Break Even Analysis: Definition, Formula, and Uses
Table of Contents

- jaro Education
- 6, May 2024
- 10:00 am
Break-even analysis is an instrument that neither proceeds to profit nor proceeds to lose money – this is called the Break-Even Point (BEP). It is primarily an internal tool that the management uses to make decisions, but it is normally not disclosed to third parties such as investors or regulators. But when you are taking a business loan, this bank may require it as a business plan.
You then compile your fixed costs and variable costs and then compare them to the amount that you are selling each unit for and the amount of profit that you are generating per unit to calculate your break-even point.
Fixed costs are those that do not change as the amount sold changes. This consists of such items as rent or mortgage on your office or store, equipment, salaries, interest on a loan, property taxes, and insurance.
Variable costs vary according to your sales. These can involve such issues as hourly pay, sales commissions, raw materials, utility expenses, and shipping. In essence, these are the expenses related to the production and distribution of each product you sell.
Being aware of these costs allows you to know how many units you have to sell to cover your costs, as well as start making a profit.
What is Break-Even Analysis?
Break-even analysis is used in finance to assist companies in calculating the stage at which the total revenue of a company will be equivalent to the total costs of a company, in other words, at which there is neither profit nor loss. This particular place is called the break-even point (BEP).
Break-even analysis simply answers the following question in simple words:
What is the number of products or services that I must work on to pay all my costs?
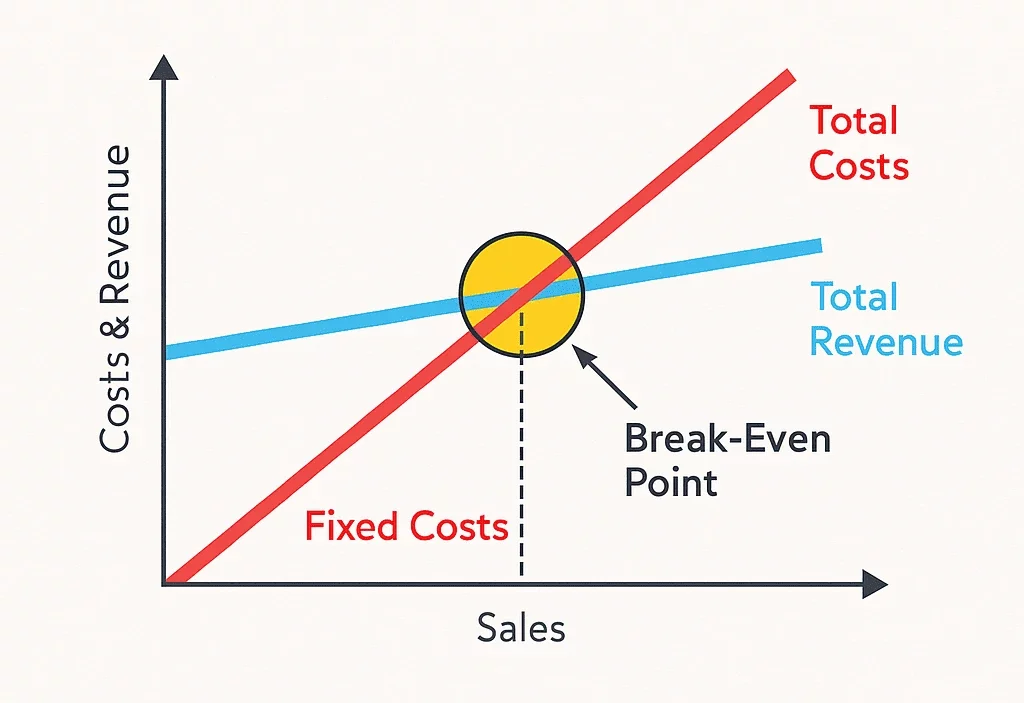
What is Break-Even Point Analysis?
The analysis of the break-even point can assist you in determining where:
Total revenue = total costs
At this stage, there is no profit being made by your business, but also not losing money, merely breaking even.
Why Break-Even Analysis is Important?
The importance of break-even analysis is that it can help you know at what stage your business begins to yield profits. It tells you the amount of product that you must sell at least to Importance of break-even analysis– so that you are not operating at a loss. It comes in handy when you want to price things, make budgets, or consider introducing a new product. It also helps you to have a better picture of the financial viability of your business idea. In addition, in case of a loan application, banks are usually interested in seeing the analysis to determine the risk. It is, all in all, really an awesome tool to make smarter, confident business decisions.
Key Components of Break-Even Analysis
The key components of break-even analysis are as follows:
| Component | Description |
| Fixed Costs | Costs that do not change with production or sales volume (e.g., rent, salaries). |
| Variable Costs | Costs that vary directly with production (e.g., raw materials, commissions). |
| Selling Price per Unit | The price at which each unit is sold to customers. |
| Contribution Margin | Selling Price per Unit minus Variable Cost per Unit |
| Break-Even Point (BEP) | The sales volume at which total revenue equals total costs (no profit, no loss). |
| Total Revenue | The amount earned from sales (Selling Price × Units Sold). |
| Total Costs | The sum of Fixed Costs and Variable Costs for a given level of production. |
How to Calculate Break-Even Point?
To calculate the break-even point, you can use the following formula:
Break-Even Point (in units) = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit)
Here’s how to calculate it step by step:
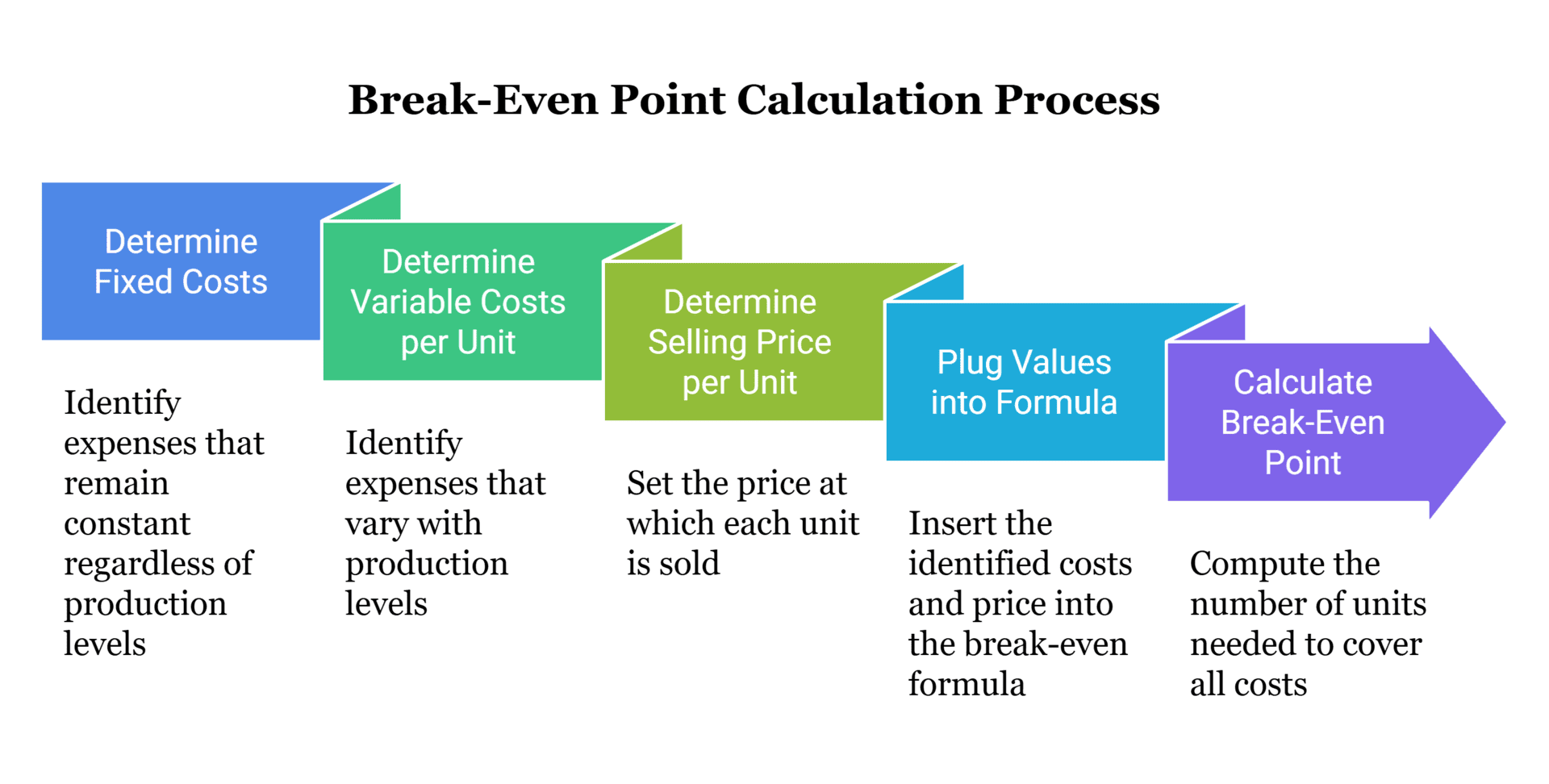
- Determine your fixed costs: These are expenses that remain constant regardless of the number of units produced or sold. Examples include rent, salaries, insurance, and utilities.
- Determine your variable costs per unit: Variable costs are expenses that vary with the level of production or sales. Examples include raw materials, labour, and shipping costs.
- Determine your selling price per unit: This is the price at which you sell each unit of your product or service.
- Plug the values into the formula: Divide your fixed costs by the difference between the selling price per unit and the variable cost per unit.
- Calculate the break-even point: The result will give you the number of units you need to sell to cover all your costs and break even.
Remember that the break-even point can also be calculated in terms of sales revenue instead of units by multiplying the break-even point in units by the selling price per unit.
Top Uses of Break-Even Analysis in Business Decision-Making
Uses of Break-even analysis can be useful in plenty of circumstances. Rick Vazza, the owner of Driven Franchising, says that on the one hand, you need to apply a break-even analysis, and, on the other hand, you have to ask the following questions about your business:
- What is my monthly goal in terms of the quantity of my product or service that needs to be sold?
- What is my estimated volume of sales?
- At what price will the figures equal my break-even calculation?
- At what price would I make an acceptable profit?
- What you want to do is have a true picture of your profit, net cash flow, and finances.
Rob Stephens, founder of CFO Perspective, said it is easier to get people to determine whether they will be able to reach that minimum than to tell them how many sales they will make.
The following are the three instances when you should consider carrying out a importance of break-even analysis:
- Assessing Profitability
The primary function of break-even analysis is to determine whether a business is breaking even or incurring losses. By identifying the break-even point, businesses can understand the revenue needed to achieve profitability. Moreover, it provides clarity on the adjustments required, whether increasing revenue or reducing costs, to attain profitability. Amidst various methods to gauge profitability, calculating the break-even point stands out for its simplicity and clarity.
- Informing Future Budgets
Break-even analysis proves invaluable for entrepreneurs and fledgling companies grappling with decisions on product offerings, sales volumes, and budget allocations. This analysis facilitates decision-making by quantifying the necessary sales volume for profitability and estimating the longevity of products. Adjusting variables such as fixed costs, sales price, and volume metrics enables businesses to formulate precise budgets for each cost component.
- Mitigating Financial Risks
Small businesses are inherently exposed to risks, particularly concerning product launches and withdrawals. Break-even analysis helps in risk assessment by revealing insights before significant decisions are made. For example, if projected demand falls short of the break-even sales volume, launching the product might not be financially viable. Identifying the break-even point offers clarity on which risks are worthwhile, enhancing decision-making processes.
- Ensuring Accurate Pricing
Once the break-even point is determined, businesses can strategically adjust pricing to achieve profitability. By understanding the required sales volume and revenue per unit, businesses can assess whether current pricing aligns with break-even objectives. If the break-even point cannot be met at the existing price, it signals a need for price adjustments. This is particularly beneficial for businesses stuck in pricing stagnation or those navigating initial pricing decisions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Break-Even Analysis
| Advantages of Break-Even Analysis | Disadvantages of Break-Even Analysis |
| Simple and Easy to Use – It’s a straightforward tool that’s easy to understand and apply. | Assumes Constant Costs – Assumes fixed and variable costs remain unchanged, which may not reflect reality. |
| Helps Set Realistic Sales Targets – Clearly shows how many units you need to sell to avoid losses | Ignores Market Conditions – Doesn’t consider demand fluctuations, competition, or market trends. |
| Supports Better Pricing Decisions – Helps identify a minimum price point to cover costs. | Not Ideal for Multiple Products – Complex when dealing with different products with different costs. |
| Improves Financial Planning – Useful in budgeting, forecasting, and decision-making. | No Focus on External Factors – Doesn’t factor in customer behavior or macroeconomic changes |
| Encourages Cost Control – Helps businesses analyze and reduce unnecessary expenses | Only a Quantitative Tool – Does not measure qualitative factors like brand value or customer satisfaction |
| Useful for Startups and Investors – Demonstrates profitability potential to investors or lenders. | Static Analysis – Needs frequent updates to reflect current financial situations accurately |
Learn Break-Even Analysis the Right Way with IIM Nagpur’s Program
IIM Nagpur’s Post Graduate Certificate Programme in Product & Brand Management is meticulously crafted for discerning executives aspiring to cultivate a strategic acumen anchored in product strategy as the linchpin for corporate expansion. This executive programme is tailored for mid- to senior-level professionals entrenched in pivotal roles within product development, management, or strategy. This avant-garde curriculum also extends its embrace to cross-functional professionals intricately woven into the product life cycle’s tapestry. The programme adopts pedagogical methods, new-age tools and techniques to harness the collective expertise and experiences of participants, fostering an environment conducive to robust learning and skill development. Astute executives navigating both the B2B and B2C domains, particularly those hailing from Retail, Product, IT, and consulting spheres, alongside visionary entrepreneurs steering family enterprises or startups and professionals within the echelons of banking and insurance, are poised to extract unparalleled value from this programme.
Jaro Education: Your Trusted Career Counselor and Guide to Success
Jaro Education has earned a strong reputation as a leading career counseling agency, guiding thousands of students and professionals toward successful careers. At the forefront of career planning and professional training, Jaro Education boasts a student success rate exceeding 85% in securing high-value employment and placements in top institutions. Through professional mentorship, programs aligned with industry demands, and personalized guidance, Jaro ensures each learner follows a path specifically tailored to their capabilities and aspirations. Whether for MBA hopefuls or working professionals seeking career advancement, Jaro Education consistently empowers individuals to make valuable choices and achieve long-term success.
Conclusion
Break-even analysis stands as a fundamental pillar of financial management for entrepreneurs, offering a thorough understanding of profitability and operational dynamics. Throughout this guide, we have understood the intricacies of break-even analysis, from deciphering fixed and variable costs to exploring its applications in pricing strategies, budgeting decisions, and risk mitigation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Break-even analysis is a financial calculation that determines the point at which total revenue equals total costs, meaning there is no profit or loss. This point is known as the break-even point (BEP).
It helps businesses understand how many units they need to sell or how much revenue they need to generate to cover their costs, making it a vital tool for pricing, budgeting, and decision-making.
The formula is:
Break-Even Point (Units) = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit)
- Fixed Costs: Costs that do not change with production levels (e.g., rent, salaries).
- Variable Costs: Costs that vary with production (e.g., raw materials, packaging).
Yes. Although services may not have physical products, break-even analysis can still be applied by calculating costs per service and determining how many clients or service hours are needed to break even.








