
In this blog, we’ll explore the nature and types of managerial economics, its core concepts, and the exciting career opportunities it offers.
Concept of Managerial Economics
It is all about using economic principles to tackle real-world business challenges. Think of it as the bridge that connects the theoretical world of economics with the practical side of running a business. This field provides managers with valuable tools and techniques to make smart, strategic decisions. Whether it’s understanding market demand, analyzing costs and benefits, or navigating competitive landscapes, it equips managers to optimize their operations and boost profitability.
At its core, it’s about making business operations more efficient and effective, ensuring resources are used wisely and goals are met. In other words, it helps turn economic theory into actionable business strategies that drive success.
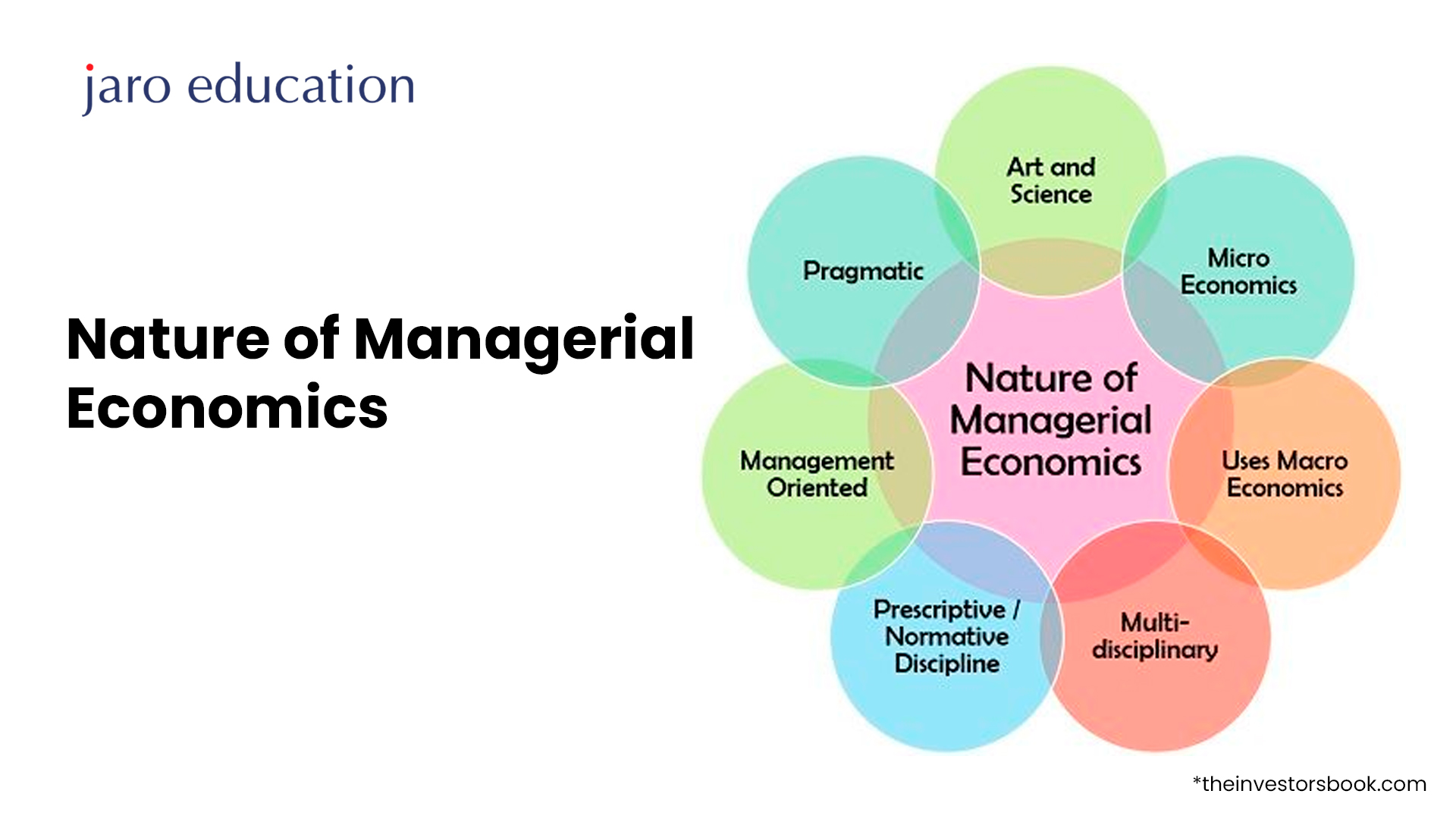
Table of Contents
Nature of Managerial Economics
Its nature can be understood through its various characteristics:
-
- Integrated Approach: It blends elements from economics, business management, mathematics, and statistics. This multidisciplinary approach helps managers make well-rounded, effective business decisions.
- Microeconomic Emphasis: Focusing on microeconomic concepts, it aids managers in understanding market mechanisms, demand and supply dynamics, and pricing strategies specific to their market niche.
- Practical Decision-Making: Applying economic theories to real-world scenarios, managerial economics equips managers with tools to make practical, applicable business decisions.
- Data-Driven Insights: Quantitative techniques and data analysis are central, providing managers with empirical evidence to inform decisions and strategies.
- Efficiency Focus: The field aims to enhance business efficiency through optimal resource allocation, cost reduction, and maximizing outputs.
- Strategic Planning: It aids in forecasting market trends, evaluating economic environments, and developing long-term strategies aligned with business goals.
- Behavioral Insights: Incorporating behavioral economics, it considers psychological factors in business decisions, enhancing marketing and customer relations.
- Adaptive Techniques: It encourages continuous strategy adjustment based on market changes, new data, and evolving economic conditions.
- Sustainability Focus: Modern practices emphasize sustainable business decisions, aligning profitability with social responsibility.
- Holistic Problem-Solving: Providing a comprehensive view, it enables managers to develop multi-faceted solutions to complex business problems.
In essence, it merges theory with practice, equipping managers with essential tools to make informed, efficient, and strategic business decisions.
Types of Managerial Economics
Managerial economics encompasses several distinct types, each playing a pivotal role in the decision-making process within organisations.
Descriptive Managerial Economics
It involves the systematic analysis of historical data and trends. This type of analysis serves as a valuable foundation for decision-makers, allowing them to establish benchmarks, evaluate past performance, and identify market trends. For example, retail managers may examine past sales data to set sales targets and assess the effectiveness of previous marketing strategies.
Normative Managerial Economics
It shifts the focus towards policy formulation and strategic planning and provides a framework for recommending courses of action based on economic analysis, long-term goals, and ethical considerations. This type of analysis is instrumental in crafting organisational policies, defining strategic objectives, and ensuring that decisions align with ethical standards. For instance, it aids in developing sustainability initiatives and corporate social responsibility guidelines.
Prescriptive Managerial Economics
It is all about executing plans efficiently and effectively. Once strategies are in place, this type of analysis guides managers in creating detailed implementation plans, allocating resources judiciously, and establishing mechanisms for monitoring progress. It ensures that strategic decisions translate into actionable steps, leading to successful execution and goal achievement.
Positive Managerial Economics
It shifts the focus to understanding and explaining the impact of economic variables on managerial decisions and outcomes. This type of analysis delves into causal relationships between economic factors and managerial choices, often relying on predictive modelling and statistical analysis. It helps managers comprehend how changes in economic variables, such as consumer income or market conditions, influence decision outcomes and risks and thereby facilitates more informed and data-driven choices.
Thus, each type of managerial economics brings a unique perspective to the decision-making process, from providing historical context and ethical considerations to guiding implementation and enhancing predictive capabilities. By incorporating these different types of analysis, organisations can navigate complex business landscapes, make well-informed decisions, and ultimately achieve their strategic objectives while staying competitive in their respective industries.
Career Options in Managerial Economics
| Career | Description |
|---|---|
| Strategic Planner | Develop long-term strategies for businesses, focusing on growth, competitive advantage, and market positioning. They analyze market trends and economic data to guide the company's future direction. |
| Operations Manager | Oversee the day-to-day operations of a business, ensuring efficiency and productivity. They use economic principles to streamline processes and improve operational performance. |
| Corporate Manager | Manage various departments within a corporation, such as finance, marketing, or operations. They apply it to optimize departmental performance and achieve organizational goals. |
| Management Consultant | Advise businesses on improving efficiency, productivity, and profitability. They use economic analysis to identify issues and recommend solutions tailored to the company's needs. |
| Project Manager | Plan, execute, and oversee projects from start to finish. They use economic principles to manage resources, budgets, and timelines effectively. |
| Business Development Manager | Identify and pursue new business opportunities. They analyze market conditions, assess economic viability, and develop strategies to expand the business. |
| Economic Researcher | Conduct research on economic issues, trends, and policies. They provide valuable insights to businesses, government agencies, and think tanks to inform decision-making. |
Conclusion
It is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their operations and achieve strategic goals. By applying economic theories to real-world scenarios, it provides managers with the necessary tools for effective decision-making, resource allocation, and strategic planning. Understanding the principles of it can lead to more informed decisions, improved efficiency, and greater business success across various industries. The insights and skills gained from this field are invaluable in navigating the complexities of the business world and driving long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
It is the application of economic theories and methodologies to solve business problems and make informed managerial decisions.
Key characteristics include its interdisciplinary nature, practical application, focus on decision-making, use of quantitative and qualitative analysis, and future-oriented approach.
Career options include business analyst, financial manager, market research analyst, consultant, and operations manager.
It provides tools and frameworks to analyze business problems, forecast trends, and develop strategies, aiding managers in making informed decisions.
It helps businesses optimize their operations, allocate resources efficiently, and achieve their financial and strategic goals.









