Demystifying Endpoint Security: Understanding How it Works and Its Importance
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 25, March 2024
- 10:00 am
With threats everywhere in the digital world, safeguarding endpoints is now the priority for an individual and an organisation alike. Endpoint security plays a critical role in the world of cyber security. It protects devices like computers, laptops, tablets, servers, and smartphones from various online threats. However, an important question remains: what is endpoint security, how does it work, and how vital is it for our digital world today? Let’s dive into it.
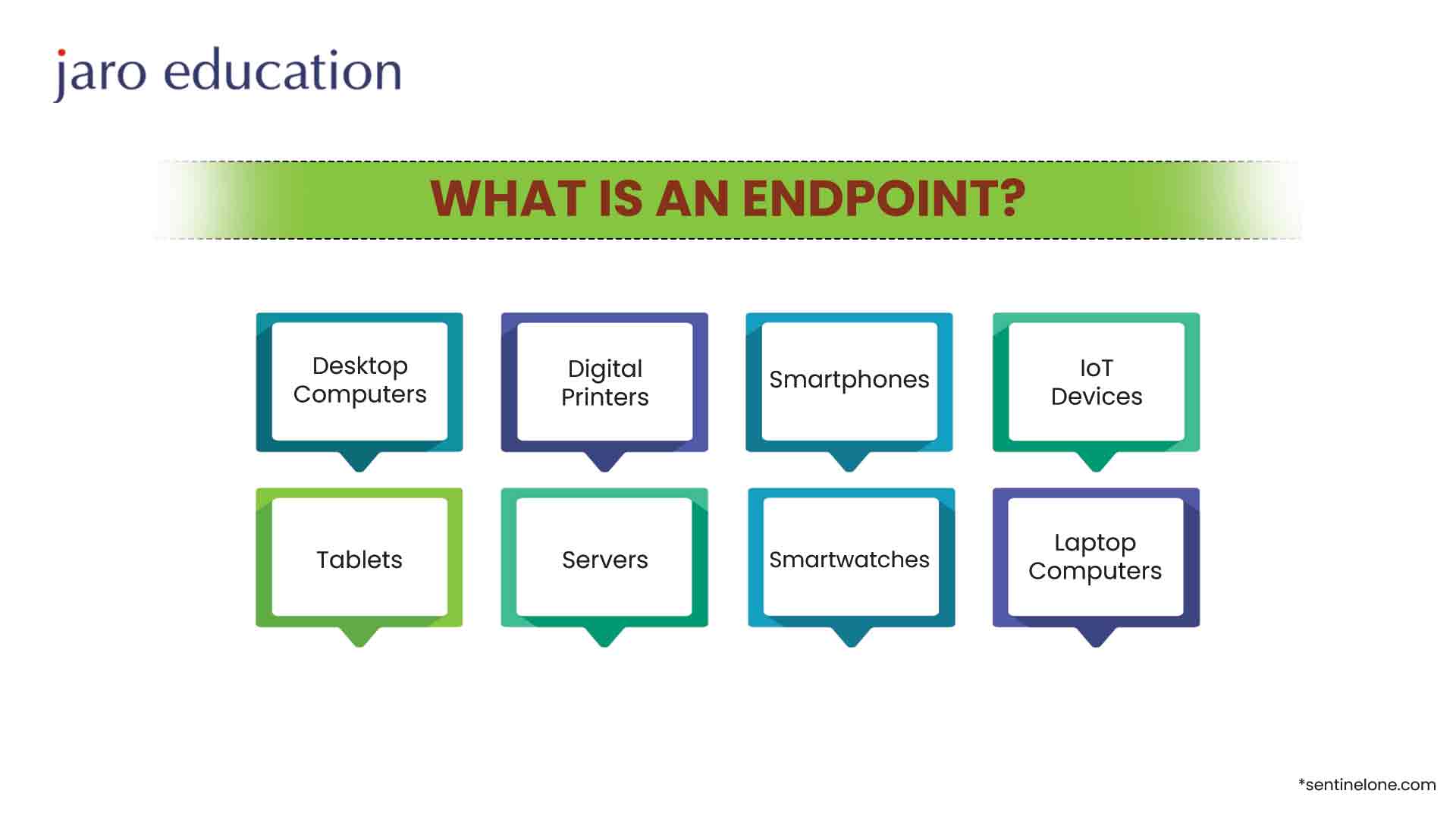
What is Endpoint?
An endpoint may be understood as the link between an employee and the company network. Along with the rise of BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) and other connected devices such as the Internet of Things (IoT), the list of possible devices that could connect to the network naturally keeps growing.
Some of the more common devices that can be considered an endpoint include:
- ATMs
- IoT-enabled smart devices
- Industrial equipment
- Laptop and computers
- Medical equipment
- Cell phones
- Printers
- Smartwatches
What is Endpoint Security?
Endpoint security is about securing endpoint devices—which can be laptops, workstations, mobile devices, or anything else that connects the network—from any malicious activity. These threats encompass a wide range of malicious activities, including malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, data breaches, unauthorised access, and more. The function of endpoint security is to safeguard not only the device itself but also the network it connects to against these risks.
In the contemporary world of IT, where remote work and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies are expanding, endpoint security becomes an essential element of the business security strategy. The spread of endpoints and the variety of operating systems and applications that operate them create great challenges for the IT security teams to protect sensitive information and keep the systems compliant with the regulations.
Endpoint security solutions typically include a combination of antivirus software, anti-malware tools, firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), encryption technologies, endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, and mobile device management (MDM) platforms. These tools work together to provide multiple layers of defence, enabling organisations to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats effectively.
Types of Cyber Threats
1. Malware
One of the basic elements on which endpoint security relies is malware protection. Malware, which is an adjectival phrase for malicious software, is a term that describes a wide range of harmful programs aimed to penetrate and destroy endpoints, steal information of a sensitive nature or disrupt operations. Classic antivirus programs constitute a crucial element of endpoint security since they not only scan files and processes for signs of known malware signatures and schemes but perform this scanning in near-real time. While cybercriminals constantly develop new means of attack and become harder to detect with each passing minute, the newest cyber security systems apply modern tools including behaviour analysis, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to detect and respond to zero-day threats and polymorphic malware.
2. Ransomwar
Ransomware, a malware that encrypts files and asks for money in return for their release, is one of the malware types that are commonly seen today. In the meantime, endpoint security solutions take measures to proactively protect systems from threats. They accomplish this in multiple ways such as endpoint backup and recovery, application whitelisting, and real-time monitoring for suspicious file encryption activity. Furthermore, education users and awareness play the prime role in preventing ransomware attacks because they mostly exploit the social engineering routes to make users unaware of receiving malicious links to click or infected email attachments.
3. Phishing
Another major security threat to endpoint security is phishing attacks which involve fake emails, text messages, or websites intended to trick the users into disclosing their secret information, such as login credentials or financial details. Endpoint security solutions aim to combine email filtering, web filtering, and browser security extensions which prevent access to malicious domains and URLs. Furthermore, user authentication mechanisms such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) add an extra layer of security by requiring additional verification steps beyond passwords alone.
4. IoT Devices
Endpoint security extends beyond traditional endpoints to include Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which are increasingly connected to corporate networks and present unique security challenges. IoT endpoints such as smart thermostats, IP cameras, and industrial control systems often lack built-in security features and are susceptible to exploitation by cyber attackers. So, endpoint security solutions for IoT devices leverage techniques such as network segmentation, device authentication, and firmware updates to mitigate these risks and protect critical infrastructure from cyber threats.
5. Internal Threat
Apart from protecting endpoints from external dangers, endpoint security solutions also safeguard against insider threats from staff or contractors who are legit accessing the company networks. Everyone who works for the same company has an insider threat hiding in all the corners. It can be accidental like downloading malware and falling into a phishing scheme, or it can be intentional like stealing data. The endpoint security systems are designed to track such user behaviours and monitor access patterns to identify any abnormal activities associated with internal threats. Thus, it is possible for the organisation to quickly respond to such incidents and be able to probe further into the origin.
How Endpoint Security Works?
1. Prevention
The antivirus endpoint security technology includes many methods of blocking threats at an early stage. This involves checking files for malware signatures, blocking malicious websites, and enacting security policies.
Antivirus software is one of the most fundamental components of endpoint security. Antivirus software scans files and programs on the endpoint for known patterns of malicious code (viruses, worms, Trojans, etc.). When a match is found, the software either quarantines, deletes, or neutralizes the threat.
Firewalls act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks (like the Internet). They monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic and decide whether to allow or block specific traffic based on predefined security rules. Firewalls can prevent unauthorized access to endpoints and block malicious traffic.
2. Endpoint Detection
The endpoint security software works continuously to monitor endpoints with the intent of identifying unmistakable abnormal behaviour. They employ top-notch scoring systems for malicious activity using threat detection algorithms, behavioural analysis and machine learning to identify events capable of causing security threats.
3. Endpoint Response
Upon identifying a security incident, endpoint security comes to identify and apply suitable actions to contain the threat and eliminate it. This may involve extracting the compromised endpoint from the network, blocking network connectivity of malicious files, or rewinding unauthorised changes.
4. Forensics and Investigation
Endpoint security software incorporates forensic features allowing investigation of the causes of the incident and its source. This consists of probe system artifacts, network traffic logs as well as trace the attack pattern and suspicious tactics of the attackers.
Importance of Endpoint Security
- Primarily and most importantly, endpoint security protects the data which is sensitive. In today’s digital world, data is the lifeblood of any organisation that comprises valuable assets in the form of financial information, intellectual property and customer details. Endpoint devices serve as a storehouse for this critical data, making them prime targets for cybercriminals seeking unauthorised access. Without adequate endpoint security measures in place, organizations risk exposing sensitive information to theft, manipulation, or unauthorized disclosure, leading to severe financial and reputational damage.
- Endpoint security is a necessary component of a risk-mitigation strategy to address a variety of cybersecurity threats. Malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, and exploit kits are used by adversaries to take control of the endpoint devices and to get through into the networks. Entering the internal networks, these threats can disrupt systems, get confidential information and spread wide destruction. As an endpoint security solution, antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint firewalls play critical roles against threats and give organisations the power to detect and block the attacks before they can harm.
- Endpoint protection is really important for the protection of systems and networks. Endpoint devices serve as the frontline defence against external threats, acting as gateways that control access to sensitive resources and data. Implementing strong endpoint security measures will allow organizations to strengthen their security posture even more, as it will increase their level of defence against various cyber threats and vulnerabilities that are always evolving. This, in turn, helps to enhance the resilience of systems and networks, minimizing the likelihood of successful cyber-attacks and their associated impacts.
- Moreover, endpoint security is the key factor in preserving regularity and fulfilling the standards of the trade. Data protection and privacy law compliance is today a necessity and not a choice for every company that operates within a complex regulatory environment which includes the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). In this case, such regulations, mainly, will provide a high security standard for sensitive data and protection against unapproved access. As such, if an enterprise fails to follow these rules, corporate fines, legal liabilities, and reputation problems, it may face. By implementing robust endpoint security controls, organizations can demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements, thereby mitigating legal and financial risks.
- Thus, endpoint security is crucial for safeguarding remote and mobile devices, which have become increasingly prevalent in today’s mobile workforce. With the rise of remote work and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies, employees are accessing corporate networks and sensitive data from a diverse array of devices and locations. This poses significant challenges for organizations, as it expands the attack surface and introduces new vulnerabilities. Endpoint security solutions, such as mobile device management (MDM) and endpoint encryption, help organizations secure these devices and enforce security policies, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected regardless of where it is accessed.
Final Thoughts
Endpoint security is of paramount importance in today’s interconnected and digitised world. By protecting endpoints against cyber threats, organizations can safeguard sensitive data, mitigate risks, and ensure the integrity of systems and networks. Furthermore, endpoint security is essential for maintaining regulatory compliance, safeguarding remote and mobile devices, and preserving the trust and confidence of customers and stakeholders. In an era marked by relentless cyber-attacks and evolving threats, investing in robust endpoint security measures is not just a prudent decision but a critical imperative for organizations seeking to protect their assets, mitigate risks, and maintain a competitive edge in the digital age.
So, take the proactive step to safeguard your endpoints and protect your digital assets today. Invest in an Executive Program in Artificial Intelligence and Cyber Security for Organizations [EPAI&CSO] by IIM Indore to ensure comprehensive protection against evolving cyber threats.










1 thought on “Demystifying Endpoint Security: Understanding How it Works and Its Importance”
Informative article! It clearly explains what endpoint security is and emphasizes its importance in protecting networks from various cyber threats.