What is IPO: Full Form, Meaning, Types & Benefits
Table of Contents

Stepping into the world of finance often means encountering buzzwords that dominate the news cycle. Among these, the Initial Public Offering, or IPO in stock market, stands out.
So, if you’ve been asking what is ipo in stock market and how you can benefit from it, you’ve come to the right place. In this blog, we have demystified the entire process, covering its meaning, types, and the strategic benefits of an ipo in stock market for both companies and investors.
What is IPO in Stock Market?
*jainam.in
Simply put, an IPO in stock market is the first time a private company sells shares of its stock to the general public. Before this offering, the company’s ownership was restricted to founders, early employees, and select private investors. By launching the IPO in stock market, the company transitions into a public entity, allowing its shares to be traded openly on a stock exchange. This is the official gateway from the private world to the public market.
Why Companies Launch an IPO: The Catalyst for Growth
The decision to execute an IPO in stock market is the culmination of years of rapid growth and strategic planning. The move is fueled by two fundamental objectives:
- Massive Capital Infusion: The primary goal is to generate a substantial amount of equity capital. This non-debt funding is crucial for major initiatives like geographical expansion, significant research and development (R&D), or debt reduction.
- Liquidity Event: An IPO in stock market provides the founders and early investors with an opportunity to monetize their investments. They can sell their stake, realizing the handsome profits accumulated over the private ownership period.
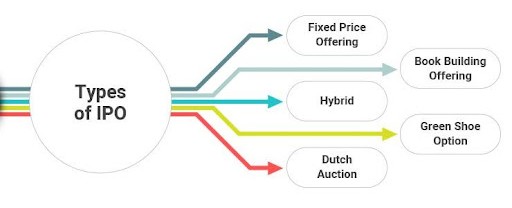
Understanding IPO Types
*samco.in
When launching an IPO in stock market, the company must decide on the mechanism for pricing the shares. This choice dictates how investors will apply and how the final share price will be determined. The two primary methods are the Fixed Price Method and the Book Building Method (the modern standard).
Key Differences: A Comparison Table
| Feature | Fixed Price IPO | Book Building IPO |
|---|---|---|
| Price Determination | Fixed and declared beforehand in the prospectus. | Discovered dynamically through investor bids within a price band. |
| Price Band | Not applicable; single price. | Sets a Floor Price (low end) and a Cap Price (high end). |
| Investment | Full payment of the fixed price is required at the time of application. | Payment is based on the determined Cut-Off Price. |
| Demand Indicator | Poor indicator; demand is only known after the IPO closes. | Excellent indicator; subscription levels are monitored in real-time. |
Strategic Advantages of an IPO in Stock Market
The decision to launch an IPO in stock market creates a powerful two-sided reward system, offering distinct and transformative benefits for both the issuing corporation and the public investors who participate. The intense effort required for the offering is often justified by these significant long-term and short-term gains.
I. Benefits of IPO in Stock Market for the Issuing Company
The primary motivation for executing an IPO in the stock market is institutional transformation and sustainable growth.
1. Massive Capital Infusion (Financial Fuel)
This is the ultimate objective. By selling shares in the ipo in stock market, the company raises substantial, non-repayable equity capital. This infusion strengthens the balance sheet and provides the necessary non-debt funding to finance large-scale strategic projects, such as major geographical expansion, significant research and development (R&D), or large-scale acquisitions, without incurring interest-bearing debt.
2. Enhanced Visibility and Credibility (Brand Building)
Listing on a prominent stock exchange instantly elevates the company’s global profile. This increased stature and media visibility foster greater consumer and client trust, often resulting in easier client acquisition and better terms from suppliers and creditors. The transparency required for an ipo in stock market lends significant credibility.
3. Liquidity Event and Exit Route
The IPO in stock market provides founders, early employees, and venture capitalists with a defined and transparent exit strategy. They gain the ability to monetize their years of investment and risk by selling their stakes on the public market, realizing handsome profits.
4. Talent Recruitment and Retention
Publicly tradable stock enables the company to offer highly attractive employee stock ownership plans (ESOPs). These options motivate and help retain top-tier talent by giving employees a direct, tangible stake in the company’s future success and market value.
II. Benefits of IPO in Stock Market for the Public Investor (The Subscriber)
For retail and institutional investors alike, participating in an IPO in stock market offers unique opportunities that are largely unavailable in the secondary market.
1. Opportunity for Listing Gains
Investors who are successfully allotted shares during the IPO in stock market process often stand to benefit from “listing gains”. This is the immediate profit realized if the stock opens on the exchange at a price higher than the issue price, a result of pent-up demand.
2. Early Access to Growth Stories
An IPO provides the first opportunity for the general public to become part-owners of potentially high-growth companies in emerging or disruptive sectors. This early access allows investors to compound wealth alongside the company’s growth from a foundational level.
3. Diversification and Portfolio Building
IPO in stock market investing offers a way to diversify a portfolio into new industries or business models that were previously inaccessible, moving beyond established large-cap companies.
4. Increased Transparency
Companies that complete the ipo in stock market process are subject to rigorous regulatory oversight and mandated financial reporting (quarterly and annually). This public scrutiny provides investors with a high degree of transparency and audited financial information for informed decision-making.
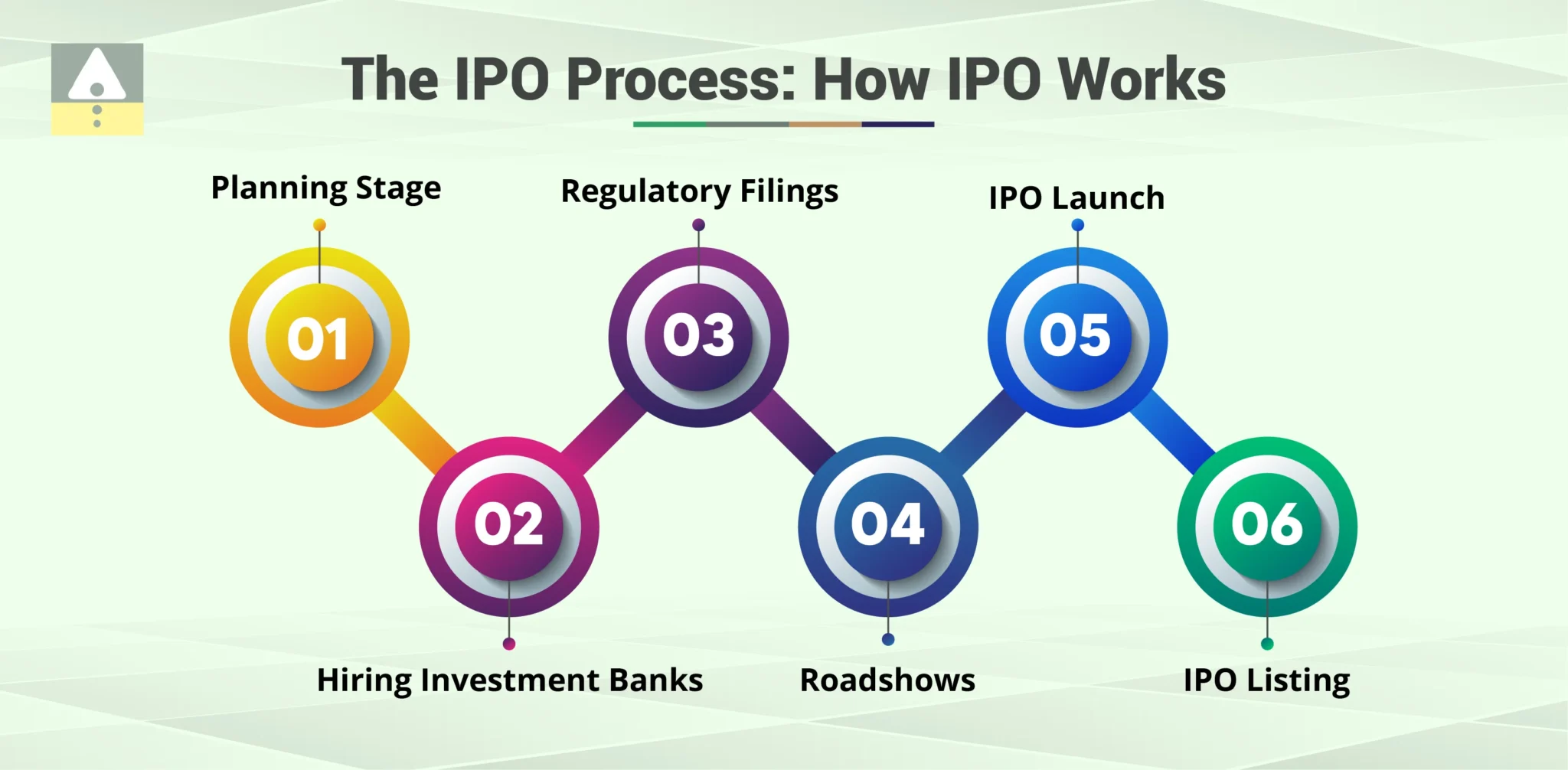
How the IPO in Stock Market Works: The Step-by-Step Process
The journey of an IPO in stock market is a highly choreographed, lengthy process that can take many months. It is overseen by investment bankers and regulated closely to ensure a fair and transparent transition for the public. Here’s how a company moves from a private entity to a publicly traded stock:
Phase 1: Preparation and Regulatory Approval
- Hiring Underwriters: The company first appoints merchant banks (underwriters). These banks guide the process, determine the optimal valuation and pricing strategy, and ensure all legal requirements are met.
- DRHP Filing: The company and underwriters prepare the extensive Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP). This document details the company’s history, financials, management, and the planned use of the proceeds from the ipo in stock market.
- Regulator Scrutiny: The DRHP is filed with the market regulator (like SEBI), who scrutinizes every detail to protect potential investors subscribing to the upcoming ipo list entry.
Phase 2: Pricing, Roadshows, and Investor Bidding
- Roadshows & Pricing: Once approved, the company conducts roadshows, presentations to large institutional investors, to gauge interest. Based on this, the final Red Herring Prospectus (RHP) is published, which includes the official price band for the stock.
- Subscription: The IPO in stock market officially opens for public subscription, usually lasting a few days. Investors (Retail, HNI, QIB) place their bids for the shares within the stated price band.
Phase 3: Allotment and Listing Day Success
- Final Price & Allotment: After bidding closes, the final price (Cut-Off-Price) is determined. Shares are then allotted fairly. If the IPO is oversubscribed, retail investors typically receive shares through a lottery system.
- Listing: The shares are officially listed on the stock exchange (e.g., NSE/BSE). This day marks the moment the stock begins trading in the secondary market. The excitement surrounding the listing gain (the difference between the issue price and the listing price) dominates the market news.
Master the Financial Markets with Jaro Education
To truly leverage the opportunities presented by the IPO in stock market and navigate the complexities of investment and corporate strategy, you need specialized, structured knowledge. Jaro Education helps you bridge this critical knowledge gap by offering premium finance programmes in collaboration with India’s leading institutions.
We provide executive education designed to accelerate your career and give you the competitive edge required to succeed in complex areas like investment banking and corporate finance.
Our expertly curated programs, such as the PG Certificate Programme in FinTech (IIM Nagpur), the Executive Programme in Business Finance (IIM Ahmedabad), and the Post Graduate Certification Programme in Financial Management (IIM Tiruchirappalli), offer the precise skills needed to analyze prospectuses, assess company valuations, and make informed decisions on the next big ipo in stock market.
Conclusion
The IPO in stock market is one of the most exciting financial events for a company and a compelling, if risky, opportunity for investors. Your success in this space depends not on luck, but on thorough preparation. By diligently tracking the upcoming ipo list, carefully reading the RHP, and looking past the initial hype, you can confidently participate in the ipo in stock market and build a robust, informed financial future.
Ready to take control of your investment journey? Explore Jaro’s cutting-edge programs in financial management and corporate finance and start making informed, strategic investment decisions today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a 'Green Shoe Option' and an IPO?
An IPO in stock market is the act of initially listing the shares. The Green Shoe Option (or overallotment option) is a clause in the IPO agreement that allows the underwriter to sell up to 15% more shares than initially planned if the public demand is exceptionally high. This helps stabilize the price after listing.
Is it mandatory for a company to issue an IPO?
No. A company can remain private indefinitely. The decision to execute an IPO in stock market is a strategic choice driven by the need for massive capital, liquidity for early investors, and the desire for greater public visibility.
What is the Gray Market Premium (GMP) related to the upcoming IPO list?
The Gray Market Premium (GMP) is an unofficial, informal price at which shares of an upcoming ipo list entry are traded before the official listing. While a high GMP suggests a strong debut, it is unregulated and should not be the sole basis for your investment decision.
What happens to the funds if the IPO is cancelled or withdrawn?
If the IPO in stock market is cancelled due to poor subscription or regulatory issues, the funds that were blocked in your account via ASBA will be immediately released and available for use, typically within a few days of the announcement.
Which categories of investors are given priority in the IPO allotment?
No category is explicitly given priority, but the total issue is divided into segments: Qualified Institutional Buyers (QIBs), Non-Institutional Investors (NIIs), and Retail Individual Investors (RIIs). Each segment has a reserved percentage of the shares, ensuring fair access across different investor types for every ipo in stock market.

















