What is the Future of Generative AI?
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 20, March 2024
- 10:00 am
Generative AI has emerged from years of progress in AI. It has evolved from machines that only take commands to ones that can create. Rooted in 1960s chatbots, a game-changer came in 2014. Generative adversarial networks (GANs) enable the authentic replication of real people. According to a 2025 report by McKinsey, over 70% of businesses are expected to adopt Generative AI tools for content creation, reducing manual work by up to 40% in industries like marketing, entertainment, and publishing.
This article will explain generative AI. We’ll cover its evolution, current uses, and more. Let’s start!
How Does Generative AI Work?
Generative AI is revolutionizing the way we create content—whether it’s art, music, text, or even video. But how does it work? Let’s break it down with an interactive, engaging explanation!
Ready to dive into the magic behind the scenes?
*Rezo.ai
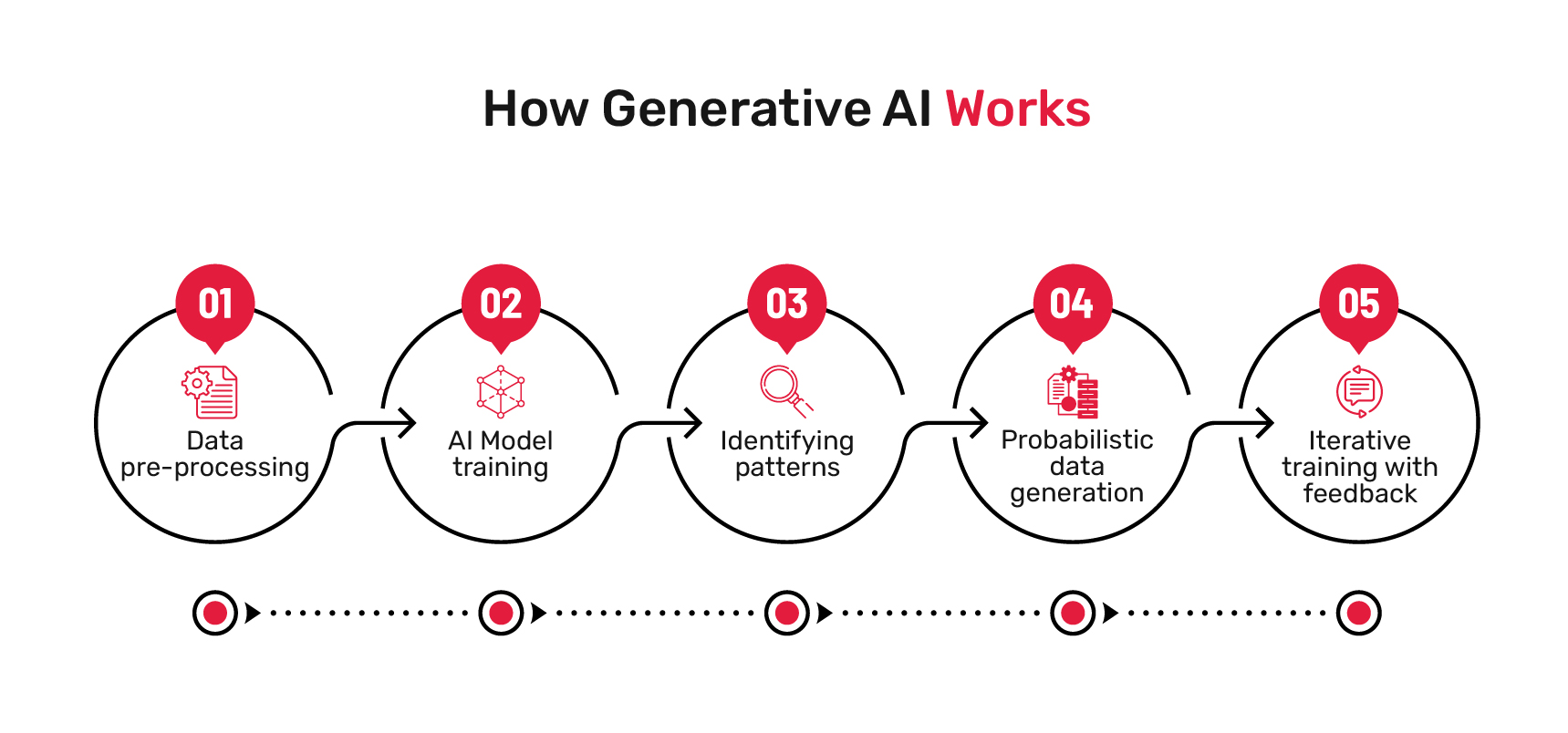
1. Data Collection
A large dataset will contain examples of the type of content the generative AI application will generate. For example, if it is intended to create images of cats, a dataset of various cat images will be collected.
2. AI Model Training
The generative AI courses train on the collected dataset. Techniques, such as deep learning, are commonly applied. They include generative models like GANs and VAEs. The model finds patterns in the training data. It learns its features and structures to grasp its essence.
3. Identifying Pattern
The trained generative AI application creates a representation in latent space. It is a math representation of the patterns it learned from the training data. This latent space acts as a representation of a compressed, abstract representation of a dataset
4. Data Generation
This latent space representation can then be used to generatively generate new content. For example, it can sample points in the latent space and decode them to the original format. To generate images of cats, it would sample points in the latent space and decode them into new cat images.
5. Iterative Training and Feedback
Generative models are mainly trained through an iterative process. It involves training, testing the output, and adjusting the model’s parameters. This makes the content more acceptable and realistic. This goes on until it produces satisfactory results.
Generative AI Models

Welcome to the Generative AI tool Playground!? Dive into how the generative AI models GPT, GANs, and VAEs work, in a very hands-on way, of course! Let’s take an interactive journey into these powerful tools. They create everything, from art to music, text, and even videos.
*neuron.ai
Generative AI Models
Dall-E, ChatGPT, Deepseek, and Bard emerge as standout generative AI tool interfaces, each showcasing distinctive capabilities and evolutionary trajectories.
- Dall-E

* Thingslab
It is an exemplary multimodal generative AI tool and is trained on an extensive dataset pairing images with text descriptions. Proficiently connecting words to visual elements, it excels in understanding and generating content across various media—vision, text, and audio. Developed with OpenAI’s GPT implementation in 2021, the upgraded Dall-E 2, introduced in 2022, enables users to craft diverse imagery styles prompted by user inputs.
- ChatGPT

*WIRED
It is a globally lauded generative AI tool chatbot that garnered attention with its November 2022 launch. Built on OpenAI’s GPT-3.5, it introduced an interactive chat interface with user feedback, departing from the previous API-only model. The subsequent release of GPT-4 in March 2023 enriched ChatGPT further, notably incorporating conversation history into responses for a more authentic and dynamic interaction.
- Bard

*CodeStore
Microsoft’s counterpart to ChatGPT experienced a tumultuous journey marked by initial inaccuracies and erratic behavior. Following Google’s hurried launch of Bard after Microsoft integrated GPT into Bing, it faced criticism for misinformation regarding the Webb telescope’s discovery of a planet in a foreign solar system. Despite early setbacks, Google’s updated Bard, utilizing the advanced large language model PaLM 2, demonstrates enhanced efficiency and visual responsiveness, underscoring Google’s commitment to refining generative AI course interfaces.
- Deepseek

* NPR
DeepSeek is very much like ChatGPT; it has its website and a mobile app where you can type in a little text box and hear it talk back to you. What sets it apart is how it came about. On January 20, after its recent prime-time outing, R1, a reasoning model, was birthed just weeks after V3, the company’s last model, whose crowning features were witnessing some truly impressive performances on AI benchmarks. DeepSeek’s models were soon realized to be performing at par or even exceeding some of those developed by OpenAI, Meta, and Google.
Generative AI Applications
* Markovate
Generative AI tool emerges as a potent catalyst for transforming organizations, particularly in environments where a deep understanding of AI or data science may be limited. Its exceptional capability to expedite the deployment of AI applications is noteworthy, making it accessible even with a modest amount of data through APIs or prompt engineering. While substantial customization benefits from expert guidance, the impact of generative AI courses is palpable across three primary skill categories:
1. Content & Idea Generation
This facet of generative AI tools sparks creativity by generating original outputs across various media. Whether crafting a captivating video advertisement or creating a novel protein with antibacterial properties, generative AI use cases demonstrates its proficiency in ideation and content creation.
2. Increasing Productivity
Generative AI tool excels in enhancing productivity and accelerating manual or repetitive tasks. From automating email composition and coding to summarizing complex documents, its role in streamlining these operations significantly contributes to overall operational efficiency.
3. Personalizing Experiences
Generative AI use cases stands out in tailoring content and information to specific target audiences. Whether developing chatbots for personalized user interactions or devising targeted marketing strategies based on the nuanced behavioral trends of individual customers, the technology proves invaluable in crafting personalized and engaging experiences.
Future of Generative AI
Welcome to the future! Generative AI is changing our world. It lets machines create new content, solve tough problems, and collaborate with us in new ways. Generative AI tool can design art and music. It can also revolutionize industries like healthcare and education. Its potential is limitless.
But what exactly will the future look like with AI as a co-creator? How will it shape the way we work, live, and innovate?
The horizon of generative AI courses is laden with promising prospects, set to redefine technological landscapes and societal paradigms. Here, we outline key trajectories and trends that may shape the future of generative AI:
1. Advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs)
The continuous progression of Large Language Models (LLMs), as exemplified by OpenAI’s GPT series, signifies a transformative journey towards more sophisticated and context-aware generative capabilities. This evolution foresees a range of improvements, including heightened levels of natural language understanding, intricately refined conversation dynamics, and a more nuanced approach to content generation.
These expected advancements in LLMs suggest a future where generative AI tool will understand language at a high level. It will also respond with better context. This will lead to more accurate and nuanced content creation. The development of LLMs is key to advancing generative AI courses. They promise a future where language models can interact with users. These interactions will show a deeper understanding of context, nuance, and human communication.
2. Multimodal AI Integration
The trajectory of generative AI applications is steering towards seamless Multimodal AI Integration. In the future, generative AI models are anticipated to effortlessly incorporate information from diverse modalities, encompassing text, images, and audio. This integration marks a pivotal advancement, unlocking the potential to develop comprehensive and interactive generative systems.
These futuristic models are poised to demonstrate the remarkable capability to simultaneously generate content across a spectrum of media types, creating a harmonious convergence of textual, visual, and auditory elements. The integration of multiple modalities not only enhances the versatility of generative systems but also opens new avenues for creating rich, immersive content experiences that transcend traditional boundaries and engage users across various sensory channels.
Enhanced Customization and Control
As generative AI systems proliferate, there is a clear shift toward prioritizing enhanced customization and control. This shift emphasizes empowering users with advanced customization options and greater control over the outputs generated by these systems. It involves a refined approach to prompt engineering, enabling users to adjust style preferences and fine-tune the specificity of the generated content.
The overarching goal is to provide a more personalized and tailored experience, allowing users to exert greater influence over the nature and characteristics of the content produced. This trend reflects a commitment to accommodating individual preferences, promoting user agency, and enhancing the adaptability of generative technologies to meet diverse user needs and expectations.
4. Ethical and Bias Mitigation
In generative AI, a critical imperative is Ethical and Bias Mitigation. Looking forward, there is a pressing need to confront ethical concerns and proactively address biases in generative outputs. Developers are expected to prioritize the implementation of safeguards to prevent the unintentional amplification of biases inherent in training data.
This commitment is driven by a vision of fostering responsible and equitable deployment of generative models, ensuring that the technology adheres to ethical standards and avoids perpetuating biases that may exist in the data. The future of generative AI envisions a proactive and conscientious approach to mitigate ethical challenges, promoting fairness, transparency, and ethical considerations in the development and utilization of generative technologies.
5. Domain-Specific Generative Models
An emerging trend in generative AI tools points towards the development of Domain-Specific Generative Models. This trajectory envisions the creation of more specialized generative models meticulously crafted for particular domains or industries. These models are anticipated to go beyond generalized capabilities, showcasing a heightened understanding of the specific context and nuances intrinsic to their designated fields.
The result is expected to be more precise, tailored, and domain-specific content generation. By aligning closely with the intricacies of particular industries, these specialized generative models aim to deliver outputs that are not only contextually accurate but also attuned to the unique requirements and intricacies of the targeted domain, marking a significant step towards enhanced relevance and applicability in diverse professional sectors.
6. Real-Time Applications
Generative AI applications is transitioning towards Real-Time Applications, marking a paradigm shift towards interactive use cases. The future envisions instant and dynamic engagement, including real-time content creation during live conversations, dynamic customization of visual elements, and on-the-fly generation of responses tailored to evolving contexts.
This evolution signifies a departure from static and pre-determined outputs, allowing generative AI tool to seamlessly adapt and respond in real-time to the dynamic nature of user interactions. The move towards real-time applications reflects a desire to enhance user experiences, fostering immediacy, responsiveness, and adaptability, and has the potential to revolutionize how generative technologies are integrated into live scenarios across diverse domains.
7. Collaborative and Creative Tools
Generative AI tool is positioned to play a pivotal role in shaping Collaborative and Creative Tools. Looking ahead, these tools are anticipated to facilitate seamless collaboration between humans and AI, fostering synergy in brainstorming, design ideation, and content creation across a spectrum of creative domains. The vision is to create an interactive and collaborative ecosystem where generative technologies complement human creativity, serving as catalysts for innovation.
Future tools are expected to bridge the gap between human ingenuity and AI capabilities, offering a harmonious collaboration that amplifies creative processes and yields novel, imaginative outcomes. This evolution represents a transformative approach to creative workflows, where generative AI applications becomes an integral and synergistic part of the collaborative creative journey.
8. Continued Integration into Industries
Generative AI is on the verge of experiencing Continued Integration into Industries, heralding transformative shifts in workflows and the automation of creative and repetitive tasks. Anticipated is the widespread adoption of generative technologies across diverse sectors such as healthcare, education, entertainment, and design.
This integration holds the promise of bringing about significant advancements, streamlining processes, and introducing innovative solutions within these industries. By leveraging the capabilities of Generative AI courses, organizations across various sectors aim to enhance efficiency, foster innovation, and unlock new possibilities, marking a paradigm shift in how generative technologies are applied to address industry-specific challenges and opportunities.
Thus for Generative AI tool, the future holds immense promise for reshaping technological and societal paradigms. This future is not just about technological advances but also about integrating AI into our daily lives and industries in a more personalized, ethical, and comprehensive manner.
Amidst this transformation, the Executive Programme in Marktech and AI-Driven Marketing offered by IIM Indore stands as a critical educational initiative for professionals aiming to leverage the power of generative AI courses in marketing. This course equips participants with the expertise to navigate the digital marketing landscape, utilizing generative AI applications to forge effective, personalized, and engaging marketing strategies.
Conclusion
Generative AI tool emerges as a transformative force, with the potential to revolutionize how we create, interact, and envision the future of content across a multitude of domains. Its trajectory from early chatbots to sophisticated generative adversarial networks marks a journey of immense progress and innovation, hinting at a future where AI’s creative capabilities are boundless.
The economic implications, as highlighted by McKinsey, underscore the significant impact generative AI could wield on the global stage, offering both remarkable opportunities and complex challenges. The future hinges not just on technological advancements but on our collective ability to guide these developments with foresight and responsibility. Ensuring that generative AI tool enhances human creativity, enrich our experiences, and operate within an ethical framework will be crucial.









