Understanding the Role of a Relationship Manager in a Bank:
A Comprehensive Guide | Jaro Education
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 6, January 2024
- 9:00 am
One of the most important economic areas in an economy is the banking sector, which offers financial services and goods to consumers, companies, and governments. In 2021, the global banking sector was valued at $2.48 trillion, according to Statista. In a market this size and diversity, banks must set themselves apart from the competition and provide value-added services to their clients. The relationship manager is one of the main positions that banks use to do this.
A relationship manager is a specialised kind of financial advisor who helps a particular clientele—high-net-worth individuals, corporate clients, or small enterprises, for example—achieve their financial objectives. Depending on the needs and interests of their clients, a relationship manager often offers financial advice, investment advice, credit solutions, and other forms of support. Additionally, a relationship manager serves as a point of contact between the customer and the bank, guaranteeing optimal customer satisfaction and service.
This blog delves into the nuanced responsibilities and significance of a Relationship Manager in a bank, shedding light on their role and the impact they have on fostering client satisfaction and organizational growth.
Introduction to Relationship Manager Role: Who is Relationship Manager
A relationship manager is a specialist who helps a business establish and preserve good relationships with its clients or customers. Their responsibilities include comprehending the needs of the customer, offering customized solutions, resolving problems, and guaranteeing customer satisfaction. Along with increasing the company’s profitability and reputation, they also hope to create new business opportunities.
As per BCG as client whisperers, a relationship manager armed with advanced business analytics, relationship managers not only enhances a bank’s bottom line by 10% to 15% but also forges profound connections by understanding and addressing clients’ current and future needs.
The role of a relationship manager can change based on the business, sector, and kind of clients they work with. Typical categories of relationship managers include:
1. Banking relationship manager
Banking relationship managers work with a bank’s individual or corporate clients, providing them with a range of financial services and products, including deposits, loans, insurance, and investments. They also take care of transactions, risk management, compliance, and account opening.
2. Customer relationship manager
Customer relationship managers work with a company’s current or potential clients, offering them advice, assistance, and information about the goods and services offered by the business. They also manage complaints, loyalty programs, and customer feedback.
3. Vendor relationship managers
They negotiate terms of service, prices, and contracts with a company’s external suppliers or vendors. They also handle any problems or disputes and keep an eye on the performance, quality, and delivery of the vendors.
4. Employee relationship manager
Employee relationship managers work closely with staff members to guarantee their health, happiness, and output. They also deal with performance reviews, disagreements, and grievances from employees.
5. Public relations manager
A public relations manager collaborates with the public, media, and other company stakeholders to establish and uphold a favorable image and reputation for the business. In addition, they manage campaigns, events, press releases, and crisis situations.
What Does a Relationship Manager Do?
Here are the what a relationship manager do on their everyday basis:
Client Relationship Management
At the heart of a relationship manager’s responsibilities lies the cultivation and management of client relationships. This involves not only understanding the financial goals of clients but also ensuring that every interaction contributes to building trust and satisfaction. The section explores how relationship managers become the primary point of contact for clients, creating an environment of personalized and efficient banking services.
Financial Advisory and Planning
A pivotal aspect of the role is providing financial advice that goes beyond routine transactions. Relationship managers are financial strategists, guiding clients through investment opportunities and financial planning and ensuring that their financial portfolio aligns with their aspirations.
Cross-selling and Upselling
Relationship managers are instrumental in promoting additional banking products and services. This involves identifying opportunities for cross-selling and upselling, contributing not only to the client’s financial growth but also enhancing the revenue streams of the bank. The section sheds light on the strategic approach relationship managers adopt in expanding the scope of their clients’ financial portfolios.
Collaborating with Different Departments
Effective collaboration is a cornerstone of a relationship manager’s role. This section emphasizes how relationship managers work seamlessly with various departments within the bank, ensuring that client needs are met efficiently. Whether coordinating with credit departments or investment teams, their collaborative efforts contribute to a holistic approach to client satisfaction.
Risk Management and Compliance
Navigating the complex landscape of risk management and compliance is another facet of a relationship manager’s responsibilities. Relationship managers mitigate risks and ensure that all client interactions align with regulatory standards, safeguarding the interests of both the client and the bank.
Responsibilities and Duties of a Relationship Manager in a Bank
Relationship managers do more for their clients than only act as a point of contact between them and financial institutions. They also help them find sales prospects and investigate creative company concepts. Working together with employees who interact with customers is essential for gaining a thorough grasp of their demands and inspiring the group to provide the best possible service.
Relationship managers also carry out a wide range of duties that support the success of the financial institution and its clients in addition to these main duties:
Ensuring Customer Satisfaction:
Client satisfaction stands as a paramount objective. Relationship managers are dedicated to ensuring clients are content with the assistance received. In cases of dissatisfaction, it becomes their responsibility to exhaust every avenue to rectify issues and enhance overall satisfaction.
Facilitating Strategic Meetings
Relationship managers play a crucial role in organizing meetings with both new and existing clients. These sessions delve into client goals and objectives, fostering an environment where collaboration thrives, and tailored financial strategies are developed.
Strategic Development and Implementation
The role extends to the development and implementation of marketing strategies aimed at expanding the customer base. This proactive approach not only enhances business but also explores new avenues for growth.
Continuous Research
Relationship managers are committed to staying abreast of the latest products and ideas. Through continuous research, they introduce relevant concepts to clients, aligning opportunities with individual financial growth.
Sales Opportunity Exploration
Seeking new sales opportunities is imperative. Relationship managers focus on identifying and leveraging opportunities to enhance business, ensuring sustained growth for both clients and the financial institution.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Relationship managers actively engage in assessing and mitigating risks associated with client portfolios. This involves a meticulous examination of potential risks, developing strategies to address them, and ensuring a resilient financial foundation.
Credit Management
In collaboration with credit departments, Relationship managers are responsible for managing credit aspects for clients. This includes evaluating creditworthiness, facilitating loan approvals, and ensuring adherence to credit policies.
Market Trends Analysis
Staying attuned to market trends is crucial. Relationship managers analyze market dynamics, identifying trends that could impact clients’ financial positions and providing proactive advice to navigate changing landscapes.
Client Education
A pivotal responsibility involves educating clients about financial products, market trends, and potential opportunities. This empowers clients to make informed decisions, fostering a sense of financial literacy and mutual growth.
Skills and Qualifications Required to Become a Relationship Manager
Candidates for relationship manager in a bank must meet specific qualifications and possess a blend of skills that set the stage for success. Here’s a comprehensive look at the essential requirements:
Minimum Bachelor’s Degree
An aspiring Relationship Manager is the attainment of a minimum Bachelor’s Degree in a related field. Candidates are strongly encouraged to pursue degrees in fields such as business studies, finance, or accounting, as these disciplines provide a comprehensive and advantageous knowledge base for navigating the intricate landscapes of banking and financial services.
While not obligatory, candidates pursuing a career as relationship managers stand to gain significant advantages from holding degrees in business studies, finance, or accounting. These fields provide a comprehensive educational foundation, offering insights that prove invaluable in the dynamic landscape of financial services.
In addition to a Bachelor’s degree in business studies, finance, or accounting, further enhancing one’s qualifications through Jaro Education’s online finance courses can be highly beneficial. These courses, delivered by seasoned professionals from top institutions, deepen the understanding of financial management and investment analysis. Tailored for both aspiring students and current professionals, they complement the foundational knowledge gained in undergraduate studies.
Certifications
Relationship managers are urged to pursue continuous learning and certifications throughout their careers. These not only enhance career prospects but also signify a commitment to staying updated in a dynamic industry.
Certified Financial Planner (CFP)
Acknowledged globally, the CFP certification signifies mastery in financial planning. Relationship managers with a CFP credential showcase a heightened ability to provide comprehensive and strategic financial advice.
Certified Sales Professional (CSP)
Tailored for professionals engaged in sales, the CSP certification validates a deep understanding of sales principles and techniques. Relationship managers equipped with CSP certification are adept at navigating sales-related aspects of their roles.
Certified Management Accountant (CMA)
Focused on management accounting, the CMA certification denotes expertise in financial management and strategic planning. Relationship managers holding a CMA credential demonstrate a nuanced understanding of financial management principles.
Certificate for Financial Advisors
This certification is designed to augment the skills of financial advisors, providing them with specialized knowledge in client advisory roles. Relationship managers with this certificate showcase expertise in providing tailored financial advice.
Years of Experience
Candidates are expected to bring valuable experience to the table, ideally in banking or customer service. Candidates with a history of hands-on experience in banking or customer service bring a wealth of insights to the role. This accumulated knowledge empowers relationship managers to adeptly understand and address client needs, foster enduring relationships, and contribute meaningfully to the success of financial institutions.
Technological Proficiency
Relationship managers must possess not only financial acumen but also mastery of various technological tools is imperative, as it empowers relationship managers to navigate seamlessly through digital landscapes, streamline client management processes, and enhance overall efficiency.
The ability to proficiently use financial software, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, and other digital tools is a fundamental requirement. Relationship managers leverage these technologies to analyze data, track client interactions, and ensure a streamlined and organized approach to managing client relationships.
Understanding of Banking Regulations
Relationship managers operate within a complex regulatory environment, and a solid grasp of these regulations is essential to ensure adherence to ethical standards and legal frameworks. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in navigating the intricacies of financial regulations, showcasing a commitment to conducting business in an ethical and compliant manner.
Relationship Manager Salary
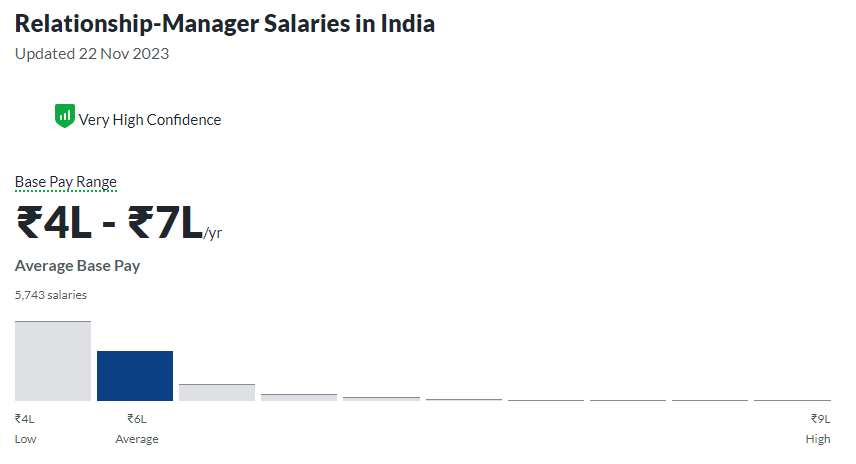
*glassdoor.in
As per data from Glassdoor, relationship manager salaries in India, the base pay range reflects a high level of confidence, spanning from ₹4,00,000 to ₹7,00,000 per year. The average base pay stands at ₹6,00,000 annually, with a range that encompasses a low of ₹4,00,000 and a high of ₹9,00,000.
When considering additional cash compensation, relationship managers in India receive an average of ₹1,00,000, with a range extending from ₹60,000 to ₹2,40,000. These figures provide a comprehensive overview of the compensation landscape for relationship managers, derived from insights gathered from 5,743 salaries submitted anonymously on Glassdoor. These statistics offer valuable insights into the remuneration structure for individuals in this role across various industries and sectors in India.
Client Relationship Building
In the role of a relationship manager, the focus revolves around the art of cultivating and sustaining client connections. Here’s a succinct overview of essential practices
Understanding Client Needs
The Relationship Manager actively listens to comprehend each client’s distinctive objectives.
Tailoring Solutions
Crafted solutions are personalized to align seamlessly with individual client goals.
Effective Communication
The Relationship Manager ensures clear communication of financial concepts, maintaining transparency throughout.
Anticipating Needs
Proactive measures are taken to anticipate market trends and potential shifts in the client’s financial landscape.
Providing Value
Beyond transactions, the Relationship Manager delivers insightful advice and valuable educational resources.
Swift Issue Resolution
Challenges are addressed promptly, reinforcing client satisfaction and trust.
Regular Check-Ins
Structured check-ins are scheduled to uphold strong, personal connections with clients.
Continuous Feedback Loop
Strategies evolve based on ongoing client feedback, ensuring a responsive and adaptive approach.
Assessment of Customer Needs
A pivotal aspect of the relationship manager’s role is conducting a thorough assessment of customer needs. This strategic process serves as the cornerstone for fostering meaningful connections with clients and tailoring financial solutions to their unique requirements.
1. Active Listening and Understanding
The first step in Customer Needs Assessment is active listening. Relationship managers engage in in-depth conversations to understand clients’ financial aspirations, challenges, and immediate needs. This lays the foundation for building a comprehensive understanding of the client’s financial landscape. According to Deloitte’s Consumer Banking Survey: Understanding Customer Needs, 58% of customers who thought their bank understood their needs were likely to recommend them to others, compared to just 9% of those who didn’t feel that way
2. Comprehensive Financial Analysis
Armed with insights from initial interactions, relationship managers perform a comprehensive financial analysis. This involves evaluating existing financial portfolios, identifying areas for improvement, and assessing the client’s risk tolerance to align future strategies accordingly.
3. Identification of Goals and Objectives
Customer needs assessment delves into the identification of short-term and long-term goals. Whether it’s purchasing a home, funding education, or planning for retirement, understanding these objectives is crucial for tailoring financial solutions that align with the client’s aspirations.
4. Risk Profile Evaluation
Assessing the client’s risk profile is integral to the assessment process. Relationship managers evaluate the level of risk a client is comfortable with, guiding investment strategies and ensuring financial plans align with the client’s risk tolerance and preferences.
5. Customized Financial Solutions
Based on the insights gathered, relationship managers craft customized financial solutions. These solutions span a spectrum of offerings, including investment strategies, retirement planning, and risk management, designed to address the specific needs and goals identified during the Assessment.
6. Ongoing Evaluation and Adaptation
Customer Needs Assessment is not a one-time endeavour. Relationship managers continually evaluate and adapt financial strategies as the client’s circumstances evolve. Regular check-ins ensure that the financial solutions remain aligned with the client’s changing needs and market dynamics.
Challenges Faced by Relationship Managers
While the role of a Relationship Manager in a bank is inherently rewarding, it comes with its set of challenges that demand resilience and strategic acumen. Understanding and addressing these challenges is integral to excelling in the dynamic field of Relationship Management.
Client Diversification
Adapting to diverse client needs, risk profiles, and communication preferences.
Market Volatility
Maneuvering through unpredictable market fluctuations to provide informed financial advice.
Regulatory Dynamics
Navigating evolving financial regulations while ensuring compliance.
Economic Uncertainties
Proactively assessing and mitigating the impact of economic uncertainties on clients’ financial stability.
Time Management
Balancing multiple client relationships, staying informed, and addressing administrative tasks efficiently.
Adaptability to Change
Embracing industry changes, adopting new technologies, and adjusting strategies accordingly.
Future Trends
Relationship Management in banking is poised for transformative shifts as industry trends continue to evolve. Staying attuned to these future trajectories is essential for relationship managers to adapt and excel in their roles proactively.
1. Digital Transformation
Automation and AI Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence and automation tools will streamline routine tasks, allowing relationship managers to focus more on strategic client interactions.
Enhanced Digital Platforms
Future trends suggest the development of more user-friendly and sophisticated digital platforms for seamless client engagement.
2. Personalized Financial Technology
Tailored Financial Apps
The rise of personalized financial apps will empower clients to manage their finances more independently while relationship managers provide guidance.
Robo-Advisors
The prevalence of robo-advisors will necessitate relationship managers to collaborate effectively with automated advisory services.
According to the Digital Banking Experience (DBX) report, nearly 70% of bank customers want their banks to provide them with more individualized advice and direction.
3. Data Analytics and Predictive Insights
Advanced Analytics
Utilizing advanced analytics tools for data-driven insights, enabling relationship managers to anticipate client needs and offer proactive solutions.
Predictive Modeling
Embracing predictive modeling to assess potential risks and opportunities, enhancing the precision of financial strategies.
4. Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
Biometric Security
Implementing biometric security measures to enhance data protection and instil greater confidence in clients.
Blockchain Integration
Exploring blockchain technology to secure and streamline financial transactions within the banking sector.
5. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Focus
Integration of ESG Principles
Incorporating ESG principles into financial planning, reflecting a growing awareness of sustainable and ethical investment practices.
Client Education on ESG
Educating clients on the implications of ESG factors in their financial portfolios and aligning strategies with ethical considerations.
In alignment with the transformative shifts in banking, the PG Certificate Program in Corporate & Strategic Finance by IIM Mumbai becomes increasingly relevant. This program equips participants with advanced skills in finance, including investment analysis and financial strategy. It prepares them to adapt to future trends like digital transformation, data analytics, and the evolving regulatory environment. Emphasizing both technological proficiency and strategic financial planning, it positions individuals to excel in senior finance roles, leveraging IIM Mumbai’s academic excellence in a rapidly changing banking landscape.
Conclusion
For people who are passionate about finance and customer service, a career as a relationship manager at a bank may be both demanding and fulfilling. A relationship manager at a bank offers individualised and customised solutions to help clients reach their financial objectives. In order to guarantee their pleasure and allegiance, relationship managers also establish and nurture solid bonds with customers.
Technical expertise, people skills, and in-depth understanding of the banking and investing sectors are all necessary for the position of relationship manager in a bank. A relationship manager must also be flexible and adaptive because they work with a variety of customers, goods, and circumstances.








2 thoughts on “Understanding the Role of a Relationship Manager in a Bank: A Comprehensive Guide | Jaro Education”
I loved you better than you would ever be able to express here. The picture is beautiful, and your wording is elegant; nonetheless, you read it in a short amount of time. I believe that you ought to give it another shot in the near future. If you make sure that this trek is safe, I will most likely try to do that again and again.
Relationship managers play a vital role in banking, as explained in the article. The way they bridge customer needs with financial solutions and build long-term relationships is insightful.