Understanding Financial Reporting and Corporate Governance: Insights from IIM Ahmedabad
Table of Contents

In today’s highly competitive and transparent business environment, understanding the language of finance is no longer optional—it’s essential. Whether you’re a corporate executive, entrepreneur, financial analyst, or manager, a robust understanding of financial reporting and governance empowers you to make better strategic decisions, detect early warning signs, and ensure accountability within your organisation.
As global financial markets become more integrated and regulation becomes stricter, the role of corporate financial reporting and governance has taken centre stage. Companies are now expected not only to maintain accurate records but also to communicate their financial health in a manner that is honest, consistent, and transparent. This evolving responsibility calls for more than just traditional number-crunching; it demands insight, interpretation, and integrity.
In this article, we will explore the importance of financial reporting, break down its core objectives, analyse its key users, and examine the critical relationship it shares with corporate governance. We will also provide insights into how professionals can sharpen their skills and understanding through advanced academic programs like the Financial Reporting and Corporate Governance – IIM Ahmedabad.
What is Financial Reporting?
At its core, financial reporting is the process of disclosing financial data and information about a company’s performance, financial position, and cash flows over a specific period. It involves the preparation and presentation of standardised financial statements such as the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and accompanying notes.
Unlike internal accounting records used for day-to-day management, financial reporting focuses on presenting a fair and true picture of the company’s overall health to a wide array of external stakeholders. It forms the basis of trust between a business and its investors, regulators, suppliers, creditors, and the public.
*wallstreetmojo
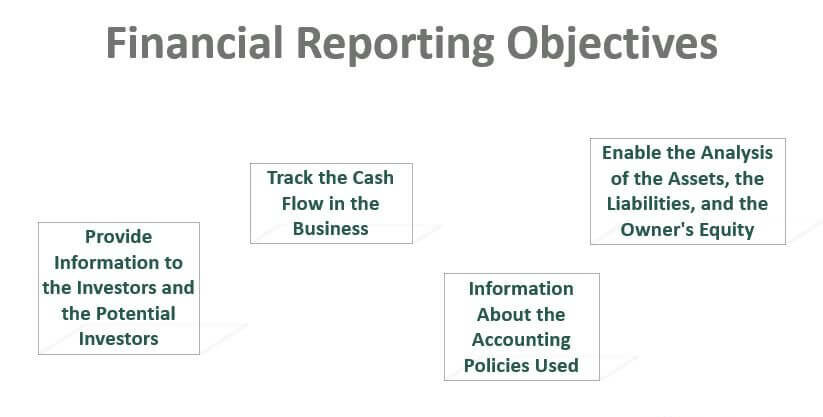
Objectives of Financial Reporting
Understanding the objectives of financial reporting is the foundation of appreciating its value in corporate strategy and governance. These objectives are not just technical—they are tied to the very credibility and sustainability of a business. The major objectives of financial reporting include:
- Transparency: Presenting accurate and timely data helps establish trust with stakeholders.
- Comparability: Standardised formats allow financials to be compared across time periods and between companies.
- Decision-making: Investors and managers use financial reporting and analysis to guide strategic choices.
- Accountability: Financial reports ensure that businesses are held responsible for how they manage resources.
- Compliance: Meeting legal and regulatory requirements through comprehensive and honest disclosures.
In essence, the objectives of financial reporting go beyond accounting—they represent the ethical compass of a business.
Who Are the Users of Financial Reporting?
Identifying the users of financial reporting helps highlight why the process must be both precise and comprehensive. Different stakeholders rely on this information for varied purposes:
Investors and Shareholders
They assess profitability, risk, and return potential before making buy-hold-sell decisions.
Lenders and Creditors
These users examine liquidity and solvency indicators to gauge whether the company can meet its obligations.
Regulatory Authorities
Government agencies and regulators ensure that businesses comply with financial and tax laws.
Analysts and Advisors
They use financial reporting and analysis to provide recommendations, forecasts, and valuation models.
Employees
Understanding company performance helps employees align with corporate goals and negotiate benefits.
Customers and Suppliers
They evaluate a company’s stability before entering long-term partnerships.
Management
Senior executives rely on both internal and corporate financial reporting to make data-driven strategic decisions.
Knowing the users of financial reporting reinforces the importance of clear, accurate, and tailored financial communication.

*themunim.com
Role of Financial Reporting and Analysis in Business Strategy
Beyond compliance, financial reporting and analysis provide a lens through which the health and trajectory of a company can be examined. Effective financial reporting and analysis supports:
- Budget planning and forecasting
- Performance benchmarking
- Cost control and efficiency improvements
- Valuation and merger readiness
- Investment and capital allocation decisions
Professionals engaged in financial performance analysis project report creation understand the deep strategic value such analysis holds. These reports don’t just capture what happened; they help predict what might happen and guide what should be done next.
Corporate Financial Reporting: More Than Numbers
While corporate financial reporting might seem like a numbers game, it’s much more than that. It embodies the ethical and governance framework of an organisation. Corporate leaders must ensure that their financial disclosures reflect both accuracy and integrity.
Key characteristics of high-quality corporate financial reporting include:
- Reliability: The data must reflect the real-world position of the company.
- Relevance: Only material information that can influence decisions should be included.
- Consistency: Reports should follow a consistent methodology over time.
- Understandability: The presentation should be accessible, even to non-specialists.
High-stakes decisions—including capital raising, restructuring, or partnerships—depend heavily on the strength of corporate financial reporting.
Link Between Financial Reporting and Corporate Governance
Financial reporting and corporate governance are two sides of the same coin. While one deals with communicating business performance, the other ensures that such communication is done responsibly, ethically, and under proper oversight.
Corporate governance provides the framework through which company objectives are set and performance is monitored. It includes:
- Board structure and independence
- Internal audit systems
- Ethics and compliance protocols
- Transparency in disclosures
- Shareholder rights
Poor governance often leads to manipulated or misleading financial reporting, which can result in fraud, loss of investor confidence, or legal consequences. This is where the knowledge of financial performance analysis, project report methodologies, and forensic tools becomes essential.
Professionals who understand both disciplines can act as guardians of financial integrity, bridging the gap between operations, compliance, and public accountability.
Bridging Theory and Practice: Learning from IIM Ahmedabad
To navigate today’s complex financial landscape, professionals must master not only the technical aspects of financial reporting but also the interpretive and ethical frameworks behind them. This is precisely the approach adopted by the Financial Reporting and Corporate Governance – IIM Ahmedabad program.
Designed for executives, entrepreneurs, and finance professionals, this four-month blended program offers a rigorous foundation in financial accounting, fraud detection, earnings manipulation, and governance principles. Participants explore the entire financial reporting lifecycle—from understanding frameworks to interpreting key documents such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
With live online sessions, immersive campus modules, and real-world case studies, the program emphasises both theoretical learning and hands-on application. Participants leave equipped not just with knowledge but with skills to make high-stakes financial decisions with clarity and confidence.
Challenges in Financial Reporting: Fraud, Earnings Manipulation & Governance Risks
Despite advancements in accounting standards and regulations, the integrity of financial reporting remains vulnerable to manipulation and misconduct. Understanding these risks is critical not only for CFOs and auditors but also for business leaders, investors, and analysts.
Earnings Management and Smoothing
Some companies attempt to portray a stable growth trajectory by manipulating revenue recognition or deferring expenses. While this may not always be illegal, it compromises the transparency that financial reporting is meant to ensure.
Off-Balance Sheet Financing
Entities may hide liabilities or inflate assets through creative structuring, impacting the accuracy of corporate financial reporting and misleading users of financial reporting about a company’s real financial health.
Related Party Transactions
Poor governance often allows insider dealings to go unnoticed. In such scenarios, the quality of financial reporting and analysis suffers, masking unethical or self-serving decisions.
Misclassification of Expenses
Categorising regular operating expenses as capital expenditures is another manipulation tactic. This artificially boosts profits and distorts performance in financial performance analysis project report evaluations.
Robust corporate governance, rigorous internal controls, and ethical leadership are necessary to prevent such malpractice and preserve the trust embedded in financial reporting.
Best Practices in Financial Reporting and Transparency
For companies that wish to build investor confidence and ensure long-term sustainability, here are some best practices aligned with global standards for corporate financial reporting:
Implement Clear Reporting Frameworks
Follow IFRS, GAAP, or relevant statutory guidelines consistently to ensure your financial reporting is legally compliant and internationally comparable.
Disclose Non-Financial Metrics
Many companies now provide ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) data alongside financials, offering a more holistic view of value creation. This transparency strengthens credibility in the eyes of all users of financial reporting.
Use Visual and Narrative Enhancements
Dashboards, charts, and management commentary enrich the traditional financial performance analysis project report format, helping stakeholders understand key trends and risks.
Prioritise Auditor Independence
An external auditor’s objectivity is crucial to preserving the accuracy of financial reporting and analysis. Avoid conflicts of interest to ensure credible review processes.
Invest in Training and Upskilling
Finance and management teams should be trained regularly in new standards, technology tools, and governance protocols. This is where executive education and specialised programs prove highly beneficial.
Role of Technology in Corporate Financial Reporting
As digital transformation reshapes every business function, corporate financial reporting is no exception. Today, technology is not only enhancing accuracy but also unlocking strategic insight.
Automation of Financial Statements
ERP platforms and cloud accounting tools can generate real-time reports, reducing manual errors and increasing efficiency in financial reporting.
Predictive Financial Analytics
Machine learning and AI can forecast future performance based on historical data, enabling forward-looking financial reporting and analysis.
Fraud Detection Tools
Advanced analytics can flag inconsistencies or anomalies in transactions, empowering internal auditors and finance teams to prevent manipulation before it occurs.
Digital Dashboards
Executives can now access custom financial performance analysis project report dashboards with real-time KPIs, enhancing visibility and response time.
The future of financial reporting is agile, data-driven, and digitally integrated, requiring finance professionals to stay ahead of both technical tools and strategic thinking.
Creating a Financial Performance Analysis Project Report: Step-by-Step
Many professionals and students are often tasked with preparing a financial performance analysis project report, especially in academic or consulting environments. Here’s a simplified approach to creating a thorough and credible report:
Step 1: Choose the Company
Pick a public or private company and obtain its annual financial statements for at least three consecutive years.
Step 2: Analyse the Key Financial Statements
Break down:
- Revenue trends (growth, seasonality)
- Cost structure (fixed vs. variable)
- Operating income and net margin trends
- Liquidity, solvency, and profitability ratios
Step 3: Compare with Industry Peers
Benchmark the company’s ratios and performance indicators against industry averages or a major competitor. This gives context to your financial reporting analysis.
Step 4: Interpret the Findings
What do the trends indicate? Is profitability improving? Are assets being used efficiently? Use charts and graphs to support your narrative.
Step 5: Add Strategic Commentary
Link the financial insights to business strategy. For example, if the company’s margins are narrowing, is it due to rising raw material costs or aggressive pricing? This bridges financial reporting and analysis with strategic foresight.
A great financial performance analysis project report doesn’t just explain “what happened”—it also explores “why” and “what’s next.”
Final Thoughts
In a world shaped by rapid change, globalisation, and digital acceleration, financial reporting is no longer confined to accountants and auditors. It is a critical leadership skill. Similarly, governance is no longer a compliance checkbox—it is a measure of a company’s integrity and sustainability.
Together, they form the foundation of ethical leadership, sound decision-making, and long-term stakeholder value. Leaders who understand corporate financial reporting, who recognise the importance of clarity in communication and governance, will always be ahead of the curve.
If you’re looking to sharpen your understanding of both domains and apply it confidently in the real world, the Financial Reporting and Corporate Governance – IIM Ahmedabad program is a smart investment in your future.
Jaro Education invites professionals and decision-makers to enrol in the Financial Reporting and Corporate Governance – IIM Ahmedabad program. With expert faculty, real-world cases, and a blended learning experience, the course prepares you to lead with insight, integrity, and confidence in today’s financial landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does financial reporting impact investor confidence?
Accurate and transparent financial reporting builds trust with investors by showcasing a company’s performance and future potential. It reduces perceived risk and increases the likelihood of investment and long-term shareholder retention.
What is the difference between internal and external financial reporting?
Internal financial reporting is used by company management for strategic decision-making and may include customised dashboards or projections. External reporting follows standardised formats for users of financial reporting, like investors, regulators, and creditors.
Can poor corporate governance affect financial performance?
Yes, weak governance often results in misleading corporate financial reporting, a lack of accountability, and ultimately, financial mismanagement or fraud, undermining a company’s credibility and performance.
Is financial reporting only relevant for listed companies?
No, while public companies must disclose their financials publicly, private companies also rely on structured financial reporting and analysis to secure funding, evaluate performance, and meet legal or internal compliance standards.
What skills are needed to excel in financial performance analysis?
Professionals must master financial statement interpretation, ratio analysis, forecasting, industry benchmarking, and report writing to prepare and evaluate a comprehensive financial performance analysis project report.


















