Financial Accounting Vs Managerial Accounting
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 16, September 2023
- 2:23 am
In the world of business, two distinct branches of accounting have an integral role to play, they are financial accounting and managerial accounting. They act as essential instruments for guiding decision-making, ensuring financial clarity, and assessing the financial performance of a company. Through this blog, learn about the objectives of these accounting types along with other aspects of it.
Financial vs Managerial Accounting - Meaning
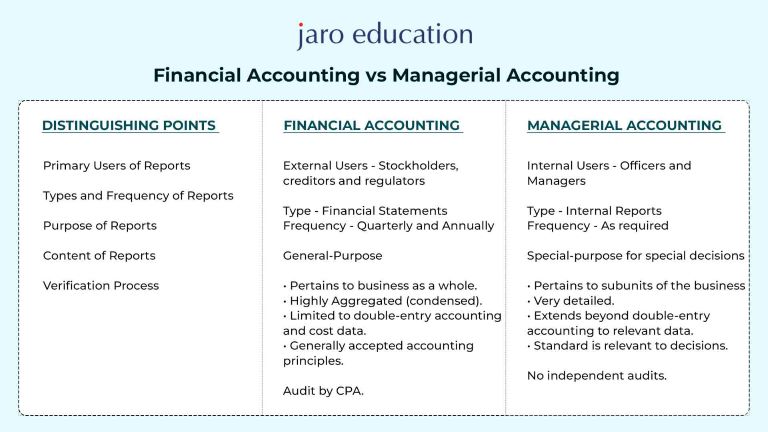
Financial Accounting
This is a process of summarising, recording and reporting all the business activities and financial transitions to the stakeholders that include the general public, investors, stakeholders, and creditors. The purpose of financial accounting is to provide correct and reliable information about the company’s performance and financial activities over a period of time. The main output of financial accounting includes income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Managerial Accounting
On the other hand, managerial accounting deals with providing accurate and reliable information to the internal management in order to plan and make decisions regarding the organisation. In order to help the managers in generating the cost structure, profit of the organisation, and efficiency of the business, managerial accounting is needed. This is not as strict as financial accounting and can be customised according to the need of the managers for the betterment of the organisation.
Primary Objective of Financial and Managerial Accounting
Financial Accounting
The preliminary goal of financial accounting is to offer a comprehensive and accurate view of a company’s financial performance and the position of external stakeholders. It aims to portray the overall financial health of the organisation.
Managerial Accounting
The main goal of managerial accounting is to provide internal managers with the information they need to make effective decisions. It emphasises improving operational efficiency, controlling costs and enhancing the organisation’s performance.
Types of Audience
Financial Accounting
In Financial accounting, the external parties are the primary audience who are interested in the financial health and performance of the organisation. The stakeholders include the general public, investors, stakeholders, and creditors. The information which financial accounting provides is very crucial for assessing the stability, profit and overall value of the organisation.
Managerial Accounting
In an organisation, the internal management team is the primary audience in managerial accounting. There are various levels of managers, like executives, department heads, and operational managers. The information provided by managerial accounting helps in making different decisions that include performance valuation, pricing strategy, budgeting, strategic planning, and allocation of resources.
*1investing.in
Focus and Reporting
Financial Accounting
In order to know the organisation’s present value and past performance, the organisation uses the historical information provided by financial accounting. This follows the Generally Accepted Accounting Principle (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). The external stakeholders can only provide a meaningful and reliable decision and analysis only if the financial accounting information is accurate, reliable, and comparable.
Managerial Accounting
As compared to financial accounting, managerial accounting is forward-looking and mainly focuses on providing information for future planning and making decisions. The managers use different tools like cost analysis, budgets, and forecasts to balance, control and optimise the different strategic goals of the organisation. The formats and methods of managerial accounting are more flexible because the information is used for internal purposes only.
Time Horizon
Financial Accounting
A Fiscal year or a quarter is used in financial accounting that deals with financial data of the past years. It gives an unbiased picture of an organisation because of its historical data.
Managerial Accounting
In managerial accounting, both historical data and future-oriented data are used to show and predict the performance of an organisation. Although it uses historical data, its main focus is to determine future performance with the help of decision-making. Managers depend upon the forecast, resource allocation, and projections in order to make a decision.
Types of Information
Financial Accounting
In Financial accounting, the overall position and financial performance are seen. The information that it includes is revenue, equity, cash flow, liabilities and assets. Financial statements like cash flow, balance sheets, and income statements are the primary outputs.
Managerial Accounting
Detailed and specific information regarding an organisation is provided in managerial accounting. In order to help managers make informed decisions and to understand operations efficiently, managerial accounting covers performance metrics, cost behaviour, break-even analysis, and budget variances.
Regulations and Standards
Financial Accounting
Financial Accounting follows a strict regulatory standard like GAAP or IFRS based on the jurisdiction. In any financial reporting, these standards help in ensuring transparency, consistency, and compatibility. The prime goal of financial accounting is to provide more reliable and unbiased data to external stakeholders in order to make credit decisions and investments.
Managerial Accounting
Managerial accounting differs from financial accounting in terms of rules and regulations. It does not follow the same standards as financial accounting. The organisation is flexible enough in choosing the different formats, frequency of reporting and methods. Thus, the flexible standards of managerial accounting make it easy for managers to deal with information according to the needs of an organisation.
External Verification
Financial Accounting
The information provided by financial accounting is audited by external auditors or parties for external verifications. This verification ensures the accuracy and reliability of financial statements presented to external stakeholders.
Managerial Accounting
Managerial accounting does not require external verification by external auditors or individuals. This accounting is used for internal purposes and is flexible according to the needs of an organisation and the managers, so it needs no external verifications.
Frequency of Reporting
Financial Accounting
Financial accounting reports are typically prepared at the end of each accounting period, which could be quarterly or annually. These reports follow specific regulations and accounting principles and are standardised.
Managerial Accounting
The management can generate managerial accounting reports as frequently as they wish to according to the needs of an organisation. They can be adjusted at different time frames like daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly depending on the requirements of the decision-making process.
Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Financial Accounting
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) in the United States or International Financial Reporting Standards(IFRS) are the two legal and regulatory frameworks which govern financial accounting internationally. They ensure consistency and comparability of the information provided.
Managerial Accounting
It is not bound by the legal regulations of financial accounting. It is flexible, acceptable, and adaptable according to the needs of the organisation and is used for internal purposes in order to make decisions for the upliftment and betterment of the organisation and its stakeholders, both internally and externally.
In essence, financial accounting and managerial accounting are two complementary branches of accounting that serve distinct purposes within an organisation. Financial accounting caters to external stakeholders by providing accurate and standardised financial information for investment and credit decisions. Managerial accounting, on the other hand, focuses on equipping internal management with relevant data for planning, decision-making, and performance evaluation.
Both types of accounting play vital roles in an organisation’s success. Financial accounting ensures transparency and accountability to external parties, while managerial accounting empowers managers to make informed decisions that optimise efficiency, control costs, and align with strategic objectives. Balancing the insights gained from both financial and managerial accounting enables businesses to navigate the complex landscape of modern commerce and drive sustainable growth.
Takeaway
Staying aware of the current trends and strategies of an organisation is crucial for success in today’s rapidly changing marketing scenario. The major dissimilarities between financial accounting and managerial accounting are based on the purpose, audience, focus and reporting, among others. It is important for an individual to understand both financial and managerial accounting to be either an external stakeholder or an internal stakeholder.
By utilising these accounting techniques, companies can get a competitive edge. Individuals can refine their skills, and achieve remarkable results in an organisation’s performance. So, make it a priority to explore these accounting statements and immerse yourself in the world of investment.
While reading the accounting statements can help you gain beneficial insights, being a part of a well-established IIM Ahmedabad’s Executive Programme in Business Finance through Jaro Education can help you gain relevant skills and a comprehensive understanding within 6-7 months of the course. So, join the program and nurture your expertise in the field of accounting.












1 thought on “Financial Accounting Vs Managerial Accounting”
An excellent explanation of financial and managerial accounting. The comparisons are clear and easy to understand, making it easier to understand how each supports different aspects of business operations.