A proactive approach for examining, modelling, assessing, growing, and optimising corporate processes and strategies is called business process management (BPM). It is distinct from task and project management as it focuses on the entire end-to-end process rather than individual tasks or one-time projects. BPM involves continuous process reengineering to streamline workflows, enhancing efficiencies and cost savings. This concept is not new and is aligned with methodologies like Six Sigma and Lean principles. BPM suites allow enterprises to coordinate employees, systems, and information to accomplish targeted company objectives using advanced analytics, activity tracking, and decision-making capabilities. The techniques for speeding digital transformation are significantly supported by these suites.
It is essential to equip yourself with the skills required to succeed as a leader in the contemporary business world in today’s revolutionary digital era when worldwide uncertainty is encouraging new-age advances across every sector. The Executive Programme in Business Management offered by IMT Ghaziabad, one of India’s top institutions, is an essential starting point in learning how to deal with the dynamic problems of tomorrow. Participants will benefit from this business management course that strongly emphasises simulations and learning.
Importance of Business Process Management
Business process management (BPM), which increases output, flexibility, and effectiveness, is essential for enterprises. The definition, design, implementation, and ongoing improvement of a company’s procedures that lead to the creation of goods and services are all included in BPM.Businesses can boost operational efficiency by streamlining operations and identifying and eliminating bottlenecks. This optimisation can lower expenses related to inefficient processes while improving the general standard of products and services offered to clients.
Different Types of Business Process Management
Based on its primary function, business process management (BPM) solutions can be divided into different categories. Successful companies widely use the following three BPM systems.
Integration-centric BPM
This kind of BPM system concentrates on managing processes mainly concerned with integrating and transferring data with existing systems like Customer Relationship Management, Human Resource Management Systems, and Enterprise Resource Planning. These systems use connectors and APIs to provide quick process execution while allowing effortless transfer of data and communication between various systems.
Human-centric BPM
Human-centric BPM systems are designed for processes that heavily involve human interactions and tasks. These processes often need approvals, collaboration, and manual interventions. Human-centric BPM platforms prioritise user-friendly interfaces, easy notifications, and efficient task tracking to ensure smooth collaboration and effective execution of human-centric processes.
Document-centric BPM
Solutions for business process management (BPM) that focus on documents, such as contracts or agreements, are designed exclusively for these procedures. As documents move through the workflow, these technologies make it possible to carry out functions, including routing, presentation, checking, and acquiring document signatures. They offer features to manage processes based on documents effectively, assuring correctness, compliance, and timely completion.
It is vital to note that many BPM systems integrate elements from each of these classifications, but depending on the particular requirements of the company or process, they may focus on one particular area.
Table of Contents
Lifecycle of Business Process Management
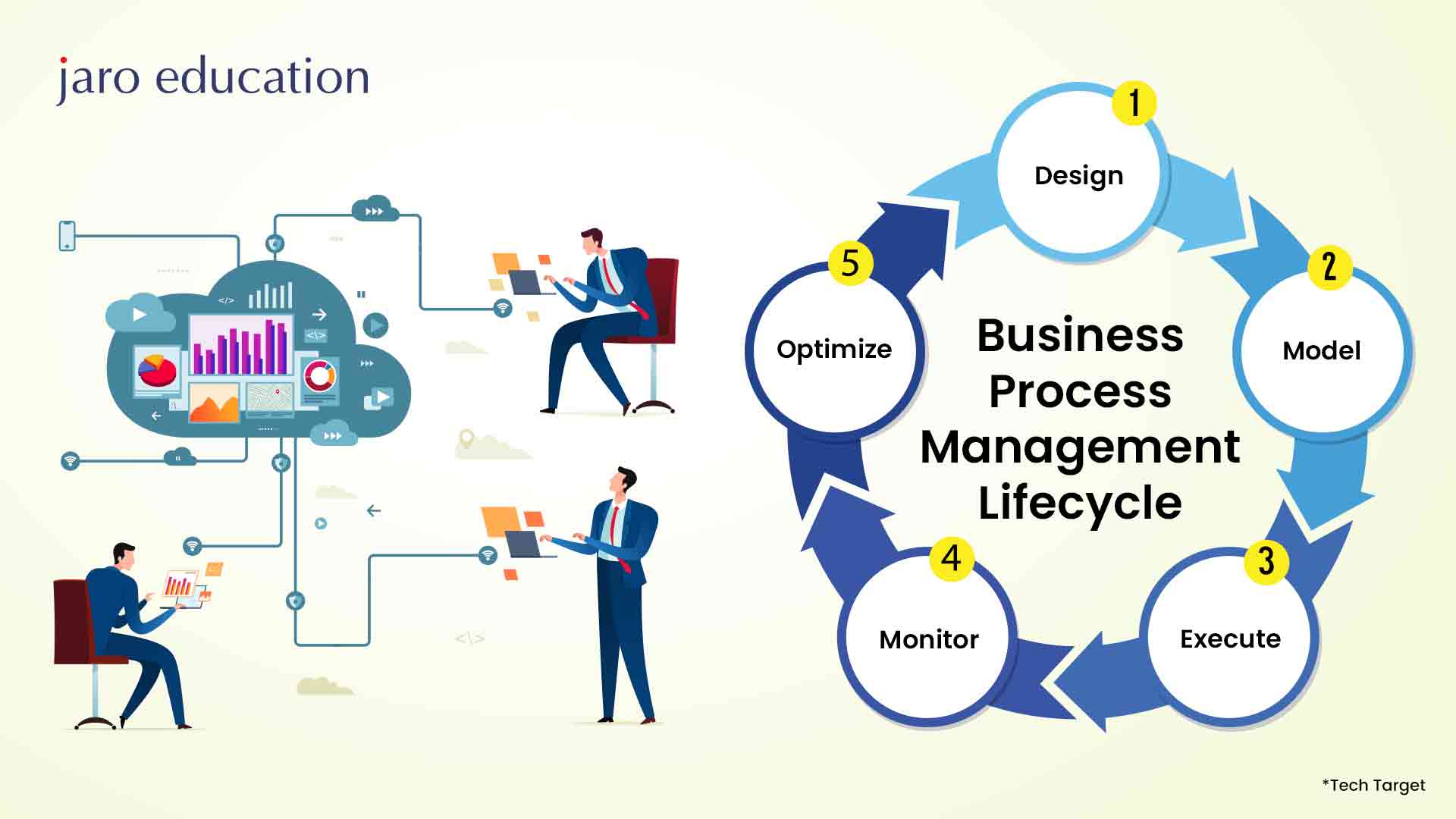
A number of essential components are included in the business process management (BPM) lifecycle to guarantee proper implementation and operation improvement. For firms looking to improve their business processes and outcomes, understanding this lifecycle is essential. The BPM lifecycle comprises a series of five steps, including:
Step 1: Process Design
The first step is to define the stages and milestones within the workflow. This helps identify areas for improvement and establish metrics to track progress. Clear definitions of individual tasks and their owners are crucial for optimising the process.
Step 2: Model
In this step, a visual representation of the process model is created. It includes important details like timelines, task descriptions, and data flow within the process. Utilising BPM software can be beneficial during this stage to facilitate modelling and documentation.
Step 3: Execute
The process is tested and implemented with a limited group, often through a proof of concept. Feedback is collected and incorporated into the process before rolling it out to a broader audience.
Step 4: Monitor
Once the process is in place, ongoing monitoring is essential. This involves measuring efficiency improvements and identifying any areas that require further optimisation.
Step 5: Optimise
The final step involves making necessary adjustments to the process based on the monitoring and feedback received. Continuous optimisation ensures that business activities are constantly improved and aligned with organisational goals.
Careful planning, efficient communication, and teamwork are necessary for the successful implementation of BPM. Teams can quickly benefit from higher efficiency and productivity if a set of activities is improved through BPM.
*Tech Target
Different Cases of Business Process Management
Software for business process management (BPM) provides a valuable framework for optimising workflow and getting rid of errors. It has shown success across a range of practical conditions, like:
1. Content distribution
Media companies can use BPM to automate the creation and delivery of content. It interfaces with work orders, rights management, and content management systems to enable a fluid workflow from content generation to delivery.
2. Customer service
By detecting common questions and permitting chatbots to respond to them, BPM will assist clients and employees. When there are a lot of service requests, this helps the team. In addition, activities can be automated, and clients can receive specific responses using call centre and chatbot transcript data.
3. Finance
Businesses can create uniform formats for purchase order submissions, allowing for quicker corporate software or hardware acquisition. BPM allows for custom workflows to address exceptional circumstances effectively.
4. Human resources
BPM benefits HR departments in simplifying document and workflow management. It provides a structured setting for processing various HR forms, including those for timesheet approvals, evaluations of performance, leave requests, and staff onboarding and offboarding.
5. Banking
Banks assess the credit risk of loan applications with the help of BPM. It gathers data from numerous sources, including potential employees, employers, and credit rating companies. BPM speeds up determining loan eligibility by controlling information flow and minimising documentation errors.
6. Order fulfilment
BPM increases the operational efficiency of order fulfilment systems. It manages special offers, order capture, and order fulfilment, enabling customer-centric order management that delivers greater business value.
These are examples of how BPM software may be used successfully across several industries to maximise processes, raise productivity, and generate superior business results.
Benefits of Business Process Management
BPM solutions provide numerous benefits that enhance organisational value through process improvement. Some of these benefits include
Increased efficiency and cost savings
The systems associated with BPM optimise existing processes and introduce structure to developing new techniques. By eliminating redundancies and bottlenecks, organisations experience improved efficiency and productivity. This leads to cost savings and enables allocating resources to other high-priority work.
Better employee and customer experiences
BPM technologies free up personnel to concentrate on their work and customers by eliminating repetitive processes and improving information accessibility. Customer happiness goes up, while employee engagement and productivity improve. Additionally, speedier staff onboarding is made possible by transparent workflows.
Expandable processes
With BPM, it is possible to execute processes effectively and automate workflows. It facilitates scaling processes across many geographic locations. With that, it clarifies roles, guarantees consistency in the processes, and spots chances for automation through business rules. As a result, teams may maintain scalability while concentrating more on innovation.
Greater accountability
BPM’s business process automation property clearly identifies task owners, improving accountability throughout the process. It improves teamwork and makes sure that everyone is aware of their obligations.
Less reliance on development teams
Low-code features are frequently provided by BPM solutions that enable business users to automate processes without necessitating a significant amount of assistance from development teams. This quick and simple onboarding procedure lowers the need for in-depth coding or technical expertise while increasing process automation throughout the firm.
These benefits demonstrate how BPM solutions drive efficiency, effectiveness, and collaboration within organisations, leading to improved outcomes while giving a competitive edge.
When should organisations start using Business Process Management?
Organisations should consider implementing Business Process Management (BPM) in various scenarios where it can result in a high return on investment. Here are some instances:
Dynamic processes with regulatory compliance changes
When business processes need to adapt to regulatory changes, such as customer information management following finance or privacy law updates, implementing BPM ensures efficient and compliant execution.
Complex processes requiring coordination across multiple units
BPM is beneficial for processes that involve multiple business units, divisions, or functional departments. It helps orchestrate and coordinate activities, improving collaboration and overall process efficiency.
Mission-critical processes with measurable impact
One should implement BPM for processes that directly impact crucial performance metrics. By managing and optimising these processes, organisations can achieve tangible improvements in key areas of their operations.
Processes dependent on legacy applications
BPM is valuable for managing processes that rely on legacy applications. It provides a structured approach to integrate and streamline these processes, improving efficiency and reducing reliance on outdated technology.
Processes with manual handling and time-sensitive exceptions
Companies can use BMP for processes that involve manual handling of exceptions or require quick turnarounds. It helps automate routine tasks, reduces manual errors, and ensures timely resolution of exceptions.
Difference between Business Process Automation (BPA) and Business Process Management (BPM)
Despite having different focuses, business process management (BPM) and automation (BPA) are linked ideas. Process automation is a goal of BPA in order to increase compliance, productivity, agility, and efficiency. It entails utilising a range of instruments and software to automate routine company operations.
Employee onboarding and offboarding, vacation requests, HR requests, cost reporting, IT support requests, and more are a few operations that can benefit from BPA. BPA concentrates on automating particular triggered events and the related chain of actions.
On the other hand, BPM is a methodical strategy for enhancing all business operations. Beyond automation, it also includes process management and optimisation for improved organisational performance. BPM strives to match organisational goals with processes, resulting in a more contented and productive workforce, enhanced customer satisfaction, higher revenues, and lower expenses.
In summary, while BPA is a subset of BPM and focuses on automating specific processes, BPM encompasses a broader scope of managing, improving, and aligning processes to achieve organisational objectives.
Conclusion
Businesses can gain advantages from BPM as it sharpens their competitive edge. Working with IBM, you’ll have access to flexible BPM solutions that simplify and improve business decisions, procedures, and content so you can speed up creativity by making each step more effective.
With the Executive Programme in Business Management at IMT Ghaziabad, you can learn the intricacies of BPM and implement them successfully. It permits professionals to use important skills, including strategic management, decision-making, and critical thinking. With this business management course, you can look forward to a flourishing career in business management. By registering in this programme via Jaro Education, aspirants can strengthen their managerial abilities and learn new skills. They can start a new career path that will help them to flourish in the commercial environment.