Corporate Tax: Definition, Deductions & How It Works
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 20, July 2024
- 11:00 am
Corporate tax is the fee governments impose on company earnings. For many nations, including India and the United States, it is a major source of income. When we discuss taxes, we are referring to the mechanism by which businesses pay the government a share of their profits.
Fundamentals of Corporate Tax Rates
A company’s corporate tax rate is the proportion of its earnings that must be paid to the government. In India, the corporate tax system is more complex than a single fixed rate, with different rates applying to various types of companies and income levels.
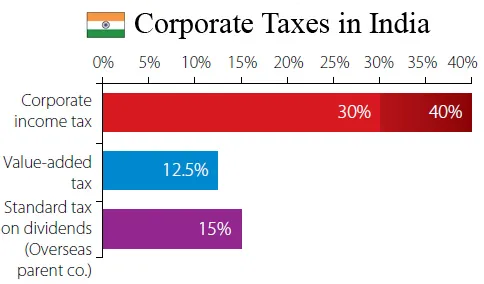
As of the 2023-24 financial year, the standard corporate tax rate for domestic companies in India is 30%. However, this rate can be reduced to 25% for companies with an annual turnover of up to ₹400 crore. Furthermore, under Section 115BAA of the Income Tax Act, domestic companies have the option to pay tax at a reduced rate of 22%, provided they forgo certain deductions and incentives.
It’s worth noting that corporate tax rates vary significantly across countries. While some nations are considered tax havens due to their very low rates, India maintains a moderate to high corporate tax rate compared to many other countries.
Corporate Tax Mechanisms in India
To understand how corporate tax is calculated in India, one must examine the concept of taxable income. Companies pay taxes on their taxable income, computed by deducting allowable expenses from their total income. These expenses typically include:
- Cost of goods sold (COGS)
- General and administrative (G&A) expenses
- Marketing and selling expenses
- Research and development expenditure
- Depreciation
- Other operating expenses
*india-briefing.com
After subtracting these costs, the remaining earnings are subject to the applicable corporate tax rate. In India, companies are required to file their tax returns by 31st October following the end of the financial year (which runs from 1st April to 31st March).
Types of Corporate Taxes in India
In India, the law treats companies as separate from their owners. The government taxes a company’s income separately from the money it pays to its shareholders. When deciding how much tax a company should pay, Indian tax law splits companies into two types:
1. Indian Companies:
- These companies do business mainly in India.
- The Indian government has registered them under Indian company law.
- This group also includes companies other countries have registered, but India fully manages and controls.
- They use only Indian rupees for their business.
2. Foreign Companies:
- These companies do business in many countries besides India.
- The Indian government does not register them under Indian company law.
- They use different currencies for their business.
Corporate Tax Planning and Strategies
Tax planning is a crucial aspect of financial management for Indian companies. The Income Tax Act provides various provisions that businesses can leverage to optimize their tax liabilities. Here are some key considerations:
Double Taxation Concerns
In India, the issue of double taxation primarily affects domestic companies. Profits are taxed at the corporate level, and then dividends distributed to shareholders may be subject to additional taxes. To address this, India abolished the Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT) in 2020, shifting the tax burden to shareholders. However, companies still need to consider the overall tax impact on both the corporate entity and its shareholders.
Methods of tax planning
Companies can use several methods to pay less tax:
- Use tax credits and deductions
- Delay getting some income
- Move profits to places with lower taxes
- Invest in things that don’t get taxed
Benefits of tax planning
Companies can use several methods to pay less tax:
- Pay less tax: Companies can pay less tax using tax-saving options like deductions, credits, and exemptions.
- Have more money to use: By paying less tax, companies have more money to put back into the business. This can help them make more profit and grow.
- Reach long-term money goals: Tax planning helps companies save for big future plans, like expanding the business.
- Avoid tax problems: Good planning helps companies avoid risks like tax audits or fines for breaking rules.
- Choose the best business type: Tax planning helps companies decide what type of business to be (like a partnership or limited company) based on which one pays less tax.
Remember, while paying less tax is good, companies must always follow the law when they do their tax planning.
Tax Deductions for Companies in India
Companies and professionals in India can deduct business-related expenses from their taxes. These expenses must be entirely for business purposes, not personal or capital expenses. Here are some deductibles given below-
- Wear and tear: Companies can deduct for the wear and tear of their assets. The rate varies from 0% to 45%, depending on the type of asset.
- Goodwill: As of 2021, companies can no longer deduct goodwill. The government removed it from the list of assets that can be depreciated for tax purposes.
- Pre-business costs: Companies can deduct certain expenses before starting or expanding their business. They can spread these deductions over five years.
- Interest: Companies can deduct all interest they pay on business loans. However, if they pay interest related to foreign companies, they can only deduct up to 30% of their earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA).
- Social responsibility: Generally, companies can’t deduct expenses for corporate social responsibility (CSR) activities. But they might be able to deduct donations to specific charities.
- Certain payments: Companies can deduct some expenses only when they actually pay them. These include contributions to employee provident funds, employee bonuses, and interest to banks.
- Fines: Companies can’t deduct fines or penalties imposed by law. However, they can deduct penalties from contracts.
- Payments to foreign affiliates: Indian companies can deduct payments they make to foreign affiliates for royalties, interest, and technical or management services. These payments must not be for capital expenses.
Remember, companies can only deduct these expenses if they’re solely for business purposes. The tax office will check to make sure companies follow these rules.
How Corporate Taxes Affect Business Decisions?
Business actions and tactics are much influenced by corporate taxes. From where a firm decides to set its operations to how it arranges its financial transactions, the tax consequences of different acts may affect everything.
Locations of Choice
Companies’ decisions to establish their headquarters or subsidiaries might depend on the differing corporation tax rates applied by other nations. Some businesses could want to decrease their tax obligations by establishing activities in low-tax nations.
Capital Entrants
The tax treatment of capital expenditures may affect the choices of a business on whether and how much to spend on new buildings or equipment. Tax breaks for certain kinds of investments might inspire businesses to distribute funds in particular ways.
Decisions About Finance
The decision a firm makes between debt and equity financing may depend on the tax deductibility of interest payments. Since dividend payments are not tax-deductible and interest payments are normally, the company tax structure might lead to a tilt towards debt financing.
Profit sharing
The idea of double taxation, where corporate profits are taxed at the corporate level and subsequently once more as dividends to shareholders, may affect how businesses decide how best to allocate their earnings. To avoid this double taxation, some can reinvest earnings instead of distributing them.
Business Model
The manner in which companies determine their structure may reflect tax considerations. For instance, some businesses might opt to register as Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) to avoid double taxation, as LLPs in India are not subject to corporate tax at the entity level.
Both legislators and business leaders rely on an understanding of these effects, as changes in corporate tax policy can have substantial implications for company behaviour and economic activity in India.
Tax Rebates for Indian Businesses
Companies in India can get several tax breaks to reduce the tax they pay. Here are some key tax breaks available:
- Companies don’t have to pay tax on capital gains.
- In some cases, Indian companies can pay less tax on dividends from other Indian companies.
- Companies can get tax breaks for exporting goods or starting new businesses in certain situations.
- If a company loses money, it can use this loss to reduce its taxes for up to 8 years afterwards.
- The government gives special tax treatment to venture capital companies and funds.
- Companies can get tax breaks if they build new infrastructure or set up new ways to generate electricity.
Evolving Trends Related to Corporate Taxes
The scene of corporate taxes changes along with the global economy. Several trends and issues are determining how companies pay taxes going forward:
- Digital Economy: Traditional corporate tax regimes now face fresh difficulties as digital companies spread beyond borders.
- Global Minimum Tax: Efforts are underway to establish a worldwide minimum corporate tax rate intended to stop international tax competitiveness.
- Environmental Considerations: Corporate tax policy is increasingly being used as a means of encouraging environmentally friendly company operations.
- Simplification: Many support streamlining business tax laws to save compliance expenses and increase efficiency.
- Transparency: Rising expectations of corporate tax openness might influence the next reporting rules.
These patterns imply that corporate taxes will remain a dynamic and changing sector needing constant attention from companies, legislators, and tax specialists.
Final Thoughts
A key element of government income, as well as company financing, is corporate tax. From knowing the fundamentals of how corporation tax works to negotiating the convoluted world of deductions and policy discussions, this study of corporate taxation demonstrates its broad effects on company choices and economic environments.
Looking to sharpen your business skills without leaving your job? Manipal University’s Online MBA Programme is the perfect fit! Dive into crucial topics like corporate finance and taxation, all from your living room. This flexible program lets you balance work, life, and study with ease. Learn from top-notch academicians and boost your career prospects.