
Operations research (OR) is a dynamic and interdisciplinary field that leverages mathematical and analytical methods to tackle complex problems and enhance decision-making processes. It plays a critical role in a wide array of industries, including manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, and finance, where the optimization of resources and improvement of operational efficiency are paramount.
In this blog, we will delve into the importance and diverse applications of OR, explore key techniques, and review essential tools and software. Additionally, we will address the challenges associated with OR and discuss emerging trends that are shaping its future.
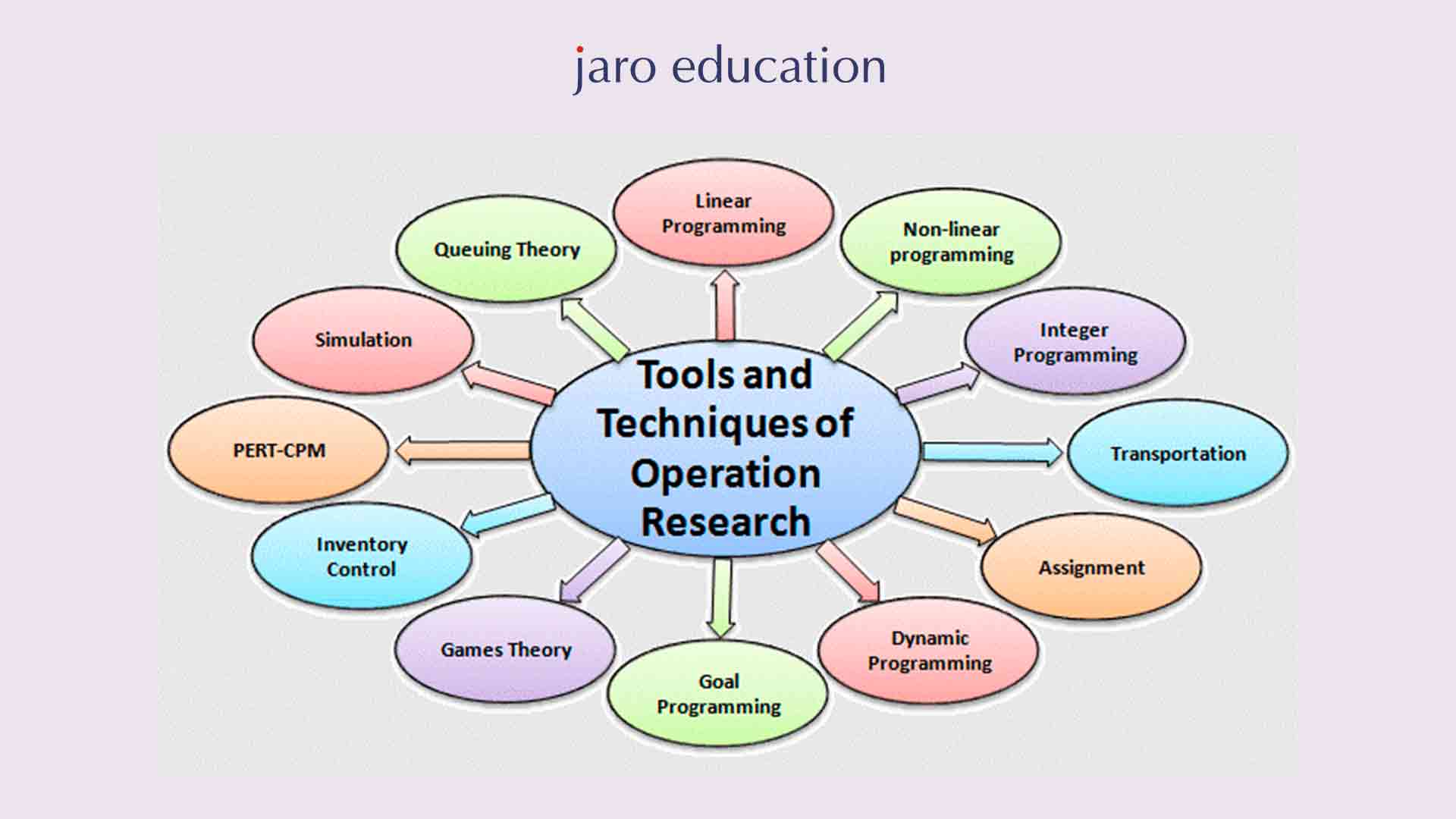
Operations Research Methods
because it can tackle a variety of problems, making our lives and businesses run smoother and more efficiently. It involves a variety of methods, each designed to tackle different types of problems, highlighting the broad scope of OR:
- Linear Programming: Linear programming is a powerful method used to find the best possible outcome in situations where you need to optimize resources. Think of it as a tool that helps you make the most efficient decisions in complex scenarios, such as allocating resources, scheduling production, or planning transportation routes. It’s widely used in OR
Table of Contents
- Queuing Theory: Helps in analyzing waiting lines or queues, making it crucial for service industries such as healthcare, telecommunications, and customer service. It aids in understanding and optimizing wait times and service efficiency.
- Simulation: Involves creating a digital twin of a system to experiment and observe potential outcomes. This method is useful in scenarios where real-world experimentation is impractical or too costly, such as manufacturing processes, financial markets, and logistics planning.
- Game Theory: Studies strategic interactions where the outcome depends on the actions of multiple decision-makers. It is widely used in economics, political science, and business strategy to model and analyze competitive situations.
- Network Analysis: Deals with the optimization of networks, such as supply chains and transport systems. This method helps in finding the most efficient routes, minimizing costs, and improving overall network performance.
Importance of Operations Research
OR is crucial for several reasons, significantly impacting various industries by improving efficiency, decision-making, and overall performance. Here’s why OR is so important:
- Improves Decision-Making: By using mathematical models and analytical methods, OR provides a scientific basis for decision-making. This leads to more accurate, reliable, and objective decisions.
- Enhances Efficiency: OR helps us discover the most effective ways to run and manage our processes. By streamlining operations, it boosts productivity and improves performance across various fields, whether it’s in manufacturing, logistics, or service industries.
- Reduces Costs: Through techniques like linear programming and network analysis, OR helps in minimizing costs related to production, transportation, inventory, and other operations.
- Solves Complex Problems: OR is adept at handling complex problems involving multiple variables and constraints. It simplifies these problems into manageable models, providing clear and actionable solutions.
- Supports Strategic Planning: OR aids in long-term planning and strategy development by predicting future trends, analyzing risks, and evaluating different scenarios.
- Improves Service Quality: In service industries like healthcare and customer service, OR helps optimize scheduling, reduce wait times, and improve overall service quality.
- Facilitates Better Use of Technology: OR integrates advanced tools and software, enhancing the ability to analyze large datasets and complex systems, leading to more informed and effective solutions.
Applications of Operations Research
Operations research is applied in various fields to optimize processes and improve decision-making. Here are some key applications:
Risk analysis
Risk analysis is an operation research application that allows businesses to detect and handle potential problems that could undermine their projects or initiatives. Moreover, risk analysis can be applied to other non-business initiatives like buying a home or event planning.
Inventory analysis
Inventory is a balance sheet asset that reflects the goods that a company intends to sell its customers in the future. In addition to the finished products, it also comprises raw materials that are used to manufacture such goods and work-in-progress goods.So, inventory analysis assists businesses in determining the appropriate quantity of goods to have in-hand, to meet customer demands while avoiding excessive inventory storage costs.
Strategic planning
Strategic planning is an application of operations research that allows organisation leaders to define their vision for the future and identify the goals and objectives of those organisations. The process involves determining the order in which those objectives should be carried out so that the organisation may achieve its stated vision. Strategic planning is often used to reflect mid-to long-term goals with a life duration of three to five years; which can be extended.
Marketing research
Marketing research is a strategy or collection of practices used by businesses to acquire information in order to comprehend their target market in a better way. Companies utilise this data to enhance their products, improve their user experience, and provide a better product to their consumers. Marketing research is usually performed to find out what people desire and how they react to items or features.Logistics
In business, logistics is the management of the flow of items between the point of origin and the point of consumption to meet the requirements of corporations and customers. The resources handled in logistics can include physical items like animals, food, liquids, materials, and equipment. Also, abstract items like data and time can be included in it.
Revenue management
Revenue management is a systematic analytics method used to forecast customer behaviour at the micro-level, with the goal of optimising product availability and price while increasing revenue growth. In other words, the fundamental goal is to offer the right product to the right buyer at the right price at the right time.
Sales analysis
Sales analysis is the process of evaluating sales data to detect trends and patterns. Sales data may assist companies in making insightful decisions regarding their product, promotions, price, promotions, customer demands, inventory and other elements of the organisation. In some organisations, sales analysis is as basic as frequently checking the sales numbers.
Scheduling
Scheduling is a part of operations research that organises, manages, and optimises work and workloads in a manufacturing or production process. It is used to plan plant and machinery resources, people resources, manufacturing processes, and material purchases.
Auctioning
To sell assets and properties to prospective purchasers, an auction is arranged. Auctioning is an open purchasing and selling mechanism in which buyers are asked to bid on specific assets and are held by owners and businesses.
Forecasting
It is a strategy that uses previous data as inputs to create educated predictions about the trajectory of upcoming trends. Forecasting is used by businesses to understand how to allocate budgets or plan for anticipated costs in the future.
Optimisation
Optimisation is a process that ensures the effective and efficient performance of business operations. It helps to reduce current expenditures while increasing operational capabilities. Business operations should thus be optimised regularly to ensure that they are functioning at an ideal level over the years.
Portfolio management
Portfolio management is focused on the financial aspect of operations research that deals with supervising a group of investments on a professional or personal level. These investments include mutual funds, bonds, cryptocurrencies, exchange-traded funds and so on. The goal of portfolio management is to assist investors in meeting their long-term financial objectives while also managing their liquidity demands and risk tolerance.
Supply chain management
The administration of the full process of converting raw materials into a finished product is known as supply chain management. It entails connecting a network of suppliers through a centralised management procedure. Each supplier serves as a link in the manufacturing cycle, from manufacturers to sellers.
*javapoint.com
Operations Research Tools and Software
There are several tools and software that make the application of OR more efficient, demonstrating the broad scope of OR:
-
- Excel Solver: A versatile tool for performing linear programming and other optimization tasks. It’s widely accessible and easy to use, making it a popular choice for many operations research applications.
- IBM ILOG CPLEX Optimization Studio: Widely used for solving complex optimization problems. This software is powerful and flexible, suitable for tackling large-scale linear and mixed-integer programming challenges.
- MATLAB: Offers a powerful environment for algorithm development, data visualization, and numerical analysis. MATLAB is favored for its robust computational capabilities and extensive range of toolboxes.
- GAMS (General Algebraic Modeling System): Designed for high-level modeling and optimization of complex systems. GAMS is particularly useful for large-scale optimization and economic modeling tasks.
- Arena: A simulation software that helps model, simulate, and analyze the performance of systems. Arena is beneficial for understanding and optimizing processes in manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and more.
These tools and software platforms are essential for leveraging the full scope of operations research, enabling professionals to solve complex problems efficiently and effectively.
Challenges and Limitations of Operations Research
While it is powerful, it does come with its challenges and limitations, which can impact the scope of OR:
-
- Data Quality: Reliable data is crucial, and poor-quality data can lead to inaccurate results. Ensuring high-quality, accurate data is often a significant challenge.
- Complexity: Some problems can be too complex for standard techniques, requiring advanced and often computationally expensive methods. This complexity can make it difficult to find and implement solutions.
- Interpretation of Results: The solutions provided by OR models need to be correctly interpreted and implemented, which can be challenging. Misinterpretation can lead to incorrect decisions and suboptimal outcomes.
- Resource Intensity: Implementing OR methods can be resource-intensive in terms of time, money, and expertise. It often requires specialized knowledge and significant computational resources, which can be a barrier for some organizations.
These challenges remind us that when applying operations research techniques, it’s important to plan carefully and think things through. This way, we can make sure the benefits really do outweigh any drawbacks.
Future of Operations Research
The future of OR looks promising, with several trends emerging:
-
- Integration with AI: Combining OR with artificial intelligence can significantly enhance decision-making processes. AI can help in processing large datasets, identifying patterns, and making predictions, thereby complementing traditional OR techniques.
- Big Data Analytics: The increasing availability of big data offers more opportunities to apply OR techniques. With access to vast amounts of data, operations research can provide deeper insights and more accurate models, leading to better solutions for complex problems.
- Sustainability: There’s an increasing emphasis on using OR to address environmental and sustainability challenges. By optimizing resource use, reducing waste, and developing sustainable practices, OR is helping industries become more eco-friendly and responsible.
- Improved Software: With the continuous advancements in software and computational power, OR is more capable and versatile than ever. User-friendly and powerful software tools are making it easier for us to model, analyze, and solve complex problems efficiently, paving the way for innovative solutions in various fields.
These trends indicate that the scope of operations research will continue to grow, providing innovative solutions and driving improvements across numerous fields and industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
The scope of OR includes optimizing processes, improving decision-making, and solving complex problems across various industries using mathematical and analytical techniques.
Common techniques include linear programming, queuing theory, simulation, game theory, and network analysis.
Industries such as manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, finance, and logistics benefit significantly from OR.
Tools like Excel Solver, IBM ILOG CPLEX, MATLAB, GAMS, and Arena are commonly used in OR .
Limitations include the need for high-quality data, the complexity of some problems, challenges in interpreting results, and the resource intensity of implementing these methods.








