What is Public Finance? Definition, Types, and Role in Economics
Table of Contents

- jaro Education
- 29, April 2024
- 10:00 am
In every nation, the government plays a pivotal role in public finance, economic development, and the advancement of societal welfare through a spectrum of functions. These functions can be broadly categorized into two types of public finance: obligatory and optional. Obligatory functions encompass vital tasks that are imperative for the government to undertake, such as safeguarding the nation from external threats, ensuring internal stability, and upholding peace and security. On the other hand, optional functions are those that, while beneficial, are not indispensable for the country’s survival.
To make all this happen, the government needs money. It manages this money through a system known as public finance. Public finance serves as a rulebook for how the government acquires and spends money. It establishes the discipline that governs the revenue generation and expenditure of public authorities, including local, state, and national administrations. In this article, you will gain detailed insights into public finance, its objectives, and its components.
What is Public Finance?
Public finance includes administering a nation’s income, debt burden, and spending through various quasi-governmental and governmental entities. This field evaluates the financial activities of public authorities, including government revenue and expenditure. Public finance examines how government actions impact public finance in economic stability, resource allocation efficiency, and income distribution among citizens.
It involves managing both revenue generation and spending across all sectors involving the public of the nation. Public finances play a critical role in economic development by fostering public finance in economic development by ensuring the efficient use of funds. This field underscores the government’s function and impact on an economy’s functioning and growth.
Role of Public Finance in Economic Development
What is the significance of public finance? Public finance is significant in supporting economic development by facilitating resource allocation, enhancing stability, and fostering sustainable growth. In economic downturns, the government can utilize fiscal policy tools like taxation and government spending to stimulate demand and invigorate public finance in economic activity. Conversely, in periods of inflation and overheating, the government can enact measures to moderate aggregate demand and manage inflation rates. These proactive steps aid in preserving price stability and establishing a favorable environment for sustainable public finance and economic progress.
By allocating resources to infrastructure development and establishing a consistent regulatory framework, the government can foster an environment conducive to business growth. Moreover, public finance can be leveraged to offer subsidies, tax breaks, and other forms of assistance aimed at bolstering vital sectors or industries essential for overall public finance in economic progress.

1. Infrastructure Development
Why is public finance important?
Public finance plays a vital role in economic development by facilitating infrastructure development, which is essential for fostering economic growth. This includes constructing and maintaining vital infrastructure such as roads, bridges, airports, seaports, railways, and public utilities. Infrastructure development is crucial as it attracts investment and stimulates public finance in economic activities. Various financing methods, such as public-private partnerships and bond issuances, are utilized by governments to fund infrastructure projects.
2. Education and Healthcare
Public finance also supports public finance in economic development by ensuring access to education and healthcare services. Education is instrumental in developing human capital, while healthcare services are crucial for maintaining a healthy and productive workforce. Governments allocate resources to build schools and hospitals, hire educators and healthcare professionals, and offer financial aid programs like scholarships to students.
3. Social Welfare Programs
Additionally, here’s what public finance is. Public finance contributes to economic development through social welfare programs that alleviate poverty and boost consumer spending. Unemployment benefits, food assistance, and other social safety nets help improve living standards and stimulate economic activity. These programs are funded through various sources, including taxes.
4. Public-Private Partnerships
Public finance facilitates public-private partnerships (PPPs) that promote public finance in economic growth by leveraging private sector expertise and resources. PPPs involve governments and private entities collaborating to deliver public services and develop infrastructure. Governments provide funding, incentives, and regulatory support to encourage private investment in public projects.
5. Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy, encompassing government spending and taxation strategies, is another tool used to promote economic development. Governments can adjust taxation to incentivize private investment and consumer spending. Increased infrastructure spending and targeted investments in key sectors can create jobs and stimulate public finance in economic activity, contributing to overall growth and reducing income inequality.
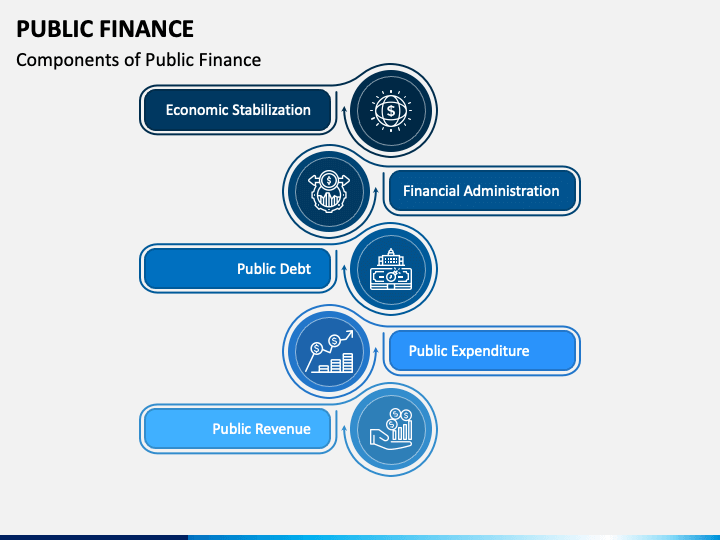
Component of Public Finance
The component of public finance has various activities focused on investing in national development, revenue generation, and financial planning. Below is a list of the key components of public finance:
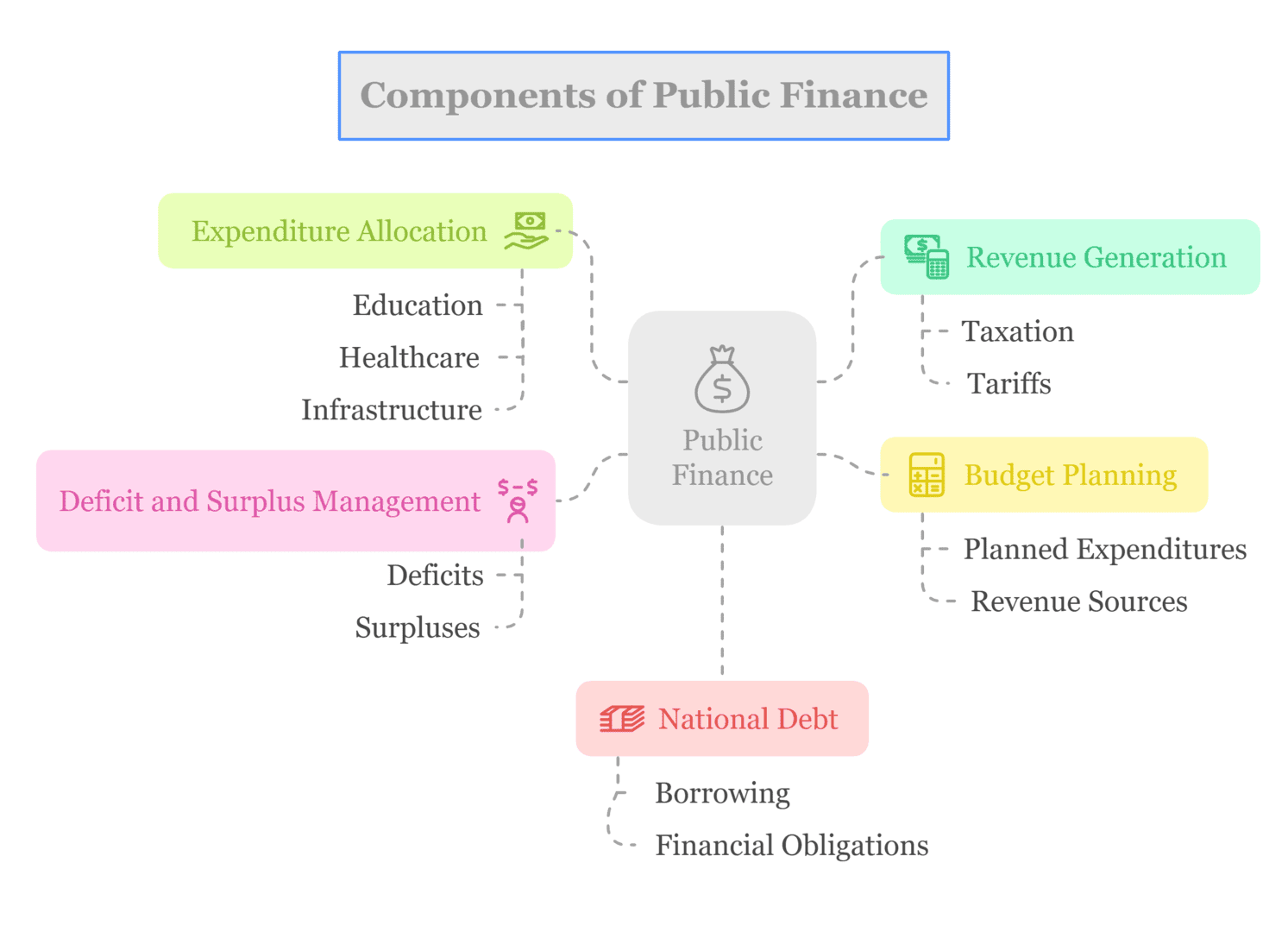
- Revenue Generation: Public finance relies heavily on revenue collection, primarily through taxation, which serves as the government’s main income source. Examples of taxes include income tax, sales tax, and property tax. Additionally, revenue is generated through tariffs on imports, duties, and other government services.
- Expenditure Allocation: Governments allocate funds for essential sectors such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and social welfare programs. These expenditures are aimed at improving the well-being and quality of life for society as a whole.
- Budget Planning: Each fiscal year, governments create budgets that outline planned expenditures and revenue sources. Budgets serve as a roadmap for financial activities and resource allocation.
- Deficit and Surplus Management: A deficit occurs when government spending exceeds revenue collection for a given period, resulting in a financial shortfall. Conversely, surpluses occur when expenditures are lower than tax revenues.
- National Debt: Governments may incur deficits by borrowing money to cover budget shortfalls, leading to national debt issuance. The national debt represents accumulated borrowing over time, reflecting the government’s financial obligations.
Objectives of Public Finance
Let’s explore the objectives of public finance economics, a crucial aspect in evaluating a government’s performance within an economy. This understanding aids in contextualizing governmental operations and resource management.
- Addressing Public Needs: What is Public Finance’s Objective?
The primary objective of public finance is to manage essential public needs such as food, shelter, healthcare, infrastructure, and education. These responsibilities fall under the government’s purview to meet fundamental public requirements, thereby contributing to public finance in economic development.
- Promoting Economic Development: Effective management of public finances fosters public finance in economic development, ultimately driving the nation’s overall growth trajectory.
- Reducing Inequality: Public finance endeavours to reduce inequality through the equitable allocation of resources. This involves implementing measures such as progressive taxation to assist disadvantaged segments of society, thereby promoting social cohesion and fairness.
- Ensuring Price Stability: Public finance strategies also focus on maintaining price stability by employing various mechanisms and initiatives to control inflation and foster sustainable public finance in economic growth.
Additional objectives beyond those mentioned above may include:
- Meeting the nation’s basic needs comprehensively.
- Creating employment opportunities to bolster workforce participation and economic productivity.
- Preserving the currency’s value in international markets, thereby ensuring public finance in economic stability and competitiveness.
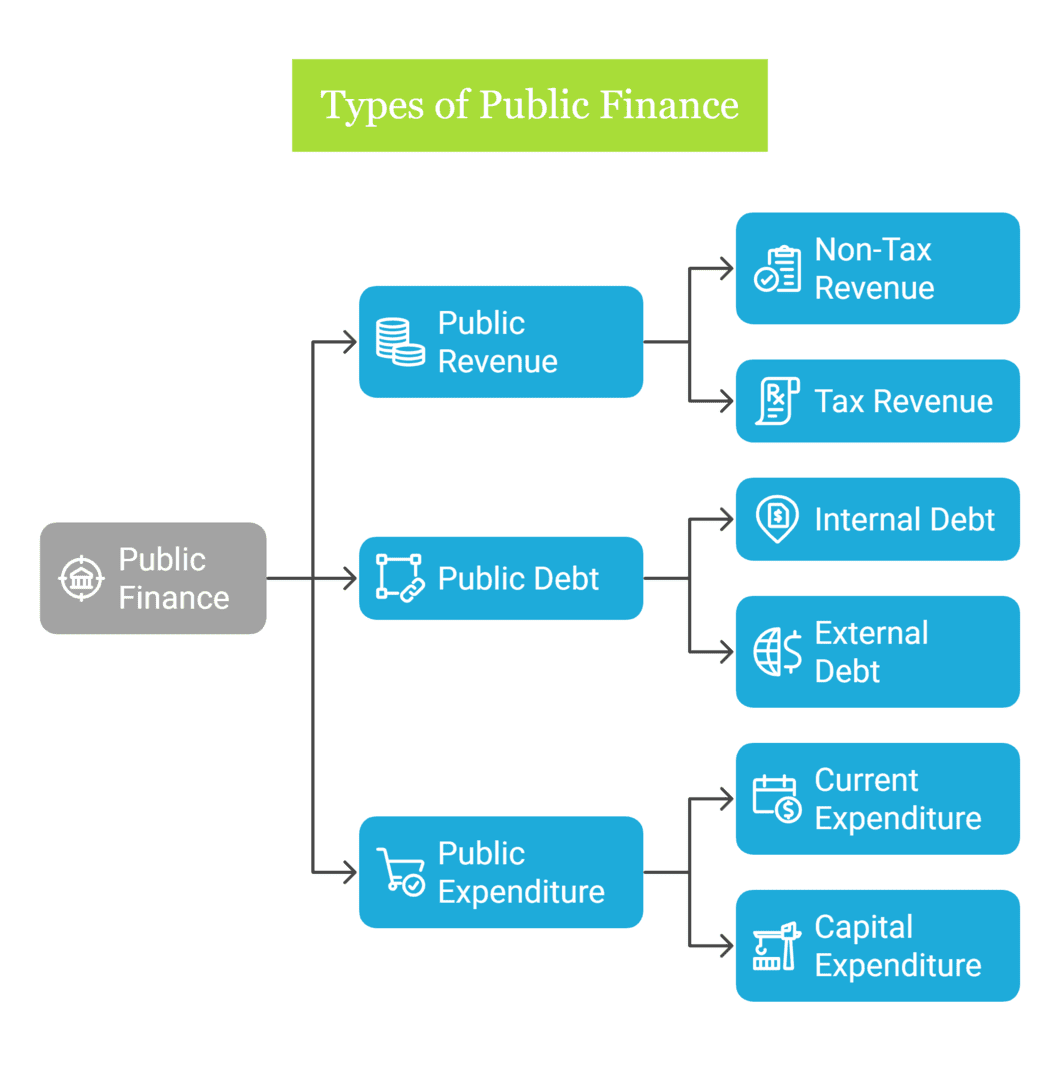
Types of Public Finance
1. Education and Healthcare
Public revenue refers to the income collected from various sources by the government or public sector. It can be categorized into two main types of public finance: non-tax revenue and tax revenue.
- Non-tax revenue includes income from administrative fees, fines, penalties, special assessments, escheat, forfeitures, gifts, grants, and irrigation charges.
- Administrative revenue includes fees, fines, penalties, special assessments, escheat, and forfeitures.
- Commercial revenue includes income from tolls, postage, borrowed funds, electricity payments, and other commercial activities.
- Tax revenue comprises income generated from progressive taxes, regressive taxes, degressive taxes, direct taxes, indirect taxes, specific taxes, and ad valorem taxes.
2. Public Debt
Public debt refers to the total amount of money that a government owes to the public as part of its development funds. When combined with any previous deficits, it is referred to as public debt. This debt can be categorized into various types of public finance:
- Internal and External Debt: Internal debt is incurred when the government borrows money domestically, often from banks, business firms, and individuals within the country. In contrast, external debt refers to borrowings from foreign entities, such as international organizations like the World Bank and the Asian Development Bank.
- Compulsory and Voluntary Debt: Compulsory debt includes obligations that the public is required to pay, such as taxes. Voluntary debt, on the other hand, includes debts where commercial banks voluntarily subscribe to securities issued through government loans.
- Productive and Unproductive Debt: Productive debt refers to loans that generate revenue for the government and are self-liquidating. In contrast, unproductive debt burdens the community and requires additional taxes for repayment and servicing.
- Redeemable and Irredeemable Debt: Redeemable debt is repaid by the government after a specified period, often involving the sale of securities to the public. Irredeemable debt, however, lacks a promised repayment date and is not reported by the government.
3. Public Debt
Public expenditure refers to the total spending by the government on various goods and services to fulfill its responsibilities and meet the needs of the public. It plays a crucial role in public finance in economic development in the functioning of an economy as it impacts economic growth, social welfare, and public services. Here are some types of public finance:
- Current Expenditure: This includes day-to-day expenses such as salaries of government employees, maintenance of infrastructure, subsidies, and administrative costs.
- Capital Expenditure: Capital expenditure is used for long-term investments in infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, schools, hospitals, and other public facilities. These investments are aimed at improving the economy’s productivity and the quality of life for citizens.
4. Financial Administrator
Financial administration in public finance involves managing government budgets, revenue, and expenditures efficiently. This includes:
- Budgeting and Planning: Estimating revenue, allocating funds, and setting financial goals.
- Financial Reporting: Transparently presenting financial information to stakeholders.
- Revenue Management: Collecting taxes and optimizing revenue streams.
- Expenditure Control: Monitoring spending, preventing waste, and evaluating program effectiveness.
- Debt Management: Issuing and managing government debt to maintain financial stability.
- Policies and Regulations: Establishing controls, audits, and risk management frameworks.
- Performance Evaluation: Assessing the efficiency and impact of government expenditures.
5. Management of Public Finance
What is Public Finance Management?
Public finance includes the methodologies, procedures, and strategies that governments employ to manage a country’s financial resources (public funds) effectively and efficiently. It revolves around the various components of public finance, the interactions among these components, and the government’s role in public finance in economic development within the financial cycle of public resources.
The financial cycle starts with budget preparation and follows with activities such as revenue generation, expenditure, accounting, and financial reporting.
Significance of Public Finance Management
Understanding public finance management is essential for both individuals and governments. Here’s why it holds critical importance:
- Promotes Investment
Effective public finance management creates a conducive environment for investment through strategic policies, incentives, free trade zones, and trade agreements. - Ensures Efficient Resource Allocation
It plays a crucial role in the optimal allocation of natural and human resources, driving sustainable national development. - Drives National Progress
Well-managed public finances are key to economic growth, infrastructure development, and the overall advancement of society. - Maintains Price Stability
Public finance helps stabilize prices and counter the negative impacts of inflation and unemployment, promoting a healthier economy. - Supports Policy Development and Innovation
It enables governments to craft data-driven policies and foster innovation, enhancing economic competitiveness and long-term growth.
Challenges Within the Public Finance
Public finance plays a pivotal role in economic development by influencing public finance in economic development and ensuring the effective utilization of public resources. Let’s explore some of the key challenges and issues encountered within this domain:
| Fiscal Discipline and Budgetary Constraints | Revenue Generation and Taxation Issues | Public Expenditure Management |
|---|---|---|
| Maintaining fiscal discipline to achieve a balanced budget while meeting the diverse needs of society is a significant challenge. Political pressures, unexpected events (such as economic downturns or natural disasters), and competing demands for public spending can strain fiscal discipline and lead to budgetary deficits | Efficiently mobilizing revenue through taxation is crucial for funding public services and infrastructure projects. However, challenges such as tax evasion, an informal economy, outdated tax systems, tax avoidance schemes, and a narrow tax base can impede revenue generation efforts. | Effectively managing public expenditures involves budget planning, allocation, execution, monitoring, and evaluation. Challenges include inefficient spending practices, lack of transparency, corruption in procurement processes, project implementation delays, and inadequate financial management capacity within government agencies. |
Emerging Challenges:
- Globalization, technological advancements, and climate change present new complexities in public finance management.
- Regulatory questions arise with the emergence of digital assets like cryptocurrencies.
- Post-pandemic corporate solvency remains a concern, highlighting the need for adaptive financial strategies.
Why Professional Certificate Programme in Investment Banking IIM Kozhikode?
The Professional Certificate Programme in Investment Banking by IIM Kozhikode offers a requisite theoretical and conceptual toolkit for understanding the primary line of businesses of investment banks and presents insight into the regulatory peculiarities and challenges of the industry, including subjects under corporate finance such as higher mathematics, public finance in economics, corporate valuation, mergers, acquisitions, and corporate restructuring within the overall program. The programme has been designed to be delivered online for the weekend as a 10-month event with expert lectures from industry-experienced faculty from IIMs, case studies of successful and failed ideas, realistic projects, modeling, simulations, and practice labs. Eventually, students will acquire the skills and knowledge needed to gain entrance into the field of investment banking.
- Analyze the core business operations of investment banks
- Understand the unique challenges and nuances of the industry
- Develop expertise in corporate finance, valuation, and restructuring strategies

Eligibility:
- Graduates (10+2+3) and Diploma Holders (only 10+2+3) from a recognized university (UGC/AICTE/DEC/AIU/State Government/recognized international universities) in any discipline. There should be a minimum work experience of 1 year after graduation on the part of the prospective candidates on the date of commencement of the programme.
- Selections would be based on a detailed Profile written in the words of the candidate describing their Academic record, Profile, Designation, Salary, Role of public finance in economic development, Responsibilities, Job Description, and a write-up on “Expectations from the Programme.”

Why Choose Jaro Education for Career Guidance and Counseling
- Expert Counselors with Deep Industry Insight
Jaro Education is renowned for its distinguished panel of career counselors, each bringing a wealth of industry-specific expertise. Their nuanced understanding of evolving job market trends empowers individuals to navigate career planning and transitions with clarity and confidence. - Personalized Career Roadmaps
Recognizing that every career journey is unique, Jaro Education offers highly tailored guidance aligned with an individual’s aspirations, strengths, and challenges. Each interaction is crafted to deliver actionable, relevant, and personalized support. - End-to-End Career Navigation
From initial career exploration to professional growth and transition, Jaro provides a holistic suite of services. Whether you’re a fresh graduate or a seasoned professional seeking a pivot, Jaro ensures comprehensive support at every stage. - Exclusive Access to Career Resources
Jaro Education offers clients privileged access to a rich repository of resources—ranging from strategic job-search tools and resume refinement to curated interview preparation modules and leadership development materials—ensuring candidates are consistently future-ready. - Fulfillment-Driven Career Alignment
By harmonizing individual capabilities and ambitions with meaningful career opportunities, Jaro fosters long-term satisfaction and well-being. The emphasis on purposeful, sustainable career choices contributes to enhanced professional fulfillment and a balanced lifestyle. - Sustained, Long-Term Career Support
Career journeys evolve—and so does Jaro’s commitment. Through ongoing mentorship, periodic check-ins, and continued access to expert counsel, Jaro stands as a lifelong partner in your pursuit of professional excellence.
Conclusion
The role of public finance in the economic development of government in the economy is crucial. Understanding public finance, along with effective management of public funds, becomes paramount for governments striving to propel economic growth and improve social welfare.
By following the principles of public finance, governments allocate resources strategically, invest in essential infrastructure, and implement policies that stimulate economic activity. Additionally, efficient management of public funds ensures transparency, accountability, and optimal utilization of taxpayer money.
Knowing about public finance helps individuals to make smart choices. It helps them to create a better economy where everyone can benefit. So, as we deal with how governments and economies work, knowing about public finance is key to making the world better for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
Public finance refers to the management of a government’s revenue (mainly through taxes), expenditure (on public goods and services), and debt. It involves the policies and decisions that determine how public funds are collected, allocated, and spent to meet the needs of the country’s citizens and the broader economy.
Public finance is important because it helps governments provide essential services like healthcare, education, and infrastructure. It also plays a key role in economic stability, resource allocation, and the redistribution of wealth to ensure social equity and reduce poverty.
Public finance can be divided into three main categories:
- Revenue (Taxation): The collection of taxes from individuals, corporations, and other entities to fund public services.
- Expenditure: The spending of government funds on various public goods and services like education, health, and infrastructure.
- Public Debt Management: The process of managing the government’s borrowing and debt repayment to ensure fiscal stability.
Public finance has a direct impact on a country’s economic performance. Proper management can ensure that resources are allocated efficiently, income inequality is addressed, and social welfare programs support vulnerable populations. On the other hand, poor public finance management can lead to budget deficits, inflation, and social unrest.
Taxes are the primary source of revenue for governments. Through taxation, governments collect funds to finance public services and infrastructure. The role of taxes in public finance is to ensure that governments can meet their financial obligations and provide for the public good.










1 thought on “What is Public Finance? Definition, Types, and Role in Economics”
In this engaging blog from Jaro Education, you’ll discover the essentials of public finance, as well as its types and core components.