-time, allowing organizations to make timely decisions.
3. Variety
Data comes in various forms – structured, semi-structured, and unstructured. This includes text, images, videos, and more. Big Data Analytics tools can handle this diverse range of data, providing a holistic view and uncovering insights that might be missed through traditional analysis methods.
Key Components of Big Data Analytics
The key components of big data analytics include:
1. Data Collection
Gathering data from diverse sources is the first step. This involves collecting structured and unstructured data from internal databases, external databases, social media, IoT devices, and more.
2. Data Storage
Managing large datasets requires robust storage solutions. Technologies like Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and NoSQL databases have become integral for storing and retrieving big data.
3. Data Processing
Analyzing vast amounts of data demands powerful processing capabilities. Technologies like Apache Spark and MapReduce are commonly used for distributed processing, enabling parallel computation to speed up analysis.
4. Data Analysis
The heart of Big Data Analytics lies in extracting meaningful insights. Advanced analytics techniques, including machine learning, statistical analysis, and predictive modeling, are employed to discover patterns and trends within the data.
5. Data Visualization
Communicating insights effectively is crucial. Data visualization tools translate complex findings into easy-to-understand visual representations, aiding decision-makers in understanding the implications of the data.
Importance of Big Data for Business
Big Data has become a crucial asset for companies in the modern business landscape. Its significance lies in the vast amount of information generated daily, offering valuable insights and opportunities for organizations to make informed decisions. Here’s an in-depth exploration of how Big Data is instrumental for companies:
1. Data-Driven Decision Making
Big Data empowers companies to make data-driven decisions. Organizations can identify patterns, trends, and correlations that might go unnoticed with traditional methods by analyzing large datasets. This informed decision-making process leads to more effective strategies and improved business outcomes.
2. Customer Insights and Personalization
Companies can leverage Big Data to gain profound insights into customer behavior. Analyzing customer interactions, preferences, and feedback allows businesses to tailor their products and services, creating a personalized experience. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also increases customer loyalty.
3. Operational Efficiency and Optimization
Big Data analytics helps companies streamline their operations. By analyzing internal processes and identifying inefficiencies, organizations can optimize workflows, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency. This leads to enhanced productivity and resource utilization.
4. Risk Management and Fraud Detection
Big Data plays a pivotal role in risk management and fraud detection. By analyzing patterns and anomalies in real time, companies can identify potential risks and fraudulent activities. This is particularly crucial in industries like finance, where timely detection can prevent significant financial losses.
5. Supply Chain Optimization
Companies with complex supply chains benefit from Big Data analytics. It enables them to track and analyze various elements of the supply chain, including inventory levels, production processes, and transportation logistics. This optimization leads to reduced costs, improved delivery times, and better overall supply chain management.
6. Market Research and Competitor Analysis
Big Data facilitates comprehensive market research and competitor analysis. Companies can gather and analyze data from various sources to understand market trends, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes. This information is invaluable for staying ahead of the competition and adapting to market changes.
7. Predictive Analytics for Future Trends
Big Data enables predictive analytics, allowing companies to anticipate future trends and market shifts. By analyzing historical data and current patterns, organizations can make proactive decisions, positioning themselves strategically in the market and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
8. Enhanced Customer Service
With Big Data, companies can improve their customer service by analyzing customer interactions and feedback. Predictive analytics can anticipate customer needs, and companies can implement chatbots or other automated systems to provide real-time assistance, enhancing the overall customer experience.
9. Innovation and Product Development
Big Data is a catalyst for innovation. By analyzing market trends and consumer preferences, companies can identify gaps in the market and develop innovative products or services. This proactive approach to product development can give companies a competitive edge in the industry.
10. Compliance and Security
Big Data analytics also plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with regulations and maintaining security. Companies can analyze data to identify potential compliance issues and implement security measures to protect sensitive information, fostering trust among customers and stakeholders.
Types of Big Data Analytics
Within this expansive field of big data, various types of analytics play crucial roles in extracting meaningful patterns and knowledge from massive datasets. Let’s find distinct categories of big data analytics that empower businesses and drive innovation.

1. Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics serves as the foundational layer, offering a retrospective view of historical data. It involves summarizing and interpreting past events to comprehensively understand what has occurred. Visualization tools and reporting mechanisms are commonly employed in descriptive analytics, enabling stakeholders to grasp trends, patterns, and anomalies within datasets. This type of analytics forms the basis for more advanced analytical techniques.
2. Diagnostic Analytics
Moving beyond the ‘what’ of descriptive analytics, diagnostic analytics focuses on the ‘why’ and ‘how.’ It seeks to uncover the root causes of specific events or trends observed in historical data. By employing techniques such as data mining and drill-down analysis, organizations can identify factors contributing to success or failure, enabling them to make informed adjustments to improve outcomes.
3. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics harnesses the power of statistical algorithms, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to forecast future trends and outcomes. This type of analytics involves creating models based on historical data and using them to make predictions about future events. Businesses leverage predictive analytics to enhance decision-making, optimize processes, and anticipate market trends, thereby gaining a competitive edge.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics takes a proactive approach by recommending actions to optimize outcomes. This advanced form of analytics combines descriptive, diagnostic, and predictive insights to offer actionable advice. By simulating various scenarios and assessing potential outcomes, prescriptive analytics guides decision-makers toward the most effective strategies, helping organizations stay agile in dynamic environments.
5. Text Analytics
Text analytics (text mining or natural language processing (NLP)) involves extracting valuable insights from unstructured text data. With the proliferation of social media, customer reviews, and other text-rich sources, businesses can analyze sentiments, identify emerging themes, and extract meaningful information. Text analytics is invaluable for understanding customer feedback, monitoring brand perception, and uncovering market trends hidden within textual data.
6. Spatial Analytics
Spatial analytics integrates geographical information systems (GIS) with big data to analyze location-based data. This type of analytics is particularly relevant for industries such as logistics, urban planning, and environmental monitoring. By examining spatial patterns and relationships, organizations can optimize routes, allocate resources efficiently, and make data-driven decisions within a geographical context.
Applications of Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics involves the processing and analyzing of vast and complex datasets to extract valuable insights and make effective decisions. This powerful tool has found applications across various industries, transforming the way organizations operate and strategize. The applications of big data analytics are:
1. Business Intelligence and Decision Making
Big data analytics empower organizations to make data-driven decisions by providing comprehensive insights into customer behavior, market trends, and internal processes. Businesses can analyze large datasets to identify patterns, forecast trends, and optimize strategies, leading to more informed and effective decision-making.
2. Healthcare Revolution
In the healthcare sector, big data analytics has been a game-changer. It facilitates personalized medicine by analyzing patient data, genetic information, and treatment outcomes. Predictive analytics helps healthcare providers identify potential outbreaks, optimize resource allocation, and enhance patient care. The integration of big data analytics has the potential to revolutionize disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
3. Financial Sector Optimization
Financial institutions leverage big data analytics for fraud detection, risk management, and customer relationship management. Analyzing vast amounts of financial data in real time allows institutions to detect anomalies and patterns associated with fraudulent activities, ensuring the security of transactions. Moreover, predictive analytics aids in assessing and managing financial risks.
4. E-commerce and Customer Experience
In the realm of e-commerce, big data analytics plays a pivotal role in enhancing customer experience. Retailers analyze customer preferences, purchase history, and online behavior to personalize marketing strategies and recommendations. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also increases sales through targeted and relevant product offerings.
5. Supply Chain Optimization
The optimization of supply chain operations is another area where big data analytics excels. By analyzing data related to inventory, logistics, and supplier performance, organizations can streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency. Predictive analytics helps in demand forecasting, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively.
6. Smart Cities and Urban Planning
Big data analytics contributes to the development of smart cities by processing vast amounts of data from sensors, social media, and other sources. This information improves traffic management, energy consumption, waste management, and overall urban planning. Cities can become more sustainable, efficient, and responsive to the needs of their residents.
7. Education and Learning Analytics
In the education sector, big data analytics aids in understanding student performance, engagement, and learning patterns. Learning analytics help educators tailor teaching methods to individual needs, identify at-risk students, and enhance overall educational outcomes. Institutions can make data-informed decisions to improve curriculum design and student success.
8. Predictive Maintenance in Industry
Industries with complex machinery, such as manufacturing and utilities, benefit from predictive maintenance powered by big data analytics. By analyzing equipment sensor data, organizations can predict potential failures and schedule maintenance activities proactively. This not only reduces downtime but also extends the lifespan of critical assets.
*pickl.ai
Challenges and Considerations of Big Data Analytics
As organizations grapple with increasing volumes of data, they face various obstacles that range from technical issues to ethical concerns. Here, we delve into the key challenges and considerations associated with big data analytics.
1. Volume, Velocity, and Variety
One of the fundamental challenges of big data analytics lies in managing the three Vs – Volume, Velocity, and Variety. The sheer volume of data generated daily can overwhelm traditional processing systems. The high velocity at which data is generated requires real-time analytics capabilities and dealing with diverse data types and sources adds complexity to the process.
2. Data Quality and Integration
The quality of the data is crucial for accurate analysis. Consistent, complete, and accurate data can lead to flawed insights and decisions. Integrating data from different sources, each with its own format and structure poses a significant challenge. Organizations must invest in data cleaning, transformation, and integration processes to ensure the reliability of their analytics results.
3. Scalability and Infrastructure
As data volumes grow, scalability becomes a critical concern. Traditional databases and infrastructure may struggle to handle the increased workload. Implementing scalable and flexible infrastructure, such as cloud-based solutions, is essential to meet the evolving demands of big data analytics.
4. Security and Privacy
Handling massive amounts of data raises concerns about security and privacy. Protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations are paramount. Organizations must implement robust security measures, including encryption and access controls, to safeguard their data and maintain user trust.
5. Talent and Skills Gap
The field of big data analytics demands a specialized skill set that includes data scientists, analysts, and engineers proficient in various tools and programming languages. The shortage of skilled professionals poses a significant challenge for organizations aiming to leverage big data effectively. Continuous training and development efforts are necessary to bridge this skills gap.
6. Cost Management
Implementing and maintaining a big data analytics infrastructure can be costly. From hardware and software expenses to hiring skilled personnel, organizations must carefully manage their budget to ensure a positive return on investment. Cloud-based solutions offer a flexible pay-as-you-go model, but monitoring and optimizing costs remain crucial.
7. Ethical Considerations
Big data analytics raises ethical concerns related to privacy, bias, and the responsible use of data. Analyzing personal information without consent, unintentional biases in algorithms, and potential discrimination are ethical challenges that demand attention. Organizations must establish ethical guidelines and frameworks to guide their data analytics practices.
8. Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the complex landscape of data protection laws and regulations is a significant consideration in big data analytics. Different regions have varying rules regarding data storage, processing, and sharing. Staying compliant with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal repercussions and maintain customer trust.
Conclusion
While big data analytics offers tremendous opportunities for innovation and business growth, organizations must navigate a myriad of challenges and considerations. From technical hurdles to ethical dilemmas, addressing these issues requires a holistic approach that combines technological advancements, skilled personnel, and a commitment to ethical and legal standards.
As the landscape of big data evolves, organizations that proactively address these challenges will be better positioned to unlock the full potential of data analytics.
As professionals turn to courses in data sciences, institutes have started offering different courses based on market trends. Students and professionals can register for M.Sc (Data Science) – offered by Symbiosis School For Online And Digital Learning. The course provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the lifecycle of data science and prepares professionals with data science knowledge, which is much needed in the market today.









