The Role of Production Managers: Skills and Responsibilities
Table of Contents

- jaro Education
- 2, February 2024
- 11:00 am
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing and service-driven industries, the role of a production manager is more critical than ever. Whether it’s ensuring timely product delivery, maintaining quality standards, or optimizing resources, production managers are the driving force behind seamless operations. They act as the bridge between planning and execution, balancing people, processes, and performance under constant pressure.
In the fast industrial world of today, keeping production efficient, of high quality, and cost-effective is something for which the production managers are held responsible. From daily production scheduling to team management and testing the quality of products, the production managers is crucial in ensuring operational excellence.
This blog will give us an insight into the job roles and responsibilities of production managers, associated qualifications, production managers skills, and the daily life of a production managers in various industries.
An Overview About Production Managers
The Production Managers are directly responsible for smooth manufacturing operations. They define policies about planning, coordination, and control of production to ensure timely manufacturing of products within cost and quality parameters. Such industries include: Automobiles, Food and Beverages, Textiles, Pharmaceuticals, Electronics, and FMCG.
According to a 2025 survey conducted by AmbitionBox and Glassdoor, production managers in India earn an average remuneration of ₹8.2 LPA, with the remuneration going up to ₹20 LPA after 10-plus years of experience.
Production Managers Roles and Responsibilities
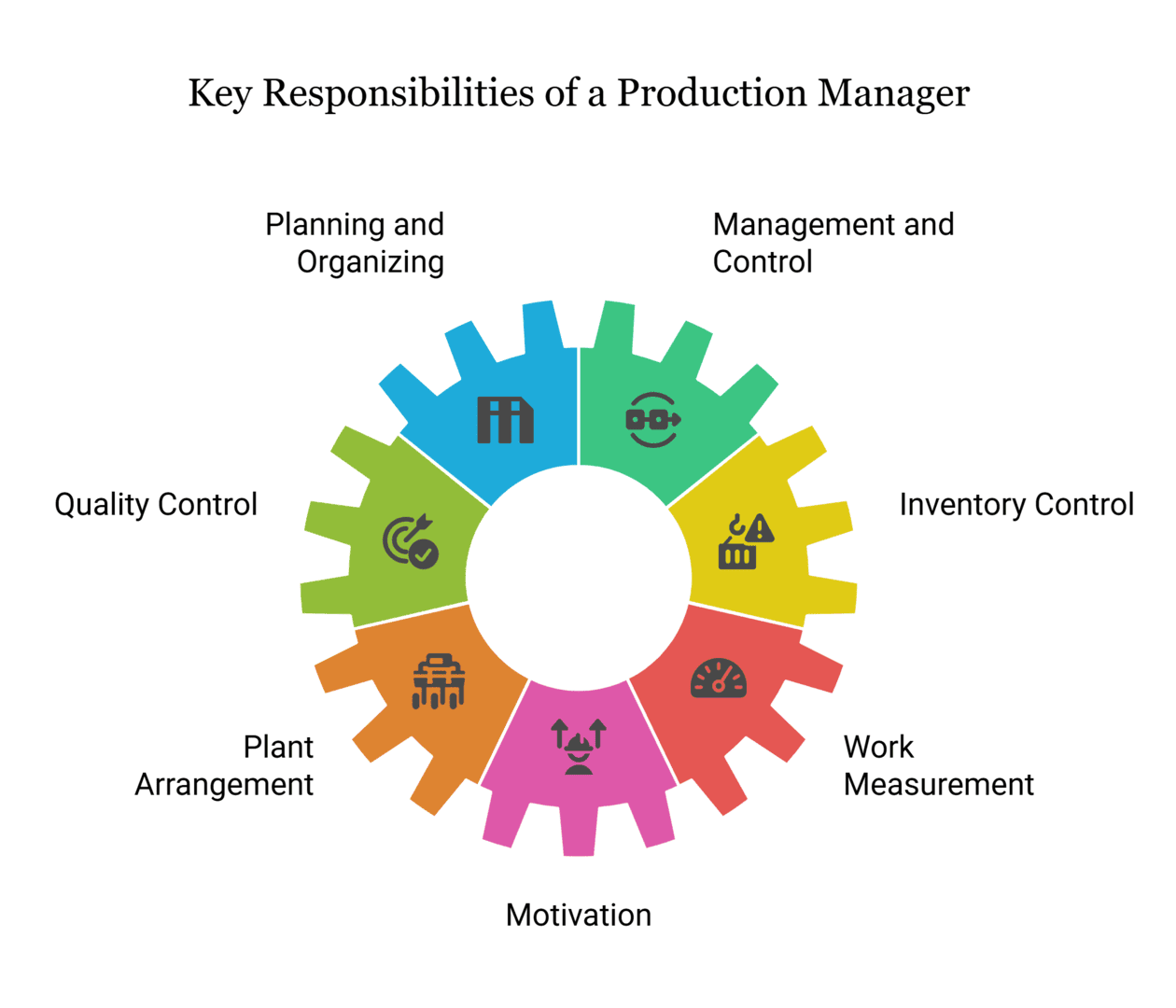
Production managers oversee the planning, coordinating, and controlling of a company’s manufacturing process. The product manager handles everything from production and quality control to on-time product delivery. The duties and responsibilities of a production manager into pre- and post-production stages ascribed are mentioned below:
Pre-Production Phase
This phase focuses on planning, preparation, and resource allocation to ensure the production process runs smoothly and efficiently. It sets the foundation for the entire manufacturing cycle.
Budget & Resources
- Formulate production budgets using sales forecasts, projected demand, and company objectives.
- Allocate resources such as raw materials, labor, machinery, and tools to ensure smooth operations.
- Negotiate vendor contracts for materials and equipment at cost-effective rates.
- Monitor and adjust budgets to avoid waste and ensure alignment with company goals.
Scheduling & Logistics
- Develop a detailed production plan and timeline based on product requirements.
- Arrange workflow sequences to prevent bottlenecks in the manufacturing process.
- Organize supply chains, raw material procurement, and transportation of goods.
- Ensure plant operations comply with legal, environmental, and safety requirements.
Staff & Talent
- Recruit and assign qualified technical staff, machine operators, and supervisors.
- Oversee labor agreements, shifts, overtime approvals, and payroll management.
- Coordinate with HR to align workforce availability with production schedules.
- Provide training or upskilling sessions to ensure operational efficiency.
Preparation & Documentation
- Create detailed process plans, including plant layouts and workflow documentation.
- Prepare and maintain inventory systems (economic order levels, stock limits, consumption reports).
- Arrange insurance coverage for workers, plant, and machinery.
- Document all production-related procedures for compliance and future reference.
Post-Production Phase
This phase emphasizes execution, monitoring, and final delivery of products, followed by evaluation and learning for continuous improvement.
Delivery & Management
- Supervise and control the production cycle to ensure deadlines, costs, and quality standards are met.
- Monitor quality control systems to guarantee products meet company and market requirements.
- Oversee third-party services (e.g., maintenance, inspection, and quality audits).
- Deliver final products on schedule to distributors, wholesalers, or clients.
Wrap-Up & Reconciliation
- Finalize vendor payments and settle outstanding invoices for raw materials and equipment.
- Return unused or rented equipment and close supplier contracts.
- Conduct wrap-up meetings with supervisors to evaluate production efficiency.
- Complete final budget reconciliation and prepare closing reports.
Marketing & Distribution
- Collaborate with sales and marketing teams to align product launches with production timelines.
- Provide input on promotional materials emphasizing product quality and efficiency.
- Support negotiations for distribution agreements with retailers or partners.
- Track product performance and customer satisfaction in the market.
Evaluation & Learning
- Analyze production data to identify areas for cost reduction and efficiency gains.
- Review quality performance and employee productivity against benchmarks.
- Document successes and challenges to improve future projects.
- Share lessons learned with peers and contribute to organizational best practices.
What Skills Do Production Managers Require?
Production managers need a blend of technical expertise and soft skills to ensure smooth, efficient, and compliant manufacturing processes across industries.
- Leadership – Motivate and guide teams to achieve production goals.
- Management – Oversee staff, schedules, and departmental operations.
- Teamwork – Collaborate effectively to meet shared objectives.
- Verbal Communication – Convey ideas clearly to teams and stakeholders.
- Written Communication – Document and share information professionally.
- Empathy – Understand and resolve team or client concerns.
- Equipment Maintenance – Inspect, repair, and maintain machinery.
- Patience – Manage stress and communicate thoughtfully.
- Project Management – Plan, organize, and monitor production projects.
- Conscientiousness – Approach tasks with precision and care.
- Time Management – Prioritize tasks and meet deadlines efficiently.
- Problem-Solving – Anticipate and resolve production challenges.
- Collaboration – Work across departments for resource allocation.
- Knowledge of Software Applications – Use tools like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint.
- Email Management – Handle frequent communication with stakeholders.
- Multitasking – Manage multiple operations simultaneously.
- Financial Expertise – Budget, forecast, and control project costs.
- Industry Knowledge – Apply sector-specific skills and standards.
- Understanding of EPA Regulations – Ensure environmental compliance.
- OSHA Standards – Uphold workplace health and safety laws.
Scope of the Role: Production Managers
The role of a production managers extends across the entire manufacturing lifecycle, ensuring that operations are efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with organizational goals. Their scope includes both strategic planning and hands-on management of daily processes.
- Production Planning – Designing workflows, scheduling tasks, and aligning production with sales forecasts and organizational objectives.
- Resource Management – Allocating manpower, machinery, and materials to optimize efficiency while minimizing costs.
- Quality Assurance – Implementing and monitoring quality control systems to ensure products meet industry and company standards.
- Process Optimization – Identifying and applying lean methods, automation, and continuous improvement initiatives.
- Workforce Leadership – Supervising staff, managing performance, and fostering a safe and motivated work environment.
- Inventory & Supply Chain Oversight – Balancing stock levels, coordinating procurement, and avoiding disruptions.
- Compliance & Safety – Enforcing OSHA, EPA, and industry regulations to maintain safe, sustainable operations.
- Financial Control – Monitoring budgets, controlling production costs, and contributing to profitability.
- Cross-Department Collaboration – Working with HR, finance, R&D, and marketing to align production with business strategy.
- Strategic Contribution – Providing data-driven insights to senior management and supporting long-term operational goals.
Jaro Education: Your Trusted Partner in Career Guidance and Counseling
Moving into Product Management from a Production Manager role can open doors to new career opportunities and greater rewards. With your strong foundation in operations, process optimization, and cross-departmental coordination, you already possess a solid base for stepping into product leadership.
By enhancing your knowledge in areas like market research, customer requirements, and product life cycle management, you can successfully transition from overseeing production efficiency to driving product innovation.
Course Highlight:
Executive Programme in Product Innovation & Design Thinking for Business Growth – IIT Delhi
Learning mode:
- Flexibility in learning: online classes on weekends or after business hours
- 3 days of intensive campus immersion modules
Duration: 6 Months
Jaro Education supports this career transformation with its Executive MBA in Product Leadership & Strategy and other industry-recognized programs. These courses help professionals gain expertise in:
- Product strategy and innovation management.
- Market analysis and customer-centric design.
- Financial planning and business model development.
- Leadership skills tailored for product-driven organizations.
Through career counseling, mentorship, and globally recognized certifications, Jaro Education ensures you are equipped to move confidently into leadership roles beyond production, including Product Manager, Operations Head, or Business Strategist.
Conclusion
To sum up, team leadership and inducing inspiration are vital competencies for a production manager to achieve operational excellence. Effective team management also involves developing talent, encouraging collaboration, and creating a healthy work environment on the factory premises.
To thrive as a product manager, professionals can choose to be a part of the Advanced Strategy For Products And Marketing – Advanced Strategy & Analytics for Products & Marketing Programme – IIM Kozhikode, as it provides you with the opportunity to interact with IIM’s core faculty and be part of live interactive lectures, which, in turn, will help you gain expertise in new-age concepts like Cluster Analysis, Logistics Regression, Perceptual Dimensions, etc. To know more, reach out to Jaro Education and learn about the admission procedure.
Frequently Asked Questions
A Production Manager is a key professional responsible for planning, coordinating, and controlling manufacturing processes. In most organizations, production manager roles and responsibilities focus on ensuring products are manufactured efficiently, meet quality standards, and are delivered on time and within budget.
The core production manager roles and responsibilities typically include:
- Overseeing production schedules and workflows.
- Managing staff, equipment, and material resources.
- Ensuring quality control and compliance with industry standards.
- Monitoring output and improving production efficiency.
- Enforcing safety protocols across the workplace.
- Coordinating with departments like logistics, procurement, and quality assurance.
Production manager jobs are available across a wide range of industries, including:
- Manufacturing and heavy industries.
- Automotive and aerospace.
- Food and beverage processing.
- Pharmaceutical and chemical sectors.
- Textiles, garments, and consumer goods.
- Electronics and FMCG companies.
To qualify for most production manager jobs, candidates typically need:
- A bachelor’s degree in engineering, industrial management, or business administration.
- A master’s degree or MBA in operations or production management (optional, but often accelerates career growth).
Yes. Employers usually expect 2–5 years of supervisory or industry experience before hiring candidates into full production manager roles. Many professionals begin as Production Supervisors or Plant Supervisors before advancing into management.
The production manager salary can vary depending on industry, experience, and location. On average, production managers earn competitive pay, with additional benefits such as performance incentives, healthcare, and retirement plans. Senior professionals often see significantly higher salary packages in large-scale industries.










