Six Sigma Concept: Everything You Need To Know About It
Table of Contents

Have you ever thought about how companies like Motorola, General Electric, and Amazon consistently provide quality products and services? Their methodology is called Six Sigma, which, although it sounds like a hard math term, is more practical than the complexity of Six Sigma may imply. Six Sigma is about improving, simplifying, and stabilizing things by reducing errors in business processes. Six Sigma concept can help you whether you manage a shop floor, are involved in healthcare, or improve customer service in IT. By using the Six Sigma rule, you can find the problems in your processes and fix them smartly and systematically.
In this blog, we will explain everything you need to know about the Six Sigma concept – its origins, how it works and its different modes, and why it is important. By the end, you will understand how this very straightforward yet extremely powerful concept is changing organisations throughout the globe.
*geeksforgeeks.org
Six Sigma: An Overview
At its core, the Six Sigma concept is a method for improving the quality of processes by identifying and removing the causes of errors or defects. Think of it like a detective for business processes. It digs deep, finds where things go wrong, and offers data-driven ways to fix them.
The name “Six Sigma” comes from a statistical concept. In statistics, “sigma” represents standard deviation, which is a measure of variation. A Six Sigma process is one where 99.99966% of all opportunities to produce a product or service are free of defects—meaning only 3.4 defects per million opportunities. That’s incredibly precise. The beauty of the Six Sigma concept lies in its versatility. Originally designed for manufacturing, it’s now used in healthcare, IT, banking, logistics, and more. No matter the industry, the goal remains the same: improve performance, reduce waste, and keep customers happy.
History: Where Did It All Began?
The Six Sigma philosophy was established in the early 1980s by Bill Smith, a quality engineer for Motorola. Smith saw that inconsistent manufacturing processes were producing unacceptably high numbers of defects. He created a methodology designed to eliminate inconsistency and improve the quality of the product. Motorola adopted his strategy, and it worked like a charm. Rewarding nearly immediate success.
Motorola experienced very quick improvement in product quality. They were one of the very first companies to win the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award in 1988. The Six Sigma concept became the envy of many corporations. Jack Welch, legendary CEO of General Electric, implemented Six Sigma techniques at GE in the mid-1990s, making it a core component of GE’s business strategy, resulting in billions of dollars in cost savings.
The Six Sigma concept began as a quality improvement approach for electronics manufacturing but quickly morphed into a universal form of business perfection methodology.
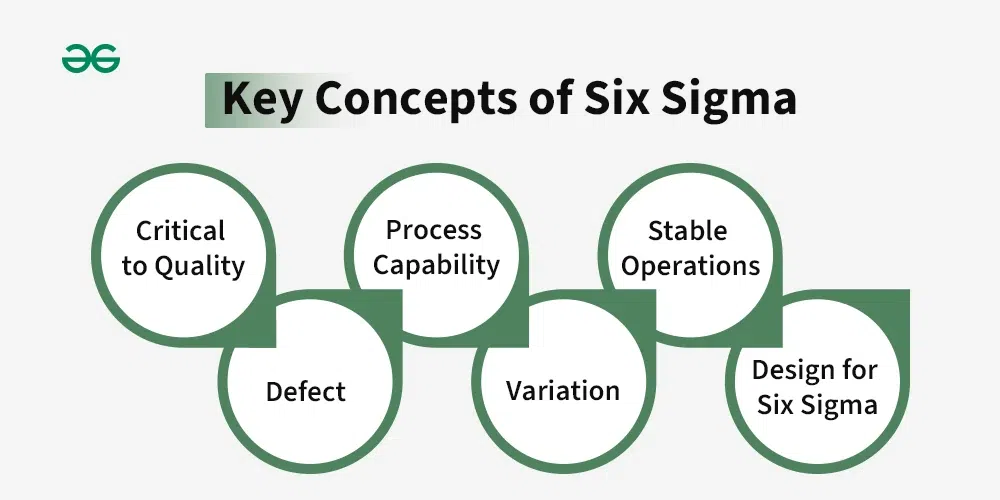
The Foundational Principles That Drive Six Sigma
The core of Six Sigma techniques is the underlying beliefs that drive each improvement effort. The beliefs outline not only how the organization will address problems but also ensure the outcomes meet business needs and customer satisfaction. Let’s discuss each belief in a more visual and relatable way.
1. Customer-Centric Thinking
The Six Sigma concept goes beyond just adapting or altering internal processes. Truly understanding what potential and existing customers value, and giving them the same consistent experiences that either meet or exceed their expectations is the primary goal. Whether it’s faster service, better product quality or seamless customer support, any advancement worked on in the ambit of Six Sigma techniques should have a benefit to the customer. Organizations that operate on this principle can overnight become more loyal to customers or more competitive to potential customers by aligning the organization to the reality of customers.
2. Making Decisions Backed by Data
In Six Sigma, opinions and assumptions are irrelevant. Decisions are based on fact; a problem is determined through data which allows for identification and solutions. With tools such as process maps, control charts, and statistical analysis, teams can see exactly where the problem is and what adjustment needs to be made. This data-driven process also eliminates guesswork and improves the odds of success because all changes in potential solutions will be tested beforehand, validated, and proven, before any action is undertaken.
3. Reducing Process Variation
One of the biggest enemies of quality is inconsistency. When processes vary, defects creep in—and that leads to customer dissatisfaction and wasted resources. The Six Sigma concept works to minimize this variability by identifying the root causes of fluctuations and standardizing operations for more predictable outcomes. A stable process is a reliable one, and the more consistent your operations are, the higher your chances of delivering quality at scale.
4. Commitment to Ongoing Improvement
The Six Sigma concept is not a project that can be completed; it is a model of continuous development. When improvements have taken effect, there is always room for improvement. Markets change, customer preferences change, and technology changes. Organizations that believe in continuous improvement are always adaptable and aspire for innovation, seeking ways to operate better, faster and more efficiently. The always mindset means never ceasing to aspire for excellence.
5. Adaptability and Responsiveness
The Six Sigma concept knows no borders when it comes to industry or type of challenge. It is a flexible framework that can be customized for anything from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare, finance, and customer service. This gives businesses a level of flexibility to respond to market changes or shifting customer expectations. Companies can recalibrate their processes using objectives of Six Sigma tools and tactics without starting over, effectively creating resilience amidst constant change in the business landscape.
The Six Sigma Methodology
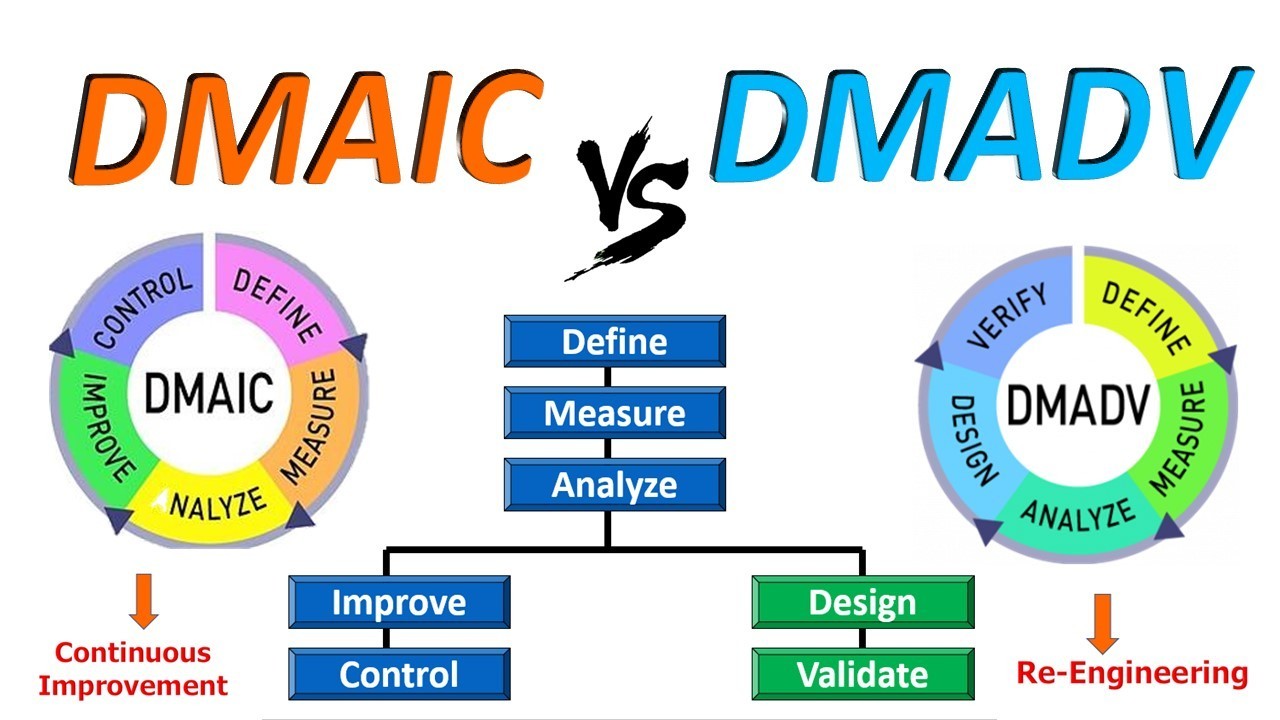
Six Sigma isn’t just a quality management system—it’s a disciplined, data-driven roadmap for identifying inefficiencies, solving complex problems, and optimizing performance. Central to this approach are two powerful methodologies: DMAIC and DMADV. While both aim to drive quality and enhance outcomes, each serves a distinct purpose depending on whether you’re improving existing systems or designing something entirely new.
*linkedin.com
1. DMAIC: Fine-Tuning Existing Processes
The DMAIC framework is designed specifically for the improvement of actual processes, especially those that are poorly performing or when quality standards are not achieved. Each phase leans on the outcome from prior phases, ensuring that the solutions are firmly grounded in actual data rather than superficial fixes.
- Define: Every successful project begins with clarity. In this phase, teams identify the problem at hand, outline specific goals, and define customer expectations. It’s about drawing the roadmap and aligning everyone towards a common purpose.
- Measure: There is no way to improve something that you do not understand. This element is data collection, and it allows you to essentially evaluate the current process so that you can set a baseline and then put the problem in measurable terms.
- Analyze: Having solid data is a good start, and the next step is really to see what is causing the inefficiencies or defects. This should provide an exploration of root cause analysis to identify more systemic or undetected patterns.
- Improve: Once the root causes are clear, this stage focuses on brainstorming, testing, and implementing targeted solutions. The goal is to enhance the process in ways that are sustainable and impactful.
- Control: Change isn’t effective unless it lasts. This final step is all about creating control mechanisms—like dashboards, SOPs, or real-time monitoring—to ensure that improvements stick and performance doesn’t backslide.
2. DMADV: Building New Processes with Precision
DMADV is used when the objective is to create a new process or product from the ground up. DMADV is a design-centered approach that allows all aspects of the design to be directly aligned with customer requirements and Six Sigma quality expectations at every stage.
- Define: Start by clearly establishing the purpose, scope, and success criteria of the new initiative. This includes capturing what the customer wants and how success will be measured.
- Measure: Define and quantify the essential characteristics and performance metrics the new design should meet. You want to make sure you are designing against measurable goals and not fuzzy hypotheticals.
- Analyze: Assess multiple design options, assess the strengths and weaknesses of every option, and outline the best option that meets both technical and customer requirements.
- Design: After you have determined the best concept, the design process starts to get real. The design phase involves planning in detail, prototyping, modeling; it is where we will really determine if the solution is viable and if it can be scaled.
- Verify: Finally, the new design undergoes rigorous testing and validation. This ensures that the process or product performs reliably under real-world conditions and meets customer expectations before it’s fully launched.
The Advantages of Implementing Six Sigma
*6sigma.us
Implementing the Six Sigma concept is not just simply optimizing a few processes, it is a paradigm that can transform how a business functions, competes, and grows. Six Sigma creates significant results by bringing statistical rigor to daily work. This methodology generates impactful results across all industries, and here are the major advantages of implementing it into your business framework:
1. Boosted Efficiency and Streamlined Operations
Six Sigma is all about doing things better, faster, and with less waste. The Six Sigma concept encourages organizations to scrutinize their business processes, eliminate waste, redundancy and unnecessary steps and implement best practices. All of this ultimately leads to: shorter process cycle times; better allocation of resources; and less stoppages. Shaving time off a process saves time, creates more products and increases productivity, all while allowing your employees to spend more time on higher value tasks.
2. Significant Cost Savings and Measurable ROI
One of the most compelling advantages of the Six Sigma concept is its direct impact on the bottom line. By targeting inefficiencies, minimizing errors, and reducing rework, businesses can dramatically lower operational costs. Whether in manufacturing, finance, healthcare, or service sectors, the savings from fewer defects and optimized performance quickly add up, resulting in a stronger financial position and improved profitability over time.
3. Data-Driven, Confident Decision-Making
Six Sigma concept provides leaders with reliable data analysis tools and metrics to support evidence based decisions. When a leader is troubleshooting a quality issue or planning a new effort, they can rely on the data for support in their decisions. Using data to make decisions builds confidence, assists in clarifying strategic priorities, and helps find root causes to problems instead of simply addressing symptoms.
4. Cultural Shift Toward Excellence and Engagement
Beyond tools and techniques, Six Sigma concept nurtures a mindset of continuous improvement. It empowers employees at every level to take ownership of their work and contribute to meaningful change. As people become more involved in solving problems and enhancing processes, engagement levels rise—and so does morale. Over time, this builds a resilient, improvement-oriented culture where innovation and collaboration flourish.
5. Proactive Risk Management and Stronger Compliance
In industries that require compliance and consistency, the Six Sigma concept is preservation. It provides structure to our methodology that identifies possible flaws before they become expensive problems – product quality, safety, regulatory standards, etc. By proactively introducing quality checks and controls into their daily operations, businesses can meet compliance and limit liabilities and brand reputation.
Final Thoughts
The Six Sigma concept is more than a set of tools for engineers and data nerds– it’s a pervasive, strategic way to approach business problems and deliver value. If you are running a production floor, working in a hospital, or starting a company, there are processes that can benefit from the principles of Six Sigma: less waste, less error, and happier customers.
When you invest in 6 sigma, you’re not only improving YOUR part of the business–you’re putting the entire organization into a position to think more about how they work, get work done faster, and do the work at the highest possible level of success.
If you want to enhance how your business works–or you are looking to upskill your career with an impressive understanding of process improvement–learning and working on your 6 sigma quality experience could be one of the smartest things you ever decide to do. You can visit Jaro Education to explore a wide range of online courses available. Jaro is India’s leading online higher education and upskilling company, bringing the industry-standard courses to equip you with the right skills and knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Difference Between Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is all about improving quality by reducing defects through data-driven analysis and process improvement. On the other hand, Lean Six Sigma blends the power of Six Sigma with Lean principles, aiming not only to enhance quality but also to eliminate waste and speed up operations.
What is Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt, Green Belt, and Black Belt?
In Lean Six Sigma, “belts” represent different levels of knowledge and responsibility:
- Yellow Belt: This is the beginner level. Yellow Belts understand the basics of Lean Six Sigma and help support improvement projects.
- Green Belt: Green Belts lead smaller projects and use data to solve problems, usually with help from Black Belts.
- Black Belt: Black Belts are experts who manage big improvement projects, coach others, and help shape strategy within the organization.
What is Six Sigma and why is it important?
Six Sigma is a set of methods and tools that helps businesses improve how they work by reducing mistakes and making processes more consistent. The goal is to deliver high-quality results with as few errors as possible—ideally just 3.4 defects per million chances. It’s all about making things better, faster, and more reliable.
Is Six Sigma really useful?
Yes, absolutely. Six Sigma helps companies save time, reduce waste, and use fewer resources when creating products or services. This leads to better efficiency, happier customers, and often, higher profits.
















