
- jaro education
- 17, April 2024
- 2:00 pm
Process management or business process management (BPM) promotes a structured approach to planning, designing, monitoring, and executing a business workflow. It helps organisations increase efficiency and productivity and eliminates redundancy and bottlenecks in processes. The process managers impose several strategies to streamline the overall process. Thus, it is necessary to know what is Process management and how it plays a role in optimising your business operations.
What is Process Management?
Process management is a business methodology that helps a business to achieve its strategic goals. It uses versatile techniques, technologies, and approaches to constantly improve processes to fulfil business goals. Process management helps to accomplish goals like – standardisation of processes to meet the quality of the products/services, alignment of the process with the company’s mission, automating and simplifying repetitive tasks, embracing new technologies, and more.
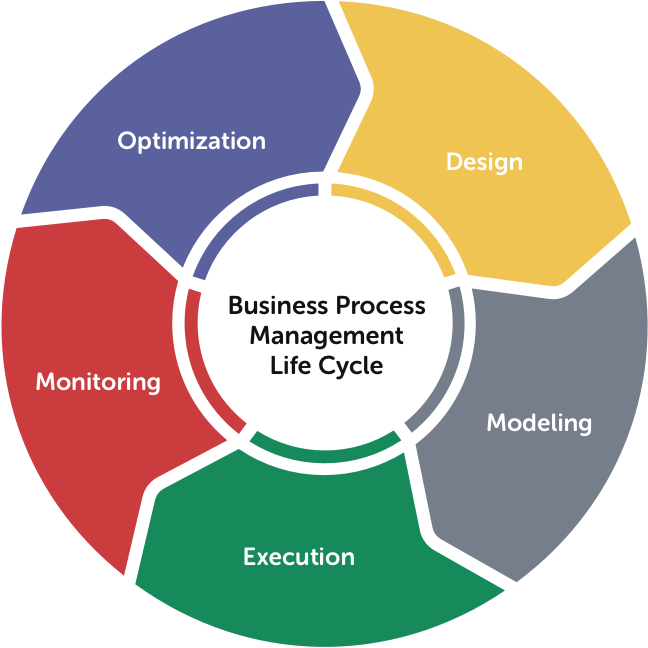
Table of Contents
*happyfox.com
Functions of Process Management in a Business
Planning
Before implementing a project management process, a company must have a plan. Two types of planning are required to achieve the desired business goals: short-term and long-term plans. These plans should help to make proper business strategies and eliminate potential concerns. For these, the organisation’s staff in charge of implementing this process must have proper project management skills.
Organising the Process
Implementing process management requires a well-organised approach. So, for this, a large project should be divided into small parts or modules. This strategy will help the employees to handle and arrange the project easily. As a result, the project execution will also become easy and free of unduly errors.
Process Monitoring
It’s essential to monitor the progress of the workflows to understand the impact of process management. Thus, the company monitors and tracks its employees to understand whether the employees can meet the actual and planned timeline for the assigned tasks. Depending on these results, the next steps would be planned to achieve the anticipated results.
Motivating the People
Moreover, process management motivates and leads the employees to be focused on their individual working goals and the organisation’s goals. For this, the employees have to go through several skill-up programs. Also, the company encourages its employees through motivational techniques like a recognition management process program, etc.
Real-life Examples of Process Management
Now that you know what is process management and its functions, it may seem like a daunting process. However, that is not the case. Following are some real-life examples of process management to help you understand how seamless the whole integration is.
Client Onboarding Process
When organisations obtain new clients, they have to conduct a professional onboarding process for them. A well-defined and clear onboarding process should have the below-mentioned steps –
- First, the business should schedule a meeting to clearly understand the client’s industry, business strategies, products/services, competitions, and requirements.
- The company then has to assess its assets and goals. It should consider how its resources can fulfil the client’s requirements.
- Next, they have to establish their KPIs. It helps the clients measure their progress.
- Finally, they should create an action plan for their team.
- After framing these strategies, they have to talk with the client and if the client is satisfied, he/she will accept the proposed strategy. Finally, the company will start working with clients.
Providing Customer Service
Customer service is the key to success for every business. It requires well-organised process management. Let’s see the crucial steps to create a strong customer service process –
- First, be aware of customers’ concerns and issues.
- Integrate a proper CRM to receive their complaints and queries.
- Acquire all the information about the issue from the CRM.
- Then, address the issue.
- Finally, inform the customers about the status of their complaint.
Moreover, the customer service process is involved with other significant processes, such as order and invoice processing, market research processing, new customer onboarding, and more.
Sales Process Management
Another significant example of process management is the sales procedure. It requires repetitive steps and workflows to meet the ultimate sales goal. A basic sales process goes through this path –
Proposal sharing > sending a quotation > negotiation between business and customers > receiving the order from customer > sales record maintaining > delivering the product/service > post-sale follow up > billing and payment process.
Content Marketing Process
In the modern era of digital technologies, companies need to focus on content marketing for multiple reasons. Whether spreading the word about the brand or a new product or service, offering solutions to customer queries, or simply providing knowledge, content marketing can address all these areas of a business.
Thus, every company should create a powerful content marketing process depending on its strategies. The basic procedure for blog content marketing should go through this way –
- At the initial stage, the writer must research, draft, and complete the blog. Meanwhile, the marketer must prepare for marketing and advertising the blog.
- After that, there will be a proofreading session to check the grammar, spelling, etc.
- The editors will modify the content, rectify the remaining errors, and check whether the content is aligned with the SEO requirements. Moreover, the SEO expert will publish it to check whether the SEO strategy is working.
- Finally, the marketer will share the content through advertising, email marketing, and social media to increase its reach and revenue.
Procurement Processing
Every company should go through a process while purchasing a good/service for their business. It’s known as procurement processing. The process includes these steps –
- Initially, they have to identify the need for the product/service.
- Then, they will contact the purchase department by providing a purchase requisition.
- After getting the requisition, the purchasing department will review it.
- Then, a requisition for budget approval will also be sent to the purchase department. This requisition includes all the financial details.
- After approving a quotation request, the purchasing department will send the quotation to the suppliers.
- Then, there will be a vendor selection. After that, a contract will be signed.
- Next, the company will receive the product and invoice slip.
- After inspecting the product’s quality, the company will approve the payment.
Process Management: Widely Popular Tools
Now, let’s shift our focus to the tools that enable process management for businesses –
Quixy
Quixy is a no-code automation platform and BPMS that helps users automate, model, optimise, and track business process workflows. It incorporates simple drag-and-drop application builders to design, build, and deploy apps. This tool’s app-building process has five simple steps. This platform offers enterprise-grade security to protect users’ data. Moreover, it can be integrated with third-party apps to enhance its capabilities.
Kissflow
Kissflow guides users to automate and execute business processes. This low-code BPM software helps users execute processes within a few steps. According to a report by Forrester Wave, this platform will become the strong performer in low-code platforms for citizen developers in 2024. With Kissflow, people should simply define their workflows, customise them, and apply for permission to onboard for working with the platform. Later, the dashboard of this platform shows insights like metrics for process efficiency, workflow visualisation, and data summary.
ProcessMaker
This BPM platform lets organisations design workflows with the user-intuitive interface and drag-and-drop functionalities. This platform comes with a personalised dashboard for processing and monitoring business requirements, SLAs, and objectives. This tool helps users capture and distribute data to automate process management tasks. It integrates with Gmail, WhatsApp, Slack, and Twitter. Moreover, ProcessMaker encourages users to create their own set of rules and conditions to send alerts to stakeholders about important updates.
Pipefy
Pipefy, the no-code BPM tool, assists organisations in streamlining and improving the performance of process management. The users can create the most efficient version of the process by implementing the right starting points and phases. It has several native integrations, 300 native connectors, and APIs to build a symmetrical working environment. This tool has a request tracker that allows employees, customers, and vendors to track their request status. This platform has been recognised as the industry leader in G2, 2023-’24.
CMW Lab
Being a low-code process management software, CMW Lab helps users build innovative business applications and manage data, documents, and tasks. The interesting fact about this platform is that it also has a mobile-friendly, personalised user interface. It includes significant features like drag-and-drop functionalities, chatting with teammates, process automation, effective work cycle management, and more. Now it has become the number one BPM software according to the Gartner Peer Insights.
Creatio
Creatio, the no-code automation platform, is an excellent BPM and project management platform. It supports the users in creating process diagrams with the visual tools and archiving them within the process libraries. It provides powerful solutions for automating marketing campaigns, sales processes, and customer service workflows. Moreover, it allows the users to collaborate with their teammates in real-time. As a result, they can visualise the processes remotely, edit the processes together, and comment on them. This platform got first place in the Customer Service Solutions Report of Forrester in 2024.
Steps to Implement Process Management In a Business
The steps of process management incorporate a structured and cyclical approach for streamlining the management, operations, and supporting process. So, let’s get into a deep dive into the process management steps –
Plan for Strategy
Every organisation wants to invest in high-impact and low-risk projects that can provide measurable results for making informed decisions. The results should also be closely aligned with the organisation’s KPIs. Thus, collaboration between management-level people is mandatory to create a solid process management strategy.
Moving on, business process management (BPM) activities are classified into three categories – human-centric BPM, document-centric BPM, and integration-centric BPM. So, different strategies are required for these categories –
- The human-centric approach is end-to-end and associated with manpower. That means the employees, customers, vendors, and other people involved in the process. This type of BPM approach includes well-crafted application interfaces, function tracking, and notifications. The best example of the human-centric approach is HR personnel’s workflows, such as posting job openings, candidate screening, interviewing, etc.
- Document-centric BPM is involved with electronic-based and paper-based document processes. This approach solves the requirements of individual organisations, industry, and business regulations. This BPM approach can be performed with workflow automation tools and techniques to improve accuracy. The perfect examples of a document-centric approach can be seen in the agreements and contracts-related tasks in finance, medical, legal, and purchasing fields.
Integration-centric BPM helps people quickly access any app, service, and data through the power of APIs. Moreover, this approach becomes suitable for automating systems like customer relationship management (CRM), human resource management systems (HRMS), and enterprise resource management (ERP) apps. The common examples of this BPM are conducting sales and marketing campaigns, sharing information about potential customers, and more.
*pyrus.com
Map Out and Design The Right Process
After the implementation of proper strategies, organisations need to map out the desired processes. Thus, they should identify the major process events, manual and automated tasks required for those events, the human resources for performing the tasks, technologies/tools, and deadlines.
Additionally, they must consider and understand the ‘as-is’ states such as bottlenecks, unnecessary error-prone tasks, delays, human errors, redundancy, high costs, compliance issues, and customer dissatisfaction to create new business requirements. After understanding the ‘is-as’ states, they have to design and depict the ‘to-be’ states. For these, one should find different methods to solve the issues, outline business process improvement, ask the stakeholders for their opinions, gain feedback for the designs, and more.
Now, organisations adopt robust methodologies for improving business processes. These methodologies help them overcome challenges, boost collaboration, and enhance positive cultural changes. Some of the popular BPM methodologies are agile management, Six Sigma, Kaizen, and Lean management. Furthermore, many organisations are using process mapping, process mining, and intelligent BPMS (iBPMS) techniques.
Build a Suitable Model and Test The Flows of The Process
Now, it’s time to conduct a test for the right design. For this, a company will design a prototype of the desired model. This prototype must include all the data flows, activities for the process, and business rules. After that, the model should be tested with simulation runs. The simulations can be run with different types of variables like costs, resources, and time. Then, based on the result, they will change and test the model again and either modify its existing workflows or implement the new ones. This simulation modelling approach becomes a cost-effective method for examining process performance in several circumstances.
Also, organisations use different business process management software (BPMS) to automate, test, and analyse the model for better performance.
Optimise The Process and Apply Improvements
Then, it’s time for process optimization and improvements. So, the organisations need to perform small group tests like proof of concept solutions. After that, they use the feedback to improve and evolve the process. In this phase, the BPMS’s in-built templates and connectors help the organisations create instinctive user interfaces.
But before the final launch, if the organisation changes the management plans and adds new resources, it needs to avoid operational interruptions, finalise the metrics, generate real-time reports, and promote adoption.
Also, they need to update job roles and responsibilities, conduct new training sessions for employees, and notify and support affected suppliers and customers. These are the essential modifications required to suit the change in the management plan.
Monitoring and Tracking The Performance Metrics
This step involves monitoring data to gather performance metrics. The monitoring and analysis of performance metrics depend upon the feasibility of the process, such as how good a workflow is for performing within a process, the functionality of a process within a large organisation, and operating a process from the technical perspective. Also, it’s necessary to have a conversation with the stakeholders to improve their knowledge about the cost, saving time, and bottlenecks.
Moreover, the BI and BPMS tools help organisations in metrics generation, visualisation, analysis, and reporting. These elements help them to know and comprehend the industry benchmarks to understand how they estimate the organisation’s KPIs. Furthermore, regular monitoring of the metrics is crucial for maintaining consistency within the process of achieving the business goals.
Optimisation of Process Based Upon The Fresh Insights
Organisations gain actionable insights after the monitoring and tracking phases. Depending upon these insights, they improve the business process. Side by side, they conquer operational efficiencies through regular innovation and iteration. Also, this phase leads them to explore other opportunities for automation, integration, and standardisation. Then, based on the changing requirements, marketplace conditions, and business strategies, they can implement new approaches to refine the process.
Challenges of Implementing Process Management in a Business
With all the necessary details of process management out of the way, let’s understand the challenges that organisations face while implementing BPM –
Process Complexity
Process complexity is one of the major concerns for BPM. The complexity occurs due to a variety of practices and systems throughout different departments and stakeholders. The lack of documentation, optimisation, clarity of roles and responsibilities, and understanding will make the process more hectic. As a result, the overall process causes several bottlenecks, inaccuracies, and failure.
To overcome this challenge, organisations should implement proper documentation and process mapping. BPM tools help create sophisticated process mapping, visual representations of the process, and identification of bottlenecks.
Lack of Control and Governance Framework
Lack of control causes potential errors, inadequacies, sacrificing quality standards, and compliance within a process. Thus, every organisation should establish a proper centralised governance structure to mitigate these risk factors.
To establish the right governance structure, an organisation should define clear policies and procedures to ensure the process management aligns with the business objective. The BPM tools can help to build the standard governing and controlling framework to maintain the governance standard.
Un-acceptance of Change
Change management is a crucial factor for BPM. However, the employees and stakeholders may be scared about changes, such as new technologies and processes. For example, a logistic company is implementing automated BPM solutions over manual BPM solutions. As a result, the employees who perform these manual tasks may resist acceptance of the new change. They may fear automation to replace their job role.
To overcome this issue, the company should conduct proper training sessions for the skill development of the employees. Also, the company must have a transparent communication strategy to help the employees understand the benefits of the changes for their growth, efficiency, and business growth.
Conclusion
Knowing the principles of process management and its functions and tools helps you, as a business owner or a professional, to fulfil organisational goals with a strategic approach. It reduces deficiencies and errors within a process. Though there are some challenges in implementing process management, acquiring effective strategies, technologies, and best practices helps to overcome these challenges. So, go for the Online MBA Programme – Manipal University Jaipur. It will help to implement a strategic approach to business process management. For more details, contact Jaro Education.
FAQs
1. How can I learn about process management?
You can take certain short-term courses to learn about process management. If you’re looking for long-term courses, then it’s better to choose a bachelor’s or master’s degree in business or a related field.
2. Is implementing process management necessary for businesses?
Yes! Process management implementation is necessary for a business. It streamlines business procedures and reduces repetitive tasks and inefficiencies.
3. Is process management considered a vital part of organisational strategy?
Process management ensures that organisations meet their business goals and improve efficiency and productivity. Thus, it’s considered a vital organisational strategy.
4. Is software necessary for process management?
Software is necessary for automating process management workflows. The BPM tools reduce repetitive mundane tasks, eliminate bottlenecks, and increase accuracy.








