What is Portfolio Management – Process, Types
Table of Contents

- jaro Education
- 23, November 2023
- 4:00 pm
Building an effective investment portfolio is not as easy as it seems. It is a calculated, sequential approach customized for each individual’s specific financial objectives/constraints. However, portfolio management is important if you want to approach stock market complexities, examine risks, and get favorable outcomes.
To understand what is portfolio management process, this blog explores the detailed process of creating a successful investment portfolio, highlighting how it needs to be uniquely tailored to your specific financial goals and constraints in a diverse financial landscape.
So, if you’re looking to enhance your career prospects in the field of investments, look no further than the Online MBA Degree Programme offered by Dr. D. Y. Patil Vidyapeeth, Pune (Deemed To Be University) through the Center for Online Learning. With UGC approval, live online degree classes, and a curriculum tailored to the ever-evolving needs of the industry, this program can boost your professional growth.
What is Portfolio Management?
Portfolio management entails a collection of assets and involves developing an integrated and strategic investment approach. This process starts with one’s ability to make a good decision, which involves developing an effective investment portfolio allocation of an asset according to its risks and its investor’s financial goals.
Mostly, portfolio management process can be done with a SWOT analysis of alternative investment pathways where an investor’s objectives are equalized with their risk tolerance. This way, it helps to earn reasonable profits and safeguard these profits against various risks.
*Green Portfolio
Portfolio diversification is another method of managing investment risks. However, this does not mean that the risk shall be eradicated. There are two primary forms of risk associated with any asset: diversifiable/unique/unexplained/unsystematic risk with unverifiable/market risk/explained/systematic risk.
To an extent, even the best portfolios don’t eliminate market risk. It can reduce the risk, which is diversifiable. The decrease in risk is accompanied by a decrease in the variability of return. As such, risk diversification is crucial in portfolio management process as it helps an investor to manage their overall risk exposure effectively.
Why Is Portfolio Management Important?

*A Digital Blogger
You don’t invest just one time, and that is why the portfolio management process is important. It implies not just continuous monitoring, but also monitoring the portfolio on a systematic and permanent basis. Situations for investors might change as time changes, and so their aspirations and objectives may differ over time. As a result, investors may require portfolio repositioning as their portfolio evolves.
However, there are certain instances when individual holdings must be changed. It is important to know that an active mutual fund may change its management. This might encourage the portfolio manager to opt for another holding of the fund. Such changes can have a great influence on the overall portfolio performance, indicating the need for continuous monitoring and managing.
Portfolio strategy is also crucial in investment. Some investors simply compile a collection of separate holdings without paying much attention to how many holdings they interact with. This, in turn, could lead to an excess allocation of finances in certain sectors, thereby placing the investors at even greater risk than expected. By aligning your investment decisions under such parameters, you can safely say that portfolio management process is a key driver in achieving those objectives.
Types of Portfolio Management
Various types of portfolio management encompass a range of approaches to investment management. Below are the key types.
| Active Portfolio Management | Passive Portfolio Management | Discretionary Portfolio Management | Non-Discretionary Portfolio Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Managers involved in active management focus on outperforming the market through an active decision-making process. They tend to subscribe to contrarian thinking, which dictates that overpriced stocks should be sold while underpriced ones should be purchased to gain profits. | In this type of management, managers believe in the Efficient Market Hypothesis, which insists that a firm’s fundamentals should be reflected in its stock prices every time. They invest in index funds, which have low turnover rates and a high long-term value.
These managers also allocate funds proportionally to market capitalization, aiming to minimize management costs while seeking stability. | In this approach, investors hand over total responsibility to portfolio managers who make investment decisions for them.
Then, portfolio managers devise a customized portfolio that takes into consideration the investor’s personal objectives, time frame, and risk tolerance. In the end, investors await returns with minimal involvement in the decision-making process. | Non-discretionary managers act as financial advisors in case of non-discretionary portfolio management.
In this type of management, the final decisions remain with investors, who are in a better position to determine whether the advice is reliable. In this type of portfolio management process, with the investor’s permission only, non-discretionary managers take action. |
Thus, every strategy of portfolio management process has its advantages and disadvantages, so every investor should take into consideration their objectives and the level of risk they can attain while choosing the right type of portfolio management.
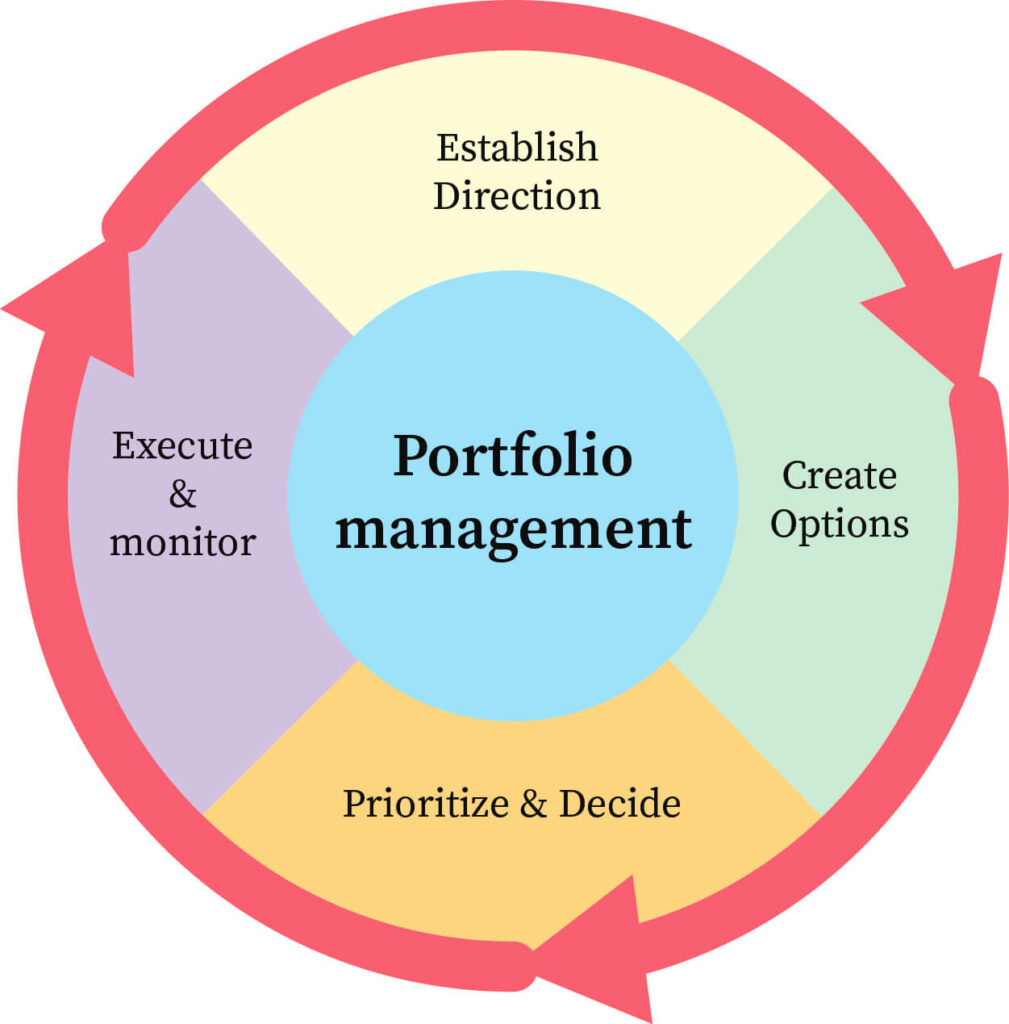
Portfolio Management Process
The portfolio management process consists of a series of essential steps, each contributing to the success of the overall investment strategy:
*Triskkell Software
1. Setting Goals
The first step involves the identification of an investor’s risk-return profile as central to establishing investment objectives. It requires creating a suitable portfolio approach that will generate desired returns while taking reasonable risks; it is essential to determine the amount of risk the investor is likely to take on and the degree to which they are ready to bear in terms of volatility.
After establishing a desired risk/return profile, benchmarks can be set to track the performance of the portfolio, as tracking the portfolio’s performance against benchmarks allows smaller adjustments to be made along the way.
2. Selection of Backup Assets
The subsequent step in portfolio management process involves assessing other potential alternative assets, which can aid in the diversification of risks as well as the reduction of losses.
Also, this step of the operation defines that there is an explicit link between the securities. Portfolios can include preference shares, equity shares, bonds, and other securities. However, investing in these portfolios depends on the investors’ risk-taking ability and capital available for investment.
3. Developing a Strategy
The next step involves generating suitable portfolio strategies from an asset mix after the portfolio management process has chosen an acceptable portfolio strategy.
A portfolio strategy is developed in two ways: Active and Passive.
4. Active Portfolio Strategy
An active portfolio strategy uses market timing, moving from one sector to another based on market conditions, securities selection, or a combination of these to generate a higher risk-adjusted return.
5. Passive Portfolio Strategy
A passive portfolio approach has a predetermined level of risk involvement and thus it is well-balanced and properly planned.
Conducting a Security Analysis
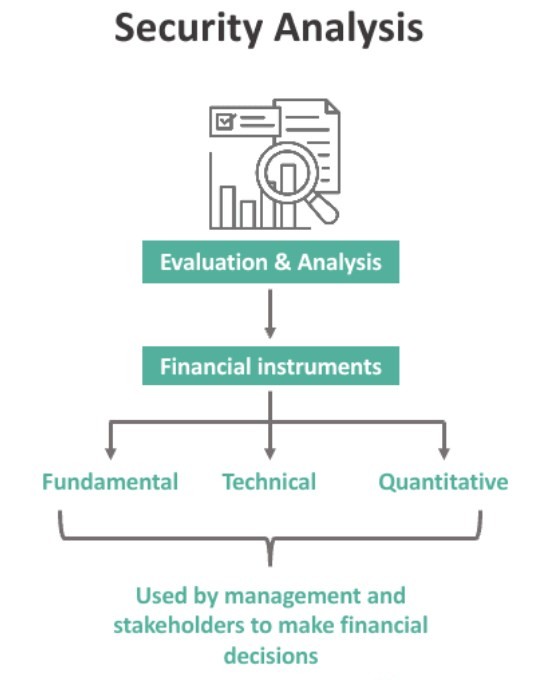
*WallStreetMojo
- The investor is directly involved in picking up stocks during this phase.
- Security analysis requires an informational background of the sources on which it operates.
- The price, potential return, and risks connected with the securities in the portfolio are all considered.
- Security analysis aids in understanding the type and amount of risk connected with a specific security in the market, as the return on investment is tied to the risk associated with the security.
- Micro and macro analysis are both used in security analysis. Microanalysis, for example, involves studying a single script. Macro analysis, on the other hand, is the study of the securities market.
Fundamental analysis and technical analysis aid in the identification of assets that can be included in an investor’s portfolio.
Acting According to Plans
Once they have selected the securities in which to invest, the next step of the portfolio management process involves putting their portfolio plan into practice i.e. Portfolio Execution. The Portfolio Execution involves buying and selling certain assets in fixed sums at predefined intervals. It is one of the most important stages of the portfolio management process because it influences the results of investments.

*Dreamstime.com
1. Portfolio Modification
It is one of the most vital stages of portfolio management.
Portfolio managers always evaluate and scrutinize the script to ensure it is in line with market situations.
After completion of the evaluation, portfolio modification involves altering a program or changing from one stock to another, stock to bond, and vice-versa.
2. Assessing Returns
In this phase, the performance of the portfolio is assessed over the stipulated period concerning the quantitative measurement of the return obtained and risk involved in the portfolio for the whole term of the investment.
Pace Up Your Portfolio Management Career With Dr. D. Y. Patil Vidyapeeth, Pune (Deemed To Be University)

*DPU.com
In the future job landscape, entrepreneurs shaping the next normal, and business leaders will need to refine their contemporary abilities. Forward the next-generation Online MBA Programme of Dr. D.Y. Patil Vidyapeeth-Centre For Online Learning (DPU-COL) and acquire those traits any future leader should have.
The future leaders nurtured by the Online MBA Programme will thrive in developing leadership skills, awareness of global issues, critical thinking, and analytical abilities to unleash their full potential. Following the UGC-prescribed credit system, this two-year program is specially designed for working professionals.
They will reflect on their convictions, assumptions, and behaviors while improving their effectiveness in social and business settings. Move on to a global career!
Jaro Education is a renowned online higher education platform that assist in career advancement. The courses, faculty, and curriculum are related to sharpening the skills and knowledge related to this field. The investment banking and financial management programs listed through Jaro Education’s platform will prepare you for the nitty-gritty of portfolio management process and firmly put you in the finance world, be it as a portfolio manager, financial analyst, or investment advisor.
These will be some of the very good resources, mentors, and career support in preparation for entering the highly competitive world of portfolio management process through Jaro Education. Choose now and step up into that brilliant, prosperous future or career in Finance and Investment Management offered by Jaro Education!
Final Thoughts
Effective portfolio management is essential for aligning investment strategies with income, age, and risk tolerance. It allows investors to mitigate risks and tailor assets to their goals, reducing confusion in the process. Whether managing a portfolio independently or with the help of a manager, choosing a viable approach and presenting it logically is crucial. Portfolio management process is the cornerstone of successful investing, protecting assets from market risks while pursuing substantial profits. By understanding its process, types, and objectives, investors can navigate the complex world of finance with confidence, making informed decisions to secure their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Portfolio Management is the process of selecting, managing, and overseeing a collection of investments (such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and other assets) to achieve specific financial goals. It involves balancing risk and return according to the investor’s objectives, risk tolerance, and investment horizon.
Effective portfolio management process is crucial for maximizing returns while minimizing risk. It helps investors achieve their financial goals by diversifying investments, ensuring a balanced approach to risk, and optimizing the performance of the portfolio. With proper management, investors can navigate market fluctuations and achieve long-term financial success.
There are several types of portfolio management strategies, each catering to different investment goals:
- Active Portfolio Management: The manager actively buys and sells assets to outperform the market, using research and market timing.
- Passive Portfolio Management: The manager creates a portfolio that mirrors the performance of a market index, aiming for long-term growth with minimal transactions.
- Discretionary Portfolio Management: The manager has full discretion over portfolio decisions, including buying and selling assets without consulting the investor.
- Non-Discretionary Portfolio Management: The investor maintains control over the portfolio, with the manager providing advice and recommendations.









