- jaro education
- 27, May 2024
- 10:52 am
When it comes to choosing a career path, individuals often have two primary options: pursuing traditional employment (jobs) or venturing into entrepreneurship (business). Both paths present unique challenges and rewards. A job typically involves working for an employer, and receiving a steady paycheck for services rendered. On the other hand, business entails setting up and managing one’s enterprise, offering more opportunities for innovation and financial rewards.
Understanding the differences and benefits of each option is crucial for aligning one’s career with long-term goals and being prepared for the demands of the chosen path. In this blog, we’ll explore what it means to be employed versus an entrepreneur, discuss the pros and cons of each, and help you make an informed decision about the best-suited career path for you. Ultimately, gaining clarity on these aspects can greatly influence your professional journey.
Understanding the Concept of a Job
A job is typically defined as employment in which an individual works under a contract for an employer, performing specific duties in return for a salary or hourly wage. Jobs are characterized by their structured nature; employees are expected to adhere to predefined roles and responsibilities set out by their employers.
Table of Contents
Jobs
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Consistent paychecks | Potential of losing a job |
| Set hours | Working under management |
| Health insurance and other benefits | Having less control over the business |
| Chances of promotion | 5 - 7 Years |
| Lead Cloud Engineer | Less work flexibility |
| Career development opportunities | Navigating corporate politics |
Pros of Having a Job
-
Steady Income:
One of the most significant advantages of having a job is the financial security it offers. Employees receive a regular paycheck, usually bi-weekly or monthly, which helps in planning and managing personal finances without the unpredictability that can come with running a business. -
Monetary Benefits:
Beyond just a paycheck, many jobs provide additional benefits, which are crucial in today’s economic climate. These can include health insurance, retirement plans such as 401(k)s, and paid leave, including vacation and sick days. These benefits are not only conducive to a healthier life but also financially beneficial. -
Less Responsibility:
When you are an employee, your primary responsibility is to fulfill your job’s specific duties. Broader company issues, such as company-wide strategy, financial health, and compliance with laws, are typically not concerns that fall within an employee’s purview. -
Career Growth:
While employed, individuals often have opportunities for professional development and career advancement. Many companies offer training programs, workshops, and promotions that allow employees to ascend through the ranks and increase their earning potential over time.
Cons of Having a Job
-
Limited Control:
Employees often have little influence over their work environment or company policies. Their role is to operate within the confines set by their employers, which can sometimes lead to dissatisfaction if those confines are too restrictive or misaligned with one’s personal values and career goals. -
Fixed Income:
The income from a job is generally fixed, as outlined in the employment contract, with predetermined raises that occur incrementally. This structure can limit financial growth potential, especially if the scope for promotions is narrow. -
Job Security:
In today’s volatile business world, job security is far from guaranteed. External factors such as economic downturns, technological changes, and organizational restructuring can lead to layoffs or downsizing, often with little notice.
Understanding these pros and cons is vital for anyone currently in the job market or considering entering it. By weighing these factors, prospective employees can better navigate their career paths and align their jobs with their long-term financial and professional goals.
To further advance your career, consider taking courses from leading universities via Jaro Education. Jaro Education distinguishes itself by offering free career guidance, a valuable resource for navigating your professional development. Utilize this support to maintain a competitive edge in the fast-paced business landscape.
Understanding the Concept of a Business?
Running a business involves setting up and managing your own enterprise, where you are the decision-maker and bear the primary responsibility for its success or failure. This path is often linked with entrepreneurship, which is the process of designing, launching, and running a new business, typically starting as a small business, such as a startup company, offering a product, process, or service for sale or hire.
Basics of Entrepreneurship:
Entrepreneurship requires a blend of innovation, courage, and resilience. Entrepreneurs must identify market needs, develop viable products or services, and effectively market them. The process includes planning, making key financial decisions, conducting sales and marketing activities, and employing staff. The ultimate goal is to grow the business and generate profits.
*collidu.com
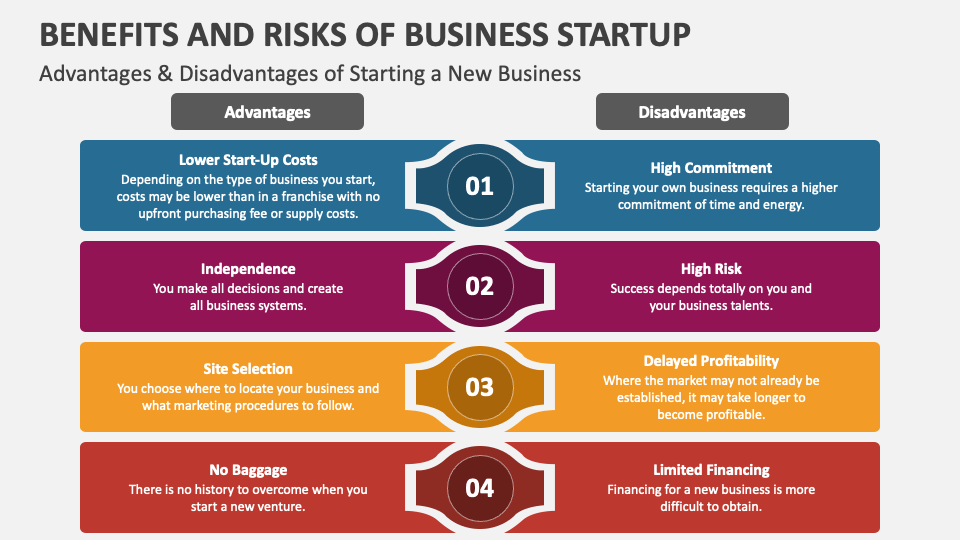
Pros of Running a Business
-
Unlimited Potential:
Unlike a traditional job where your income is somewhat fixed, running your own business means your financial gains can be limitless. The growth of your business and the profits you make are directly tied to your efforts, decisions, and the innovativeness of your offerings. -
Flexibility:
Entrepreneurs often have the luxury to set their own schedules, choose whom to work with, and decide on the strategic direction of their business. This kind of flexibility allows them to mold their work environment to best fit their personal and professional life needs. -
Personal Satisfaction:
There is a unique sense of fulfillment that comes from turning a vision into reality. Running your own business allows you to pursue passion projects and potentially create jobs and products that can have a meaningful impact on society.
Cons of Running a Business
-
High Risk:
Entrepreneurial ventures carry substantial risks. There is a high degree of financial uncertainty, and the potential for failure is significant—statistics show that many new businesses fail within their first few years of operation. -
More Responsibility:
As a business owner, you are responsible for every aspect of your business. This includes not only the strategic direction and day-to-day operations but also less glamorous tasks like HR, compliance with regulations, and managing finances. The buck stops with you, which can be a heavy burden to carry. -
Investment:
Starting a business often requires upfront capital to get off the ground, and sustaining it requires continuous investment. Depending on the business type, this could include costs related to product development, manufacturing, marketing, and staff salaries.
Running a business offers both high risks and high rewards. It demands a significant amount of work and commitment but provides opportunities for substantial personal and financial growth. Anyone considering this path needs to evaluate their willingness to take on the risks and responsibilities associated with being their boss.
Key Differences Between Job V/S Business
Control and Autonomy: Employees versus Entrepreneurs
- Employees: In a job, control over daily tasks and strategic direction is usually in the hands of supervisors and managers. Employees have specific roles and responsibilities and must adhere to company policies and directives. This structure can limit personal autonomy but provides a clear, organized work environment.
- Entrepreneurs: Business owners enjoy a high level of control and autonomy. They make decisions about the business’s direction, work processes, and priorities. This freedom allows entrepreneurs to innovate and steer their ventures in alignment with their personal and business goals. However, with great control comes great responsibility, which can be daunting for some.
Risk and Reward
- Employees: Jobs typically offer more stability in terms of income. Employees receive a fixed salary or hourly wages and may also benefit from bonuses, raises, and promotions based on their performance and company policies. However, the potential for significant financial growth in a job is often capped and predictable.
- Entrepreneurs: Running a business presents the possibility of unlimited financial returns. Earnings are tied directly to the business’s success, which can fluctuate greatly. While the potential for high returns is greater, so is the risk of losing money, especially in the volatile early stages of a business. Entrepreneurs must be prepared to handle these financial ups and downs.
Work-Life Balance: Comparing the Structured Routine of a Job with the Flexibility of Running a Business
- Employees: Most jobs come with a defined schedule, typically the standard 9-to-5, Monday through Friday. This structure can make it easier to plan for personal time and family activities. However, it can also mean less flexibility during work hours and may include time spent commuting.
- Entrepreneurs: Business owners often have the ability to set their own schedules, which can be both a blessing and a curse. This flexibility allows for adjustments based on personal needs and may enable working from home, reducing commute times. However, entrepreneurs might find themselves working odd hours, including nights and weekends, to meet business demands, which can disrupt personal life and family time.
Understanding these differences is critical for anyone standing at the crossroads of choosing between a job and starting a business. Each path offers unique benefits and challenges, and the right choice depends heavily on individual preferences, lifestyle desires, and risk tolerance.
Benefits of Choosing Jobs
- Regular Paychecks: One of the primary advantages of traditional employment is the security of a steady income. Regular, predictable paychecks simplify budgeting and financial planning, reducing the stress associated with uncertain earnings.
- Health and Retirement Benefits: Employers often provide valuable benefits, which could include health insurance, pension plans, 401(k) contributions, and even perks such as child care assistance or transportation subsidies. These benefits can significantly enhance job satisfaction and personal well-being.
- Structured Growth Opportunities: Many organizations have clear paths for career progression, helping employees develop professionally through promotions and lateral moves within the company. Additionally, companies might offer access to professional training courses, workshops, and seminars, which further skills development and career growth.
- Employment Protection: Jobs come with employment rights, including severance packages, unemployment benefits, and legal protections against unfair dismissal, providing a layer of security not typically available to business owners.
- Defined Work Hours: Most jobs come with set hours, and recent shifts in many industries toward remote or flexible work schedules have further increased the ability to balance work and personal life effectively.
Benefits of Choosing Business as Career
- Financial Upside: Unlike salaried positions, running your own business removes the ceiling on potential earnings. Your income can grow in direct proportion to the success of your business, offering potentially limitless financial rewards.
- Decision-Making Power: As a business owner, you have the ultimate authority over the strategic direction of your business, operational practices, and overall business goals. This level of control can be particularly satisfying for those who have clear visions and are entrepreneurial by nature.
- Flexible Schedules: Business owners typically have the ability to set their own schedules. This flexibility allows them to manage their professional commitments around personal obligations, such as family activities or other interests, potentially leading to a better overall quality of life.
- Fulfillment from Building Something: There is a unique sense of accomplishment and pride that comes from creating a successful business. For many entrepreneurs, the impact of their work and the legacy they build becomes a profound part of their personal identity.
- Potential Deductions: Business owners often benefit from tax strategies that can lower their overall tax burden. Deductions can include business expenses, home office setups, and the use of vehicles for business purposes, which are not available to most employees.
Conclusion
The decision between pursuing a job or delving into entrepreneurship hinges on personal factors such as risk tolerance, financial objectives, lifestyle preferences, and career aspirations. Jobs provide stability, benefits, and structured growth paths, while business ownership offers unlimited earning potential, decision-making autonomy, and the satisfaction of building something from the ground up.
Understanding these distinct differences and benefits is crucial for making an informed career decision aligned with your long-term goals. Whether you opt for a job or embark on the entrepreneurial journey, remember that continual learning, adaptability, and a clear vision are vital for success in today’s dynamic professional environment.








