Strategic Management: What are the Various Elements, Approaches and Stages?
Table of Contents

- jaro education
- 29, June 2024
- 7:00 pm
Strategic management is the foundation for propelling your organisation to new heights of success. The related notion entails making critical judgments and acting appropriately. These administrative processes move an organisation toward its ultimate goals, which are to maximise product conversion and provide expected returns on investment.
Strategic management can help an organisation gain a competitive edge over others, improve its market share and plan for future objectives. Let us dive deep into the basics of strategic management and how it can boost career in the next sections.
What is Strategic Management?
Strategic management or business management is the art, science, and craft of developing, putting into practice, and assessing cross-functional choices that will help a company accomplish its long-term goals.
- It involves defining the goals, mission and vision of the organisation, as well as creating plans and policies to attain these goals—often in the form of projects and programs—and then allocating funding to put these plans into action.
- The main aim of strategic management is to integrate and coordinate the operations of a company’s many functional departments to accomplish long-term organisational goals. When assessing a company’s entire performance and its progress toward goals, a balanced scorecard is frequently employed.
Agenda and working
At the top of the managerial hierarchy is strategic management. While higher management is ultimately accountable for an organisation’s strategy, lower-level managers and employees frequently fuel it via their actions and ideas. An organisation may have numerous workers dedicated to strategy rather than depending exclusively on the chief executive officer (CEO) for direction.
Because of this fact, organisational leaders prioritise learning from previous methods and assessing the whole environment. The aggregate knowledge is then utilised to design future initiatives and steer employee behaviour, ensuring that the entire firm moves ahead. For these reasons, effective strategic management necessitates both inside and outward focus.
Generally, strategies are conceived, designed, or directed by the CEO, sanctioned or approved by the board of directors, and then put into action under the guidance of senior executives or the organisation’s top management.
Strategic management gives the business its overall direction. Within the realm of business administration, discussing “strategic consistency” or “strategic alignment” between the corporation and its surroundings is helpful.
Example of Strategic Management
A for-profit technical university wants to double new student enrolment and graduation rates over the subsequent three years. The goal is to establish the institution as the best value for a student’s money among the region’s five for-profit technical colleges, with the aim of boosting income.
In this scenario, strategic management would mean ensuring the institution has enough funds to hire highly qualified educators and build high-tech classrooms for the students. It would also require investment in sales and marketing strategies and recruitment processes, and implementation of student retention strategies. The institution’s management will then evaluate whether its aims have been met on a regular basis.
Key Elements of Strategic Management
Strategic management is not an approach that fits everyone. However, multiple key elements have been identified as vital. These include:
- goal planning and setting
- industry and organisational assessments
- strategy development and implementation
- strategy measurement, monitoring and control
Approaches to Strategic Management
There are basically two main approaches, which are opposite to each other but they complement each other in some ways:
The Industrial Organisational Approach
- This approach is based on economic theory and it is associated with issues such as resource allocation, competitive rivalry and economies of scale.
- There are a few assumptions as well, which include rationality, profit maximisation and self-discipline behaviour.
The Sociological Approach
- This approach deals primarily with human interactions.
- Here, the associated assumptions include satisfying behaviour, bounded rationality and profit sub-optimality. An example of an organisation that follows this approach is Google.
Furthermore, the techniques of strategic management can be visualised as:
- Bottom-up processes: Here, employees make suggestions to their leaders, who then pass on the finest ideas to higher-level management. This is frequently performed through a capital budgeting procedure. Proposals are evaluated using financial criteria such as return on investment and cost-benefit analysis. Cost underestimate and benefit overestimation are common causes of inaccuracy. The agreed suggestions serve as the foundation for a new strategy, which is carried out without the need for a huge strategic design or a strategic architect.
- Top-down processes: The particular approach is the most common option by far. Here, with the help of a strategic planning team, the CEO decides and makes plans regarding the overall direction that the organisation should consider moving forward.
- Collaborative processes: This approach tends to recognize the expanding nature of strategic decisions. Some organisations have begun to experiment with this technique.orper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Hierarchy of Strategic Management
In the majority of the organisations, there exist multiple levels of management.
Strategic management is the top most, out of all the levels, as in it is the broadest — applying to all parts of the corporation and also incorporating the longest time horizon. It gives direction to corporate goals, culture, values and missions. There are typically business-level competitive strategies and functional unit strategies that can be put under this broad corporate strategy:
- Corporate strategy: It refers to the overarching strategy of the diversified firm and answers the queries like — “In which businesses should we compete in?” and “How does working in various companies produce synergy and/or contribute to the corporation’s overall competitive advantage?”
- Business strategy: It refers to the combined strategy of a single business company or strategic business unit (SBU) of a multinational enterprise. According to Michael Porter, a company must establish a business strategy that involves either cost leadership, differentiation, or focus in order to gain a sustainable competitive advantage and long-term success in its selected venues or sectors.
- Functional strategy: It consists of marketing strategies, human resource strategies, new product development strategies, legal strategies, financial strategies, supply chain strategies, and information technology management strategies. The emphasis is on short- and medium-term plans, and the scope is confined to each department’s functional responsibilities. Each functional department strives to contribute to the achievement of general company objectives, hence their plans are influenced by larger corporate strategies.
- Operational strategy: Peter Drucker’s management by objectives (MBO) philosophy promotes this additional level of strategy. It has a relatively restricted emphasis and just deals with day-to-day operational tasks like scheduling criteria. It must operate within a budget but is not permitted to change or establish that budget. Operational-level strategies are influenced by business-level strategies, which in turn influence corporate-level plans.
Many organisations believe that a functional organisational structure is inefficient for organising operations, hence they are reengineered around processes or SBUs. A strategic business unit is a semi-autonomous entity that typically manages its own budget, new product decisions, hiring decisions, and pricing setting. Corporate headquarters treats an SBU as an internal profit centre.
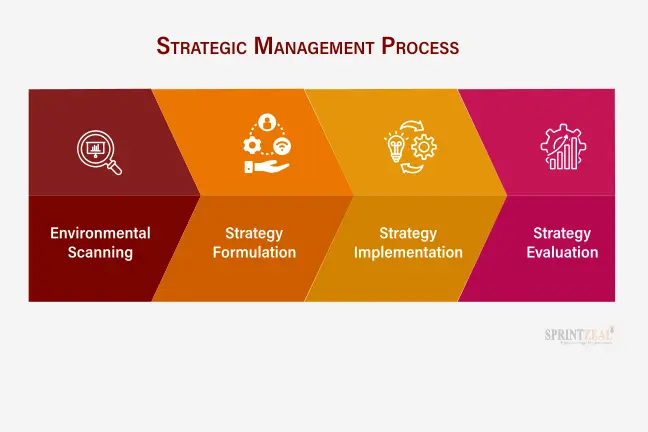
Various Stages/Phases of Strategic Management Process
Strategic management encompasses management of an organisation’s resources, analysis of internal and external forces, and development of strategies to realise objectives and futuristic goals. There are various perspectives on how to implement strategic management. Leaders have generated multiple frameworks to guide the strategic management process. Though there are a lot of differences, the process typically includes five phases/stages for the complete execution of the strategies:
1. Establishment of realistic goals and identification of direction: The first phase involves an assessment of the organisation’s present strategic direction. Here, the mission and long-term vision along with its objectives and goals is the key focus. It becomes important that the leadership is able to clearly persuade what the organisation is trying to accomplish.
2. Analysis and examination of the environment: In the second phase, the internal and external environments and their factors are identified and analysed. A tool like SWOT analysis is used to examine the strengths and weaknesses (in an internal environment), and opportunities and threats (in an external environment).
3. Development of the strategy: Whatever was learnt in the analysis stage, based on that the action plan is formulated in this phase. It then defines how the organisation will utilise the resources to get there and fulfil its goals. To quantify the success, the performance metrics are also established.
4. Execution of the strategy: This phase involves planning to implementation. The plan is put into action using the resources defined in the previous step. Powerful leadership and clarity in interaction are necessary. Each phase of the plan’s execution should be meticulously tracked and issues should be addressed as and when they arise.
5. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the implementation: Consistent evaluation of various components of the plan is required in this phase to determine how effective each one has been. This is done using the performance indicators defined during the development phase. If the intended outcomes are not attained, the plan needs to be adjusted accordingly.
Effective interpersonal interaction, collection of data and organisational culture are all critical components of the strategic management process, especially in large and complex corporations. Lack of communication and a poor corporate culture can lead to a mismatch between the organisation’s strategic management plan and the operations undertaken by the various units and divisions. Leadership should also review cross-functional business choices before executing them to ensure they are in alignment with the strategic goals.
*oreilly.com
Importance of Strategic Management
Strategic management is crucial in the business environment because it enables companies to identify opportunities for operational development. In many of the stances, they might either use an analytical method to identify prospective threats and possibilities, or just adhere to the traditional rules.
Given the organisation’s structure, a corporation might select between a prescriptive or descriptive approach to strategic management.
- A prescriptive model defines methods for development and execution.
- In contrast, a descriptive method explains how a corporation may create these strategies.
Final Words
A Strategic Management course is an organised and comprehensive endeavour that aims to provide people, teams or organisations with the knowledge, skills and tools required for effective strategic management. Such courses often include a wide variety of issues relevant to planning, executing and assessing strategies for achieving corporate objectives.
It is, thus, more than just a learning experience; a catalyst for professional advancement. You can opt for the Professional Certificate Programme in Strategic Management and by improving your strategic thinking, leadership abilities and industry knowledge, you may position yourself as a valued asset to any firm.
As the corporate world evolves, people with strategic management knowledge will drive innovation and success.
Frequently Asked Questions
The balanced scorecard is a strategic management technique which manipulates strategic goals into a set of performance objectives that can be measured, tracked and modulated, wherever necessary, such that the strategic goals are accomplished. The balanced scorecard involves the following four approaches to elevate the performance of an organisation:
- Traditional financial analysis is incorporated, which consists of metrics such as operating revenue, and sales growth and return on investment.
- Customer analysis is performed, which takes care of customer retention and satisfaction.
- An internal analysis is also carried out, which involves studying how business processes are interlinked to strategic goals.
- Additionally, a learning and growth analysis is performed as well, which involves employee retention and satisfaction, as well as the performance information services of the organisation.
A SWOT analysis is a procedure that organisations use, when planning their business strategies, for the evaluation of internal and external environments. The analysis helps in the identification and examination of the strengths and weaknesses of the organisation’s internal environment as well as the opportunities and threats in the external environment.












