An All-Inclusive Guide to Financial Regulation
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 23, March 2024
- 10:00 am
In a world where various financial institutions are connected and their financial management is getting more complicated, the topic of financial market regulation is critical. Financial regulation is the term used to describe the rules and practices that guide the operation of financial institutions and the business markets. As the new technology impacts the structure of financing, detailed comprehension of the specifics of financial regulation becomes essential for both – the specialists and the clients.
This blog explores the significance of financial regulation, highlights its relevance, and examines the trends shaping the financial services industry in India. Join us as we delve into the key aspects of this vital topic!
What is Financial Regulation?
Financial regulation may be defined as many and varied legal requirements aimed at ensuring the integrity and stability of the financial sector. It comprises supervision of financial entities relative to banks, investment entities, and insurance firms. The key objectives of financial regulation include the protection of consumer interests to foster fair trade. Engendering greater accountability in the financial markets and minimizing the options for financial crises and major failures.
Major elements of financial regulation include:
- Licensing and Supervision: Lenders must also have permits to operate which guarantee they are meeting some requirements of the law.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Rules help to shield buyers from misconduct, deception, or abuse as they access products and services.
- Anti-Money Laundering Regulations: Certain checks are done to curb bad practices in the financial system and also to improve security.
Why is Financial Regulation Important?
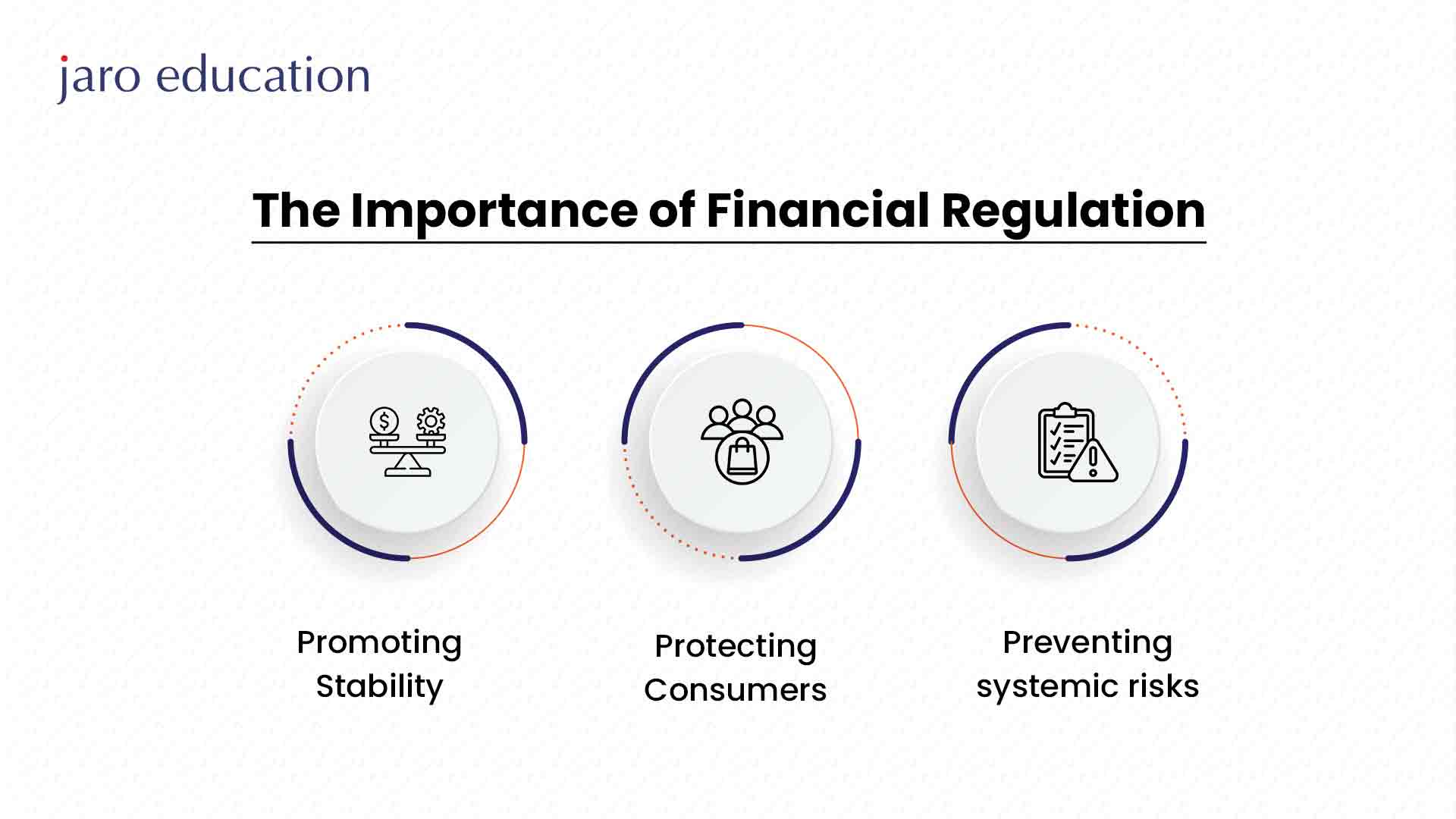
It’s important to note that financial regulation works as pillars that build up a strong and reliable financial system. Here are some main reasons why these regulations are vital:
*fastercapital.com
- Consumer Protection: There are still many complaints about financial regulation that protect consumers, allowing them to seek such legal remedies as needed. For example, legal rules demand that financial services providers report specific information to consumers to protect them from unreasonable risks.
- Market Integrity: Regulations preserve trust in financial markets by ensuring that all working processes are transparent and fixed. In this case, the investors will be encouraged to support the system to improve the economy’s performance due to their faith in the system.
- Financial Stability: Stringent measures reduce the systemic risks that are likely to cause financial meltdown. This is a clear indication that laxity in regulation, as seen during the 2008 financial crisis, can lead to significant undesirable results.
- Promoting Fair Competition: This financial regulation also helps the general public pursue fairness in competition within given institutions to avoid the monopolization of certain institutions by other institutions that would exploit the rest of the market.
Trends in the Financial Services Industry in India
The constant development of new technologies, financial products, and dynamic market trends drives the continuous evolution of financial market regulation in India. These changes will continue to reshape regulatory control over guaranteeing compliance and securing the financial system. Below are some of the main trends shaping the flow of regulators of the money market:
1. Increased Focus on Technology and FinTech
Recently, there has been significant growth in innovative financial services methods, such as digital banking platforms and FinTech, presenting both opportunities and challenges. In response, financial system stability is ensured while regulators come up with forward-looking measures that promote innovation, such as regulatory sandboxes and a digital banking license.
Regulatory Sandboxes
- A regulation sandbox is a supervised space for FinTech startups and innovators to experiment with their financial products and services within specific regulatory limits.
- Companies can build out their offerings and test out innovative solutions within these sandboxes, easing the burden of compliance.
- The benefits are reducing regulatory hurdles for startups, increasing open communication between innovators and regulators, and allowing regulators to gain hands-on insights into emerging technologies.
2. Enhanced Regulation of Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
As more investors, businesses, and governments worldwide begin to accept cryptocurrencies and digital assets as part of the broader financial system, regulatory laws are starting to catch up. Regulatory frameworks are being updated to reflect both the risks and the opportunities.
The focus is on two major areas: Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) programs, as well as establishing security and custody standards for digital assets.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC)
Cryptocurrencies are both non-decentralized and pseudonymous, which makes financial crime prevention very difficult. This has caused regulators to extend AML and KYC rules to cryptocurrency exchanges, wallet providers, and all other companies dealing with digital assets.
Security and Custody Standards
With the rise of digital assets, securing these assets and their proper custody has become a big priority among regulators.
- Custody standards: They include cybersecurity protocols, physical security and operational best practices tailored for digital assets.
- Regulatory oversight: Digital asset custodians are also being subject to frameworks to oversee them with licensing and compliance checks. It ensures that custodians of digital assets remain in high standards of security.
3. Strengthening Cybersecurity Measures
With the digitisation of financial services reaching new heights, financial institutions have also been given tremendous convenience. However, with convenience, they also face cybersecurity risks. Financial losses can occur from cyberattacks as a result of which trust in customers is diminished and financial system stability jeopardized.
As a result, Global regulators are now placing improved cybersecurity defences for financial institutions. They are also focusing on making sure that the financial system can withstand a wide range of cyber threats.
Enhancing Cyber Defenses
There are multiple standard ways that are being implemented to keep financial institutions protected from various cybersecurity threats. These standards are further divided into multiple stages, some of which are:
Risk assessment: Financial institutions are under a statutory obligation to conduct regular risk assessments to conclusively ascertain areas in which their systems and operations may have a ‘vulnerability’ factor.
- Security protocols: To stay safe from cyber threats, institutions must adopt advanced security protocols, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure software development practices.
- Employee training: Regulators require that employees be trained on cybersecurity every year because human error is a big risk factor.
- Vendor risk management: Often breaches in supply chain partners lead to losses in financial institutions. So financial institutions have the responsibility to keep those third-party vendors and service providers to a very stringent standard of cybersecurity.
4. Globalisation and Harmonisation
Financial markets have greatly benefited from the globalisation of investment, driving significant economic growth worldwide. However, this globalisation also presents challenges, such as regulatory arbitrage and the oversight of multinational financial institutions. As a result, there is an increasing focus on global coordination and harmonisation of financial regulation.
Its objective is to build a stable, transparent, and efficient international financial system by addressing regulatory arbitrage.
Addressing Regulatory Arbitrage
The issue of this disparity is mitigated by global regulatory coordination, as regulatory frameworks are aligned, loopholes are reduced, and institutions cannot exploit differences in regulatory standards. Key regulations are standardized between jurisdictions, which reduces the incentive for institutions to relocate operations to jurisdictions with more lenient regulations, thereby improving global financial stability.
| Other Trends Influencing the Regulator of Money Market | Description |
|---|---|
| Financial Inclusion | Ways to provide financial services for people in all sectors. The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana is targeting the coverage of every single Indian citizen and linking him/ her to a bank account thus increasing the inclusion of more people in the formal financial sector. |
| Sustainable Finance | Promoting responsible and sustainable practices. |
The future of financial regulation in India looks positive, with the government backing innovation and maintaining consumer protection and market stability.
Here are the financial courses to elevate their professional skills.
- Financial Management – IIM Trichy
Programme Overview of the Post Graduate Certification Programme in Financial Management – IIM Tiruchirappalli: Intended to come out fully equipped with all the information a manager is likely to need in the financial realm. Stresses the functioning of the financial decision and corporate finance.
Key Features:
- Duration: 12 months.
- Mode: Hybrid learning (virtual and campus-based learning).
- Certification: Professional certification from IIM Trichy.
- Assignments: Practical work and other assignments to keep the knowledge up to date.
- Investment Banking – IIM Trichy
Programme Overview of the Post Graduate Certificate Programme in Banking & Finance: Specializes in the structures of investment banking as well as the valuation issues. Intended to develop participant’s abilities to analyze and decide on major operations.
Key Features:
- Duration: 12 months.
- Mode: Hybrid learning (virtual and campus-based learning).
- Certification: Post Graduate Certificate from IIM Trichy.
- Industry-Relevant Curriculum: This course is updated to the current market trends.
Additional Benefits:
- Actual practical assignments or cases.
- Gaining exposure to industry information with guest speakers.
- Sharing ideas with other students and working professionals.
Students who attend finance courses by enrolling in these courses get exposure that helps them understand the aspect of financial regulation in the market. The practical orientation of the institution guarantees the graduates to be abreast with changes in the financial market.
How Can Jaro Education Help You
Jaro Education is a top online higher education and upskilling company extending services to assist students pursuing career goals that aligs with their skills. For various programmes offered by the prestigious IIMs and IITs, including the above listed programmes, we act as a marketing and technology partner. With years of experience and expertise, we have assisted thousands of students in shaping their careers. If you are enrolling in the programmes, whether for financial management or investment banking, from Trichy through us, you have the leverage to take Jaro Benefits. Wondering what are they? Here is the answer.
Jaro Expedite – Career Booster
Here you will get:
- Placement assistance
- Resume building assistance
- Virtual profile building including LinkedIn
- Lifelong career experience
So, don’t wait for time to pass—enrol in your favourite program right away! On your journey, Jaro will always be there to support you.
Final Thoughts
It can be underscored that relevant financial regulation constitutes one of the pillars of a sustainable and highly effective financial system. It can hardly be overemphasized as it shields the consumer, Foster’s market efficacy, and maintains stability in the finance sector. Finance courses aim to bridge the gap between individuals and institutions to get useful knowledge and information on matters central to the current financial world that enable an individual to fit properly in this volatile facet of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
The financial regulation provides the financial market with a high level of integrity, protects the consumers and maintains monetary stability.
Regulations are necessary to reduce fraud and guarantee transparency in businesses and other organizations to avoid disappointments with the financial situation.
It is fascinating that the application of innovative technology leads to the comprehensible creation of differential financial regulator models that support existing risks and improve compliance.
The applicable trends for the current analysis include the digital shift, improving compliance, and initiatives promoting financial access.
Seek information on the curriculum you are interested in, faculty in the college or university and flexibility in the delivery of the curriculum.










2 thoughts on “An All-Inclusive Guide to Financial Regulation”
Clear and informative blog on financial regulation! It provides a thorough explanation of key concepts and the importance of regulatory frameworks in finance.
Informative post on financial regulation! The explanation of its importance and impact on businesses is clear and insightful. Great job!