Union Budget 2024 Highlights: Education and Skilling Sector
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 25, July 2024
- 7:30 pm
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2024 on July 23. This budget is the first for the Modi 3.0 government. Everyone’s watching to see what the government is planning and what budget 2024 highlights for the upcoming financial year.
In education, there’s a lot of interest in how much of the GDP will be allocated, especially as the country aims for digital literacy with the ‘Viksit Bharat’ initiative. Industry experts are calling for more investment in education to help India become a developed nation by 2047, as envisioned by Prime Minister Modi. They are suggesting measures like GST exemptions, fair access to quality education, more investment in talent development, and improved digital infrastructure. In this article, you will get a deeper insight into the Union Budget 2024 highlights and how it will help the education and skill sector.

*taxscan.in
Overall Budget Allocation to Education and Skilling Sector
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced that the Central government will allocate Rs 1.48 lakh crore for education, employment, and skill development in the 2024-25 financial year. Students pursuing higher education in India will get financial support with loans up to Rs 10 lakh. A new scheme will be launched to train about 20 lakh youth over five years in partnership with state governments and industries.
Moreover, 1,000 ITIs will be upgraded, with courses designed to match industry needs, which was one of the most encouraging Budget 2024 highlights for the educational and skilling sector.
The Finance Minister also announced that the government will offer internships to one crore youth, each receiving a stipend of Rs 5,000 and a one-time assistance of Rs 6,000. Companies will fund these internships through their CSR initiatives.
In the February 2024 Union Budget, Sitharaman noted that higher educational institutions and women enrolling in STEM courses have increased over the past decade. She credited the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 for this growth.
However, funding for the University Grants Commission (UGC) was significantly reduced by 60.99% to Rs 2,500 crore from the previous year’s revised estimate of Rs 6,409 crore. On the other hand, central universities received an increase in grants by over Rs 4,000 crore, with Rs 15,928 crore allocated for the 2024-25 financial year.
Budget 2024 Highlights for Education and Skill
Financial Support for Student Loans
As per Budget 2024 highlights, the government will provide financial support for loans up to Rs 10 lakh for higher education in domestic institutions. She mentioned that about 1 lakh students will benefit each year from this support. Students will receive direct e-vouchers with a 3% interest subsidy on the loan amount.
Benefits:
- These initiatives will help India become a technology hub by providing a steady flow of trained professionals.
- The focus on promoting employment and upskilling will benefit not only the EdTech industry but also sectors like IT.
- Supporting the middle class through these measures is a smart policy that will drive long-term success.
- These steps will position India as a leader in key sectors.
1,000 ITIs in the Hub-and-Spoke Model
Introducing several initiatives to advance the skill development sector was the key budget 2024 highlight. These initiatives involve upgrading 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) into a hub-and-spoke model, modernizing course content to align with industry skill needs, and revising the skill loan scheme.
The Union Finance Minister also declared that the updated skill loan scheme will now provide loans up to Rs. 7.5 lakh, supported by a government-promoted fund. This revision is anticipated to benefit 25,000 students each year.
Benefits:
- This is a significant advantage for individuals pursuing vocational careers.
- Facilitates the development of practical skills and professional excellence.
- Attracts more youth to participate in the formal economy.
- Reduces the necessity for migration to urban areas by establishing manufacturing bases in or near districts.
- Promotes hyper-local job creation.
- Enhances the manufacturing sector.
- Kunal Vasudeva, Co-Founder and Managing Director Indian School of Hospitality, commented that it will contribute to India’s goal of becoming a $10 trillion economy within the next 7-10 years.
Three Scheme for Employment Linked Incentives
The government is launching three new schemes under the Prime Minister’s ‘Employment Linked Incentive’ package. These schemes focus on EPFO enrolment, recognizing first-time employees, and supporting both employees and employers. This announcement was made by the Union Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman, during the Union Budget 2024-25 presentation. Here are budget 2024 highlights for three schemes:
Scheme A: First Timers
- Provides one month’s wage to all new workers in formal sectors.
- First-time employees registered with the EPFO will receive up to ₹15,000, paid in three installments.
- Eligibility: Salary up to ₹1 lakh per month.
- Expected to benefit 210 lakh youth.
Scheme B: Job Creation in Manufacturing
- Incentivizes additional employment in the manufacturing sector, focusing on first-time employees.
- Both employees and employers will receive incentives based on their EPFO contributions for the first four years of employment.
- Expected to benefit 30 lakh new employees and their employers.
Scheme C: Support to Employers
- Covers additional employment in all sectors.
- For each additional employee earning up to ₹1 lakh per month, the government will reimburse employers up to ₹3,000 per month for two years towards their EPFO contributions.
- Aims to incentivize additional employment of 50 lakh individuals.
Centrally Sponsored Scheme
Shree Nirmala Sitharaman announced the introduction of a new centrally sponsored scheme as part of the Prime Minister’s skilling package, which will involve collaboration with state governments and industry partners. She also stated that 20 lakh students will be trained over the next five years.
Paid Internship Opportunity in Top 500 Companies
In a significant move to enhance employment, the Finance Minister unveiled an extensive program designed to offer internship opportunities at leading companies. According to the budget highlights, this marks the fifth initiative under the Prime Minister’s package. Here are some key budget 2024 highlights of the paid internship scheme:
- The scheme will offer opportunities to one crore youth in the top 500 companies over the next five years.
- Each intern will receive a monthly allowance of ₹5,000 to gain real-life work experience.
- Companies providing these internships will cover the training expenses and allocate 10% of the training cost from their Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) funds.
- According to Section 135 of the Companies Act 2013, companies with certain turnover and profitability levels must spend 2% of their average net profit from the past three years on CSR activities.
Benefits:
- The internship scheme encourages partnerships between educational institutions and top companies.
- By providing valuable work experience, the scheme equips young people with the skills needed for a successful career.
- These initiatives help build a strong, skilled workforce, contributing to the country’s economic growth.
- Companies will benefit from access to a diverse and skilled talent pool, which can help reduce recruitment time and costs.
Paid Internship Opportunity in Top 500 Companies
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, in budget 2024, highlighted important goals, including boosting agricultural productivity, creating jobs, improving skills, developing human resources, and implementing new reforms. She proposed major changes in income tax and allocated Rs 2 lakh crore to generate jobs for 4.1 crore young people over the next five years. Additionally, Rs 1.48 crore was set aside for skill development programs.
Furthermore, the Union government will give a boost to 30 lakh young people entering the job market by paying one month’s PF contribution for them.
Working Women Hostel Scheme
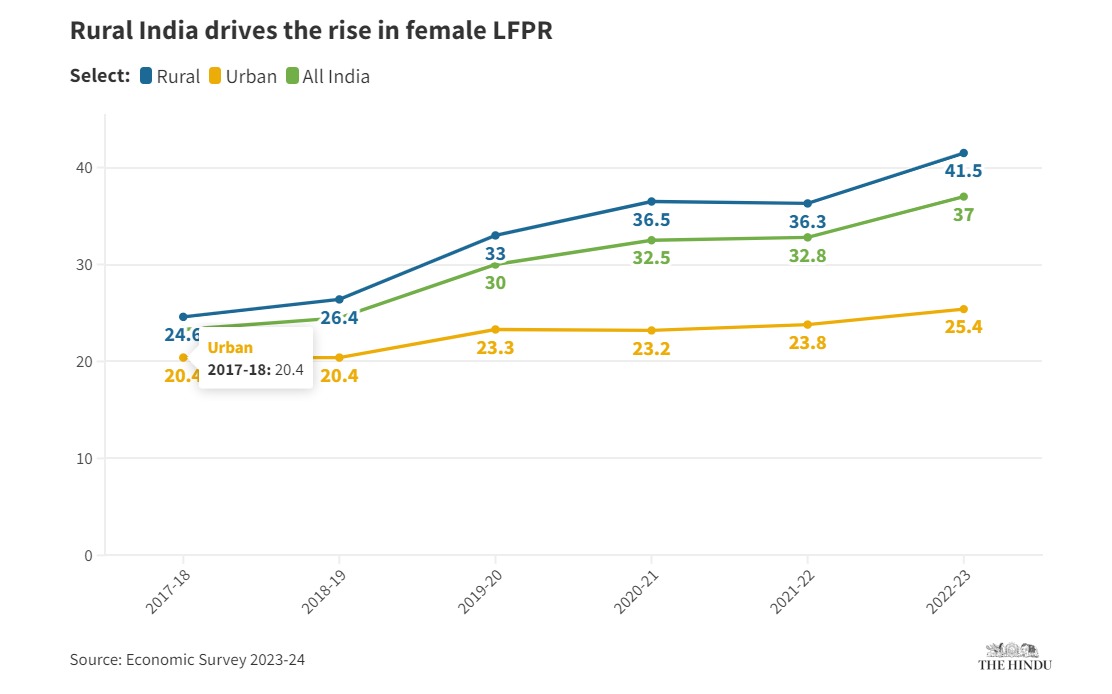
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced that the government will set up hostels for working women to encourage more women to join the workforce. She said, “We will help more women participate in the workforce by creating working women hostels in partnership with industries and establishing daycare centers. This collaboration will also focus on women-specific skill training programs and improving market access for women-led enterprises.”
The graph below illustrates the rise in the female Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) in India, with a particular focus on rural areas driving this increase.
*thehindu.com
Final Thoughts on Budget 2024 Highlights
In summary, That was the biggest budget 2024 highlights, and the government plans to invest a lot of money in education, jobs, and skill training, with a total budget of ₹1.48 lakh crore. These efforts are designed to promote growth, create more job opportunities, and help develop a skilled workforce over the next five years.












