What is Business Process Management?
Table of Contents

In the current fast-paced, highly competitive environment, organizations are under pressure to perform more, improve faster, and give more to customers. Businesses are no longer merely concerned with what they do, but how effectively they do it. This is where Business Process Management becomes a game-changer.
In essence, BPM is a systematic method that enables companies to scrutinize, plan, improve, and track their operations within. If you ever asked yourself what is business process optimization is, essentially, it implies perfecting the manner in which work is performed so that better outcomes are obtained. By optimizing processes, BPM enables businesses to save on costs, limit errors, and increase productivity between departments.
Today’s Business Process Management software is more than just straight-up automation. They’re integrated into multiple platforms, leverage real-time data, and give decision-makers meaningful, actionable insights. In a world that’s increasingly digital-first, this degree of agility and control isn’t a nicety—it’s a necessity.
Additionally, BPM crosses over with the business analytics process by developing raw data into significant trends that, in turn, inform wiser strategies. Whether it’s improving customer experiences or tightening back-end operations, BPM is a vital component of building sustainable success within today’s dynamic business world.
Understanding Business Process Management
In order to remain competitive in today’s fast-changing business environment, businesses need to regularly review how they are functioning. Enter Business Process Management (BPM)—a strategic, systematic method for optimizing an organization’s end-to-end processes. In contrast to ad hoc remedies or departmental tweaks, BPM considers the overall picture, considering how each process plays a part in broader business objectives.
The main goal of BPM is to enhance efficiency, reduce costly errors, and improve overall operational performance. Whether it’s onboarding a new employee or managing customer service requests, BPM ensures that every step is optimized. If you’re wondering what is business process refinement, it’s essentially about redesigning how tasks are executed to produce better outcomes for both the business and its customers.
Continuous improvement is one fundamental principle of BPM. It is not a single effort but an ongoing effort to change and improve workflows with the passage of time. This philosophy instills creativity and strength, particularly when supported by consistent Business Process Management tools that provide automation, monitoring, and analysis.
It should be noted that BPM is not to be confused with project or task management. Task management is concerned with personal to-do lists, whereas project management addresses temporary objectives with concrete deadlines. BPM is concerned with improving recurring, repeatable processes, however. When combined with intelligence from the business analytics process, BPM becomes an even more potent tool—providing data-driven decisions that improve both speed and quality.
Essentially, Business Process Management allows organizations to work smarter rather than harder. It creates order out of chaos and allows companies to grow efficiently, which is a critical component of long-term achievement.
Fundamental Elements of BPM
1. Modeling
Modeling starts with mapping out current workflows and designing future state workflows. Modeling workflows visually helps all stakeholders understand current inefficiencies and identify opportunities for improvement. The modeling process must incorporate process business analysis and usable workflows. You must understand what we mean by business process modeling — it’s crucial to have a broad understanding of various workflows in order to plan the future effectively.
2. Execution
Execution occurs once workflows are mapped. We can execute workflows manually or through digital platforms designed specifically for an organization’s overall process control. With tools for modern Business Process Management, consistent execution of processes helps to keep teams organized and realize workflows that should be completed to standard.
3. Monitoring
Monitoring a process’s performance is key to improvement. The critical elements of monitoring a process are key performance indicator, forecasts, metrics-based dashboards and general evaluations of outcomes in real time. Integrating the business analytics process to discover underlying patterns and inefficiencies is useful.
4. Optimization
Lastly, once you have the data, you are able to impact your organization’s process in terms of better performance, accuracy, and increased output. Generally, you will find that small and continuous changes lead to dramatic performance improvements over time. The elements discussed above are essential components of effective Business Process Management (BPM) practices and methodologies.
5. Automation
Whenever it’s possible, you should use Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to automate repetitive jobs. This will lead to fewer errors, save time, and free up staff to concentrate on work of greater value. Realizing that business process automation is crucial to the success of digital transformation.
Each of these components contributes significantly to BPM’s capability to create business agility. Companies are able to respond more quickly and more intelligently while using advanced Business Process Management tools and having fewer resources.
BPM becomes an engine that drives growth only when the outcome of the business analytics process is put together with it.
Business Process Management Types
Business Process Management isn’t a blanket solution—various processes need varied solutions.
Recognizing the different BPM types enables companies to select the most appropriate approach for certain operational objectives.
Integration-centric BPM:
- This BPM type addresses the automation of processes that involve minimal human intervention.
- It integrates multiple systems, platforms, or databases through APIs or middleware.
- If you want to know what business process integration is, imagine it as the glue that holds your tech stack together.
Human-centric BPM:
- These processes are very much dependent on human intervention, typically consisting of tasks such as approvals, reviews, or decisions.
- It is used in sectors such as HR onboarding, customer support, or compliance procedures.
- With the proper Business Process Management tools, these tasks are more efficient and easier to use.
Document-centric BPM:
- As the name implies, this type of BPM revolves around documents—contracts, reports, invoices, and so on.
- It facilitates smooth, editing, and approval of crucial files across an organization.
- Closely associated with the business analytics process, it tracks document status and monitors turnaround time.
Each BPM type has a particular operating requirement to serve.
Regardless of reducing manual effort or dealing with complicated paperwork, Business Process Management molds itself accordingly.
By knowing what business process optimization in each scenario, organizations are able to deploy wiser solutions.
And with today’s robust Business Process Management tools, these strategies can expand conveniently to accommodate growth.
And also, business analytics process insights guarantee these BPM types continue to adapt to business needs.
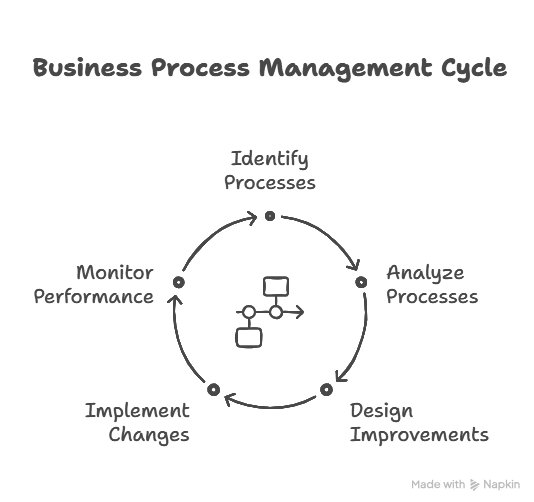
Business Process Management (BPM) Lifecycle Defined
The BPM lifecycle gives a sequential framework for enhancing the manner in which work flows in an organization.
Every phase rests on the last, with a focus on constant improvement and quantifiable results.
- Design:
This is the step of finding out existing processes and areas of pain in the organization.
The aim is to create optimal workflows that align with business objectives and customer requirements.
If you’re wondering what business process design is, it’s basically the map to improved operations.
- Model:
After the perfect process is designed, a visual model comes next.
Tools such as BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) facilitate teams to see each step clearly.
These images are an essential component of most Business Process Management software used nowadays.
- Execute:
Here, the model is executed using BPM platforms or through manual processes.
Execution validates that activities are carried out as per the redesigned workflow.
Business analytics insights can inform change during this step.
- Monitor:
Monitoring in real time enables tracking against target metrics of how well the process is performing.
Dashboards and reports bring delays or inefficiency to the fore early on.
This visibility through data informs better Business Process Management decisions.
- Optimize:
Ultimately, teams leverage feedback and analytics to improve and optimize the process.
Even minor adjustments can yield significant productivity and quality gains.
Knowing what business process optimization is closes the loop for ongoing improvement.
This life cycle keeps companies nimble, streamlined, and always in a position to adapt.
Benefits of Business Process Management (BPM)
Implementing BPM is not merely a matter of streamlining operations—it’s about changing the way your business operates at all levels.
When done properly, BPM can provide a host of significant advantages for teams, leaders, and customers.
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity:
BPM reduces the number of repetitive tasks and inefficiencies in workflows.
This translates to quicker turnaround times and more efficient utilization of resources between departments.
After you are aware of what business process optimisation is, such an advantage becomes evident.
2. Improved Agility and Flexibility:
Organizations are now able to react more rapidly to alterations in the market or in-house operations.
BPM allows process adaptation with ease without necessarily changing the whole system.
Using Business Process Management tools, there is an easy deployment of the changes.
3. Reduced Costs:
By reducing delays, mistakes, and manual labor, businesses save money.
Savings can then be invested in innovation or expansion activities.
The business analytics process can identify areas where costs can be lowered further.
4. Improved Compliance and Risk Management:
Predefined workflows ensure consistency and regulatory compliance.
This lessens legal exposures and enhances audit readiness across functions.
An ordered Business Process Management system ensures policy compliance.
5. Customer Experience Improved:
Quick response times and reliable service quality increase customer satisfaction.
Satisfied customers are more likely to come back and refer others.
Knowing what is business process improvement illustrates how it directly affects customers.
6. Transparency and Responsibility:
BPM ensures full visibility of who’s doing what and when.
This encourages ownership, minimizes confusion, and establishes trust among teams.
Most Business Process Management tools provide real-time dashboards for this reason.
Top Practices for Effective Business Process Management (BPM) Adoption
Making BPM a success takes more than software — it’s people, process, and mindset. The following are some down-to-earth tips to make your BPM initiatives a long-term success.
1. Begin Small with Pilot Projects:
Start with a simple process that has well-defined objectives and limited complexity.
Your team learns and gains confidence before moving to larger, more complex processes.
It’s a straightforward means of comprehending what business process change is in practice.
2. Involve Stakeholders Early:
Get managers, staff, and IT professionals involved right from the start.
Their feedback ensures new processes are realistic and meaningful.
Working together is simpler with intuitive Business Process Management tools on hand.
3. Use Clear Process Documentation:
Specify each step in detail using standards such as BPMN for consistency.
This helps everyone know what they have to do and what is expected of them.
The business analytics process can then be utilized to track success.
4. Focus on KPIs and Performance Metrics:
Monitor what is most critical—speed, accuracy, cost, or customer satisfaction.
Allow data to inform your decisions and ongoing improvements.
Quantifiable goals are essential to successful Business Process Management.
5. Train and Empower Employees:
Give them the tools and knowledge to innovate and adapt.
Encourage everyone to own making things better.
That’s the essence of knowing what business process excellence is.
Join the Executive Post Graduate Certificate Programme in General Management IIM Visakhapatnam
Boost your professional growth through the Executive Post Graduate Certificate Programme in General Management from IIM Visakhapatnam in partnership with Jaro Education. This esteemed programme is designed for working professionals to develop robust managerial and leadership skills in principal business areas such as strategy, finance, operations, and marketing. The strong synergy between IIM Visakhapatnam’s academic rigour and Jaro Education’s cutting-edge learning platform provides a flexible, high-quality learning experience in the form of live online sessions, real-world case studies, and practical projects. Participants get the advantages of IIM’s star faculty, a widely recognized global certification, and the benefit of valuable networking possibilities, all without having to put their careers on hold.
Conclusion
Business Process Management is a strategic strategy that enables organizations to rationalize operations, eliminate inefficiencies, and remain responsive in a rapidly changing business environment. Business Process Management is important in ensuring long-term success through aligning processes with business aims and customer requirements. Understanding what business process optimization is enables companies to release more value and responsiveness. Harnessing the appropriate Business Process Management tools enables smooth implementation, real-time tracking, and ongoing improvement. Guided by insights from the business analytics process, BPM becomes a compelling driver of digital change and long-term growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do you mean by business process management?
Business Process Management, or BPM, refers to a systematic way of designing, executing, monitoring, and optimizing business processes. It enhances efficiency, consistency, and responsiveness within an organization.
What is the main purpose of BPM?
The primary function of BPM is to automate and maximize business processes for enhanced performance, minimization of errors, and more effective outcomes. It guarantees that processes are aligned with business objectives and give maximum value.
What are the 5 stages of BPM?
There are five stages of Business Process Management: design, model, execute, monitor, and optimize. The stages ensure that business processes are improved continuously through automation and analysis.
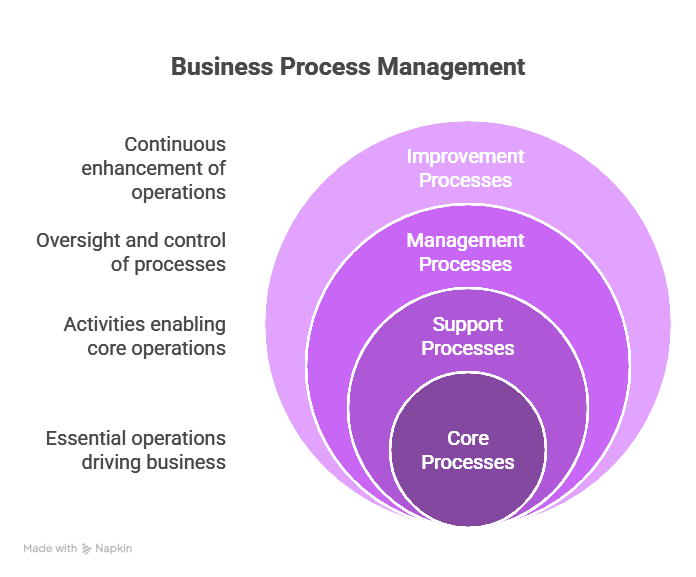
What is business process type?
Business process types are classifications like operational, supporting, and management processes. Each serves a particular function in the accomplishment of organizational goals through formalized workflows.
How to define business process?
A business process is a collection of organized activities or tasks carried out to realize an organizational objective. It determines how work flows between teams, systems, and departments.




















