Qualitative & Quantitative Research Methods: Discover the Astonishing Differences
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 30, November 2023
- 4:00 pm
Be it companies launching new products, economists trying to assess a situation, or scientists gathering data for their experiments, one thing common is the research methodology used. There are two approaches to gathering information and data – qualitative and quantitative research methods. Each has its significance, applications, and specialties. Depending on the probable outcome, experts conduct qualitative and quantitative research accordingly.
As businesses expand and economies grow, demand for professionals who can conduct research and equip decision-makers with data, information, and insights to make strategic decisions will grow with time. This blog highlights the difference between qualitative and quantitative research methods, their applications in the real world, and if you want to build a career as a research expert, then what course should you be eyeing?
Defining Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methods
Both research methods have a unified aim – providing information, insights, and data used to make concrete decisions. But the game is all about what methodology researchers use to gather information.
Take it this way, for offroading, nobody will drive a sedan. On the other hand, driving through congested locations, nobody will drive an SUV. Similarly, qualitative and quantitative research methodology is carefully picked by researchers based on what they want to obtain from the sample sets.
In qualitative research methodology, researchers collect and analyze non-numerical data (text, videos, audio files) to get a grip on concepts, opinions, and experiences. This methodology is used to collect in-depth insights or generate new ideas for research. How this research is conducted, and what data collection tools are used, will be explained in upcoming sections.
In quantitative research methodology, researchers collect and analyze numerical data to find patterns, and averages that enable them to make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to the mass. This research method is the exact opposite of qualitative research methodology.
*DataExpertise.in
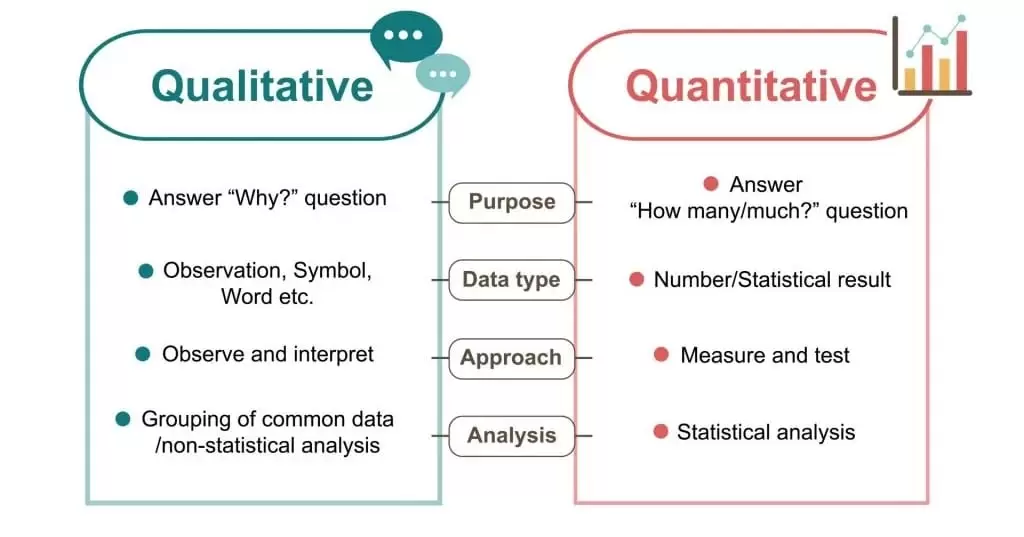
Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methods
Now that you know what these two research methods do, let’s tone down the difference between qualitative and quantitative research methods –
| Aspect | Qualitative Research Method | Quantitative Research Method |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | Few respondents | Many respondents. |
| Survey Tools | Interviews, focus group discussions, observations, ethnography, and literature reviews. | Surveys, experiments, structured observations, and questionnaires. |
| Type of Questions | Open-ended questions to take their point of view | Close-ended, multiple choice questions or rating scales to know their point of view. |
| Primary Objective | Qualitative research methodology is used to understand meanings, explore new ideas, and behaviors, and form theories. | Qualitative research methodology is used to analyze numerical data and quantify variables by using logical, statistical, and mathematical techniques to test hypotheses. |
| Nature of Data | Expressed in words. Non-numeric statements and opinions. | Expressed in numerical data via graphs, values, and scales. |
| Data Analysis | Inductive, thematic, and theoretical. | Deductive, statistical, and numerical. |
| Research Perspective | Subjective in nature. | Objective in nature. |
Data Collection Methods in Qualitative Research Methodology
While the aim of both research methods is the same, they differ a lot in nature, applications, and data collection methods used. By now, you surely would have noticed this huge difference between qualitative and quantitative research methods.
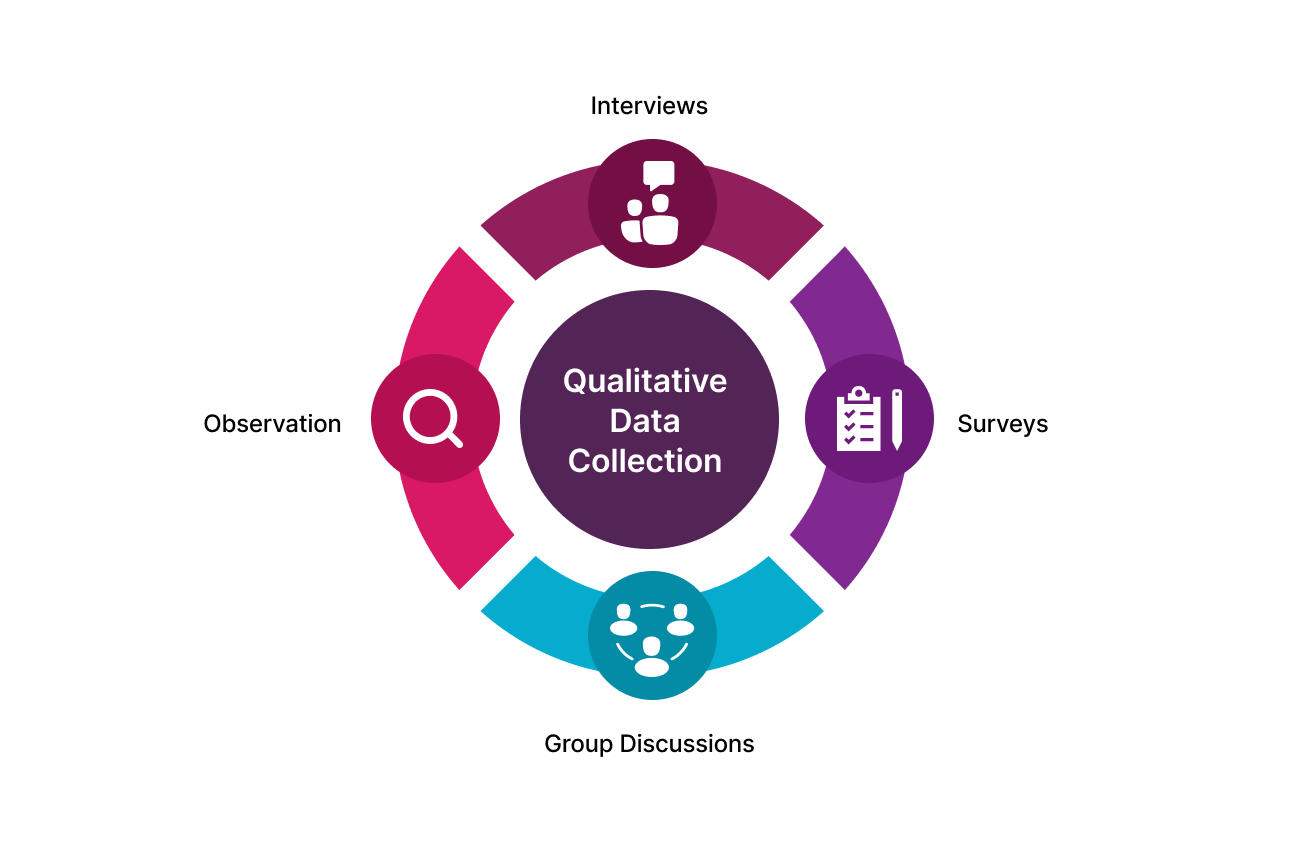
If you want to conduct qualitative research methodology, then below are some tools that you will be using throughout your research journey –
- Interviews – You ask open-ended questions to the respondents verbally. You can interview participants online, or offline. Interviews are done to know each person’s point of view and their thought process. However, interviewing is time-consuming and you should follow this approach only when your sample size is a handful.
- Focus Group Discussions – You make a group of people sit together and give them a topic to discuss collectively. This way, you note down their opinions, and how a group perceives a particular topic.
- Content Analysis – Researchers use archival and secondary works published by other authors and analyze the content. This can be media covering a story, series of blog posts, comment posts, films, cartoons, advertisements, brand packaging, or photographs on social media.
- Observation – It is an observational study used in social science, education, healthcare, marketing, and design. The observation provides detailed information about the behavior, attitudes, perceptions, and experiences of individuals or a community.
- Ethnography – For some time, researchers participate in a community to monitor behavior, and culture, and note down their opinions as a community or a group.
*brocoders.com
Data Collection Methods in Quantitative Research Methodology
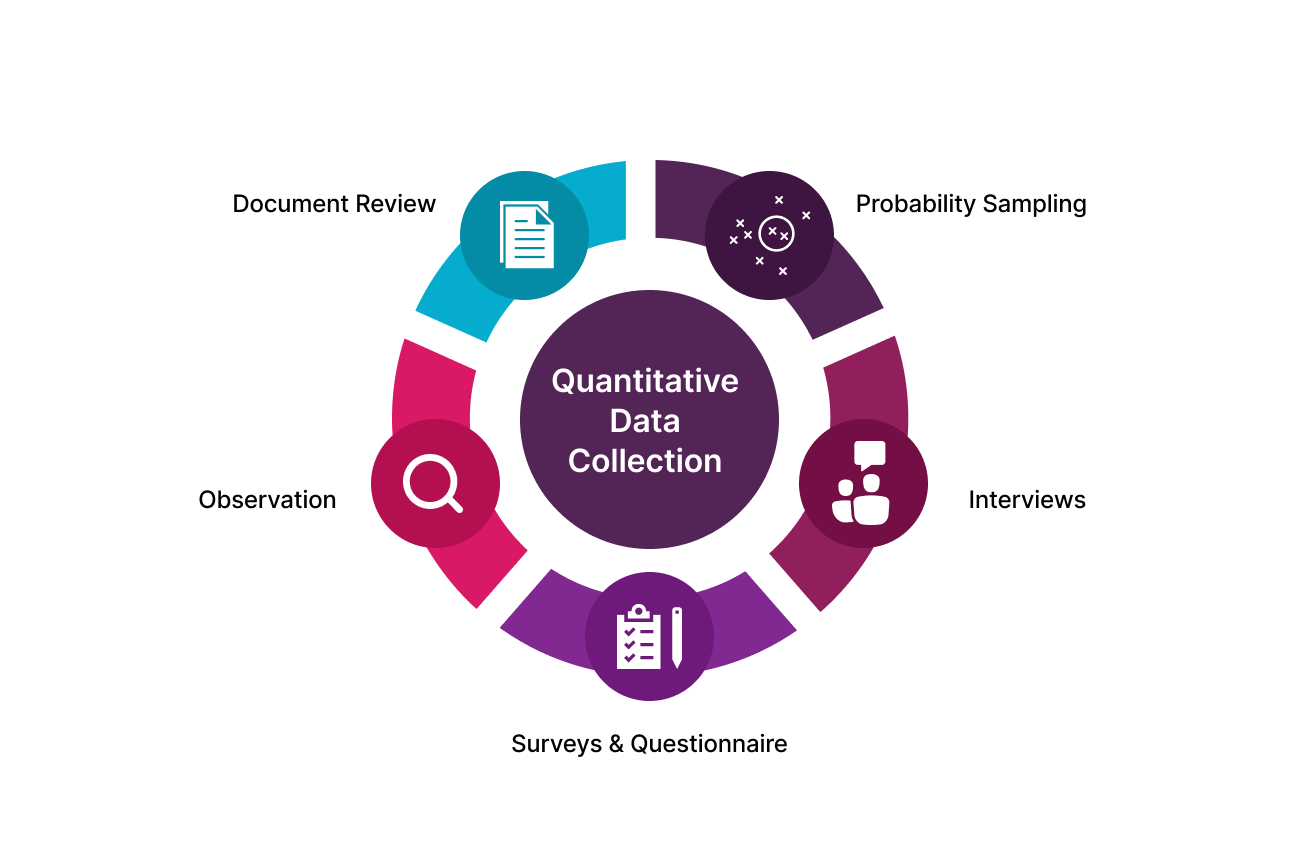
If you are a quantitative research professional then you deal with loads of numbers, charts, and trends. Here, your data collection tools differ slightly from qualitative research methodology. Here are some data collection tools to conduct quantitative research –
Quantitative Surveys – These surveys have closed-ended questions so that responses are comparable. Only a small portion of the survey has open-ended questions. To gather respondents for quantitative surveys, researchers use the probability sampling method. Following are 4 types of probability sampling –
| Simple Random Sampling | A straightforward approach involving random individuals from the population without grouping them. |
| Stratified Random Sampling | Divides the population into subgroups and selects a random sample from each stratum. |
| Cluster Sampling | Dividing the population into clusters and then randomly selecting clusters. |
| Systematic Sampling | It begins with random sampling and then researchers select the nth number of the population (every 10th or 12th respondent) |
- Experiments – Researchers manipulate one or more variables and observe the effects on a specific outcome. Experiments are either done in a closed laboratory or in the real world.
- Secondary Data Analysis – This involves using existing data to answer a new research question. This method is cost-effective and efficient but it’s crucial to ensure that the data is appropriate for research questions.
- Computerized Tracking – It deals with tracking and collecting data automatically from digital sources like social media, online purchases, or web analytics.
*brocoders.com
How Do You Analyze Quantitative Data?
Qualitative research methodology is all theory and based on views and opinions. It is comparatively easy to come to a conclusion based on the data pulled. But for quantitative research, there are scientific and statistical ways to read the data through charts, and analysis. Let’s have a look at them –
| Descriptive Statistics | Used to describe basic features of data like mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range. |
| Inferential Statistics | It is used to make generalizations about a population based on sample data. It includes hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis. |
| Data Visualization | You create charts, graphs, histograms, scatterplots, bar charts, and other visual representations to help identify patterns and trends. |
| Time Series Analysis | It involves analyzing data collected over time to identify patterns and trends. |
| Multiverse Analysis | Involves analyzing data with multiple variables to identify relationships between variables. |
| Factor Analysis | It involves identifying underlying factors or dimensions that explain the variation in the data. |
| Cluster Analysis | It identifies groups or clusters of observations that are similar to each other based on multiple variables. |
Practical Applications of Qualitative and Quantitative Research
So far, we have covered the basics of qualitative and quantitative research – definitions, differences between the two, and data collection methods. Before we highlight India’s best program to master qualitative and quantitative research methods, let’s understand where these research methods are being used, what for, and how important they are in the real world.
Examples of Qualitative Research Methodology –
- Research – Qualitative data is used in exploratory research to get hold of unfamiliar topics. Researchers use this data to create hypotheses and build a deep understanding of the main premise.
- Evaluation – Researchers use the data to evaluate the impact of a program on the people who participate in it.
- Needs Assessment – Qualitative data is used in needs assessments to understand the needs of the population. Researchers try to understand prominent needs and develop strategies to address those needs.
- Case Studies – The data generated by qualitative research methodology is often used in case studies to understand the details, context, experiences, and perspectives of the people involved in the case.
- Market Research – Qualitative research methodology is used in market research to understand consumer behavior and preferences and gain insights into consumer attitudes, opinions, and motivations.
- Social and Cultural Research – The data is also used to understand social phenomena like culture, norms, and social relationships.
Examples of Quantitative Research Methodology –
- Average height and/or weight of population.
- Temperature of a city/state.
- Number of cars sold in a month.
- Amount of rainfall in a specific area.
- Average GPA of 100 students.
- Amount of sugar in food items.
- Stock prices.
- Crime rate in a particular area.
Is a Career in Qualitative and Quantitative Research Rewarding?
Research and development are crucial parts of business, science, and technology as well as for the economy. For continuous product development, for a better understanding of the target market, and to understand unknown situations, qualitative and quantitative research becomes the need of the hour.
During the pandemic, how did the economy come to know that it really is a pandemic? How did the nations realize which part is most affected? It was all based on research.
Whenever a new product enters the market, the general public only interacts with the advertisement. However, from what is to be shown in advertisements to the minute intricacies of the upcoming product – everything is connected to qualitative and quantitative research or a mix of both.
Having said that, here is a sneak peek at the average salaries of qualitative and quantitative research professionals –
| Levels | Average Salary of Quantitative Researcher (per annum) | Average Salary of Qualitative Researcher (per annum) |
|---|---|---|
| Entry | ₹5.2 lakhs - ₹60 lakhs | ₹1.8 - ₹6 lakhs |
| Average | ₹5 lakhs - ₹15.4 lakhs | ₹4.8 - ₹6.5 lakhs |
| Senior | ₹15.4 lakhs - ₹1 crore | ₹2.7 - ₹7.5 lakhs |
Executive MBA - Dayananda Sagar University is Your Gateway To Become a Professional Research Analyst
There is no doubt that research is a cornerstone of knowledge, and discovery allows people to explore, understand, and explain various phenomena of the real world. As a research professional, you’ve got to have a good grip on qualitative and quantitative research methods.
To ensure that you get a good grip on this dynamism, we present India’s best programme to master qualitative and quantitative research methods – Executive MBA – Dayananda Sagar University which provides flexible online classes and alternate weekend on-campus sessions (that can be availed from remote locations). This executive MBA program will help you to scale up your corporate personality and upskill you as a qualitative and quantitative research professional. Here are the course details –
| Duration | 17 months |
|---|---|
| Eligibility Criteria | 3-4 years graduation degree holders from recognized universities. Minimum 1 year of full-time work experience |
| Specializations To Choose From | Global Business / Marketing Management / Operations Management / Project Management / Business Analytics / Financial Management and much more. |
| Program Fee | Application Fee: ₹1,000 Total Program Fee: ₹2,25,000 |
| Installment Pattern | Installment 1: ₹48,000 Installment 2: ₹45,000 Installment 3: ₹45,000 Installment 4: ₹45,000 Installment 5: ₹42,000 |
Jaro Education: Your Gateway To Access World-class Educational Programmes
-
- Constant Learning Support – Jaro Education provides unparalleled career guidance and support to young aspirants with immersive lifelong learning experiences. From finding a course to mentorship – Jaro Education has dedicated support for students.
- Doubt Resolution – With Jaro Education, you get to learn from seasoned academicians, faculty, and industry leaders. Throughout the course, you get the opportunity to be a part of discussions and forums for enhanced learning experience.
- Networking – Jaro Education has an alumni network of 3,50,000+ professionals. As an aspirant, you get full access to this alumni network with other perks and benefits. Stay up-to-date with the latest industry insights from your alma meter and get full to Jaro Connect Portal
- Placement Support – Once your certification course is completed, Jaro Education takes the responsibility to enhance your personality, and provides you with immerse opportunities to get places as a seasoned analyst. With the Jaro team, worry less about the future, and focus on the present.
| Admission Criteria | 3-4 years graduation degree holders from recognized universities. Minimum 1 year of full-time work experience. |
| Course Content | Human Resource Management, Accounting, Marketing Management, and much more. |
| Specializations | 10+ options to choose from. |
| Fee Structure | Application fee - ₹1000 Total Programme Fee - ₹2,25,000 Installment 1 - ₹48,000 Installment 2 - ₹45,000 Installment 3 - ₹45,000 Installment 4 - ₹45,000 Installment 5 - ₹42,000 |
The Executive MBA by Dayanand Sagar University can be a great kickstarter for your career in the corporate world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Indeed, it is a great career option if you like to interact with people, take their interviews, and drive conversations to figure out concrete trends, and information. As economies grow, and businesses prosper, both entities will need professional research analysts to help them drive strategic decisions. Be it marketing, finance, science and technology, economy, or corporate – there will always be demand for skilled qualitative and quantitative research professionals.
Qualitative research methodology is focused on non-numeric insights, data, and inputs. On the other hand, qualitative research methodology deals with hardcore numerical, charts, trends over time, and statistics.
To build a solid career as a research analyst, Executive MBA – Dayananda Sagar University is the best online certification programme.




![Email-Marketing-and-How-to-Do-It-Right-[2024-Guide]](https://jaro-website.s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com/2024/09/Email-Marketing-and-How-to-Do-It-Right-2024-Guide.jpg)




