C vs. C++: Key Differences Every Programmer Should Know
Table of Contents

Programming has come a long way since the invention of the first high-level languages. Some of the most impactful and seminal are C and C++ programming languages. Both have defined the construction of modern software, operating systems, and applications today. However, although they share commonalities, they vary in style, characteristics, and usages.
If you’ve ever been curious about why C and C++ are different, this in-depth guide will make you understand the distinct features, strengths, and when and why to use which. Let’s go in-depth into the difference between C and C++, why both are so relevant even today, decades after they were developed.
What is C?
Before we delve into the difference between C and C++, it’s crucial to know what C really is.
C is a programming language created in the early 1970s by Dennis Ritchie of Bell Labs. It was originally intended to build the UNIX operating system and later became the basis for numerous other programming languages.
In C and C++ programming, C is termed as the “mother of all programming languages” since it laid down many of the fundamental concepts, such as data types, loops, and conditional statements, that influenced subsequent languages.
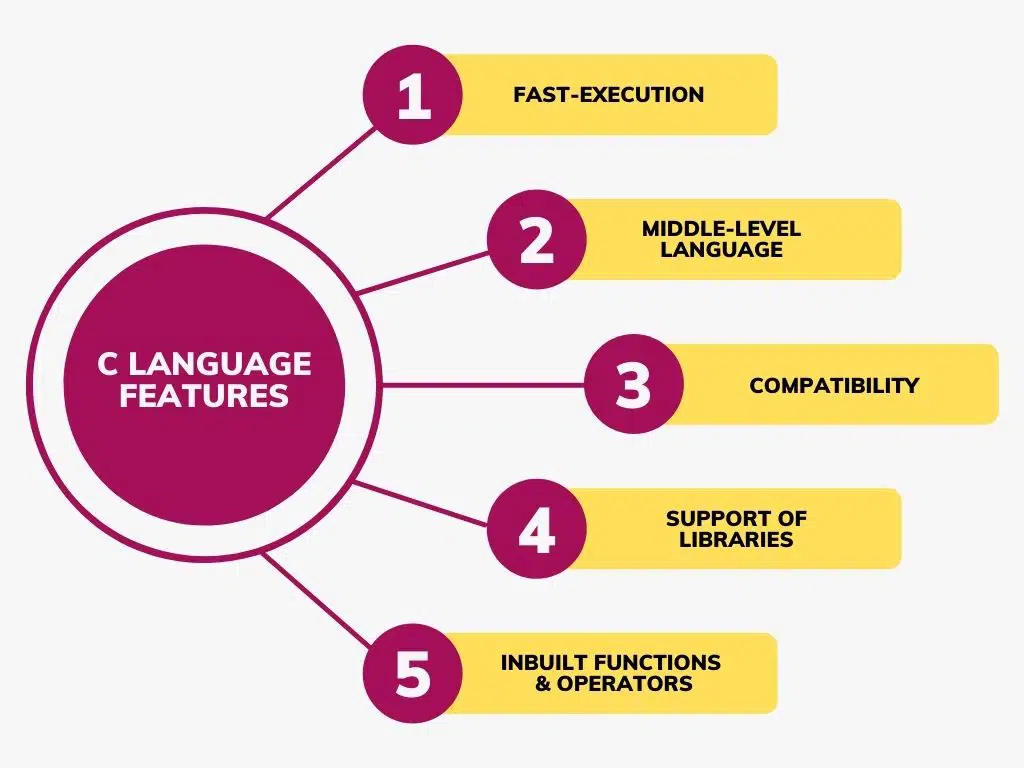
Major Features of C
Procedural language: C is a structured, step-by-step programming paradigm in which programs are segmented into functions.
Low-level memory access: C provides direct memory manipulation through the use of pointers, thus making it very powerful for system programming.
Portable and efficient: C code can be executed on many machines with little modification, making it very portable.
Compiled language: C code is compiled to machine code directly, which gives high performance.
While considering the differences between C and C++, keep in mind that the simplicity and efficiency of C are best suited for operating systems, embedded systems, and hardware-related software.
*Great Learning
What is C++?
Let’s shift to C++, which builds upon and improves the features of C.
C++ was created by Bjarne Stroustrup in the early 1980s as an object-oriented addition to C. It contains all the capabilities of C, plus several very influential additions that make it ideal for contemporary software development.
The primary intention behind C and C++ programming was to introduce object-oriented concepts—such as encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism—into the procedural paradigm of C so that code could be more modular, reusable, and scalable.
Key Characteristics of C++
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): The greatest distinction between C and C++ is here. C++ promotes classes, objects, inheritance, and polymorphism.
Rich Standard Library: C++ has very rich libraries that ease complex programming tasks.
Compatibility with C: C++ can execute the majority of C programs, allowing for a seamless switch for C developers.
Abstraction and Encapsulation: C++ facilitates concealing implementation details and making reusable parts.
Support for both low-level and high-level programming: This dual capability makes C and C++ programming versatile for a wide range of applications.
Features of C Programming
Understanding the features of C helps us see how it differs from C++ in programming style and capabilities.
1. Simplicity and Efficiency
C has a clear and easy-to-understand syntax. Its efficient memory management and low runtime overhead make it a popular choice for system programming.
2. Procedural Approach
C breaks problems down into smaller tasks or functions. This makes debugging and testing simpler, though large programs can be hard to maintain.
3. Low-Level Access
C provides direct access to memory through pointers, allowing for system-level resource management. This is a key advantage in embedded and operating system development.
4. Portability
Programs written in C can be easily compiled and run on different machines, making it a good choice for cross-platform development.
5. Rich Function Library
The standard C library includes many built-in functions for input-output operations, memory management, and string handling.
In short, C and C++ programming share common roots, but C stands out for low-level control and execution speed.
Features of C++ Programming
Now let’s look at what sets C++ apart and clarify the differences between C and C++.
1. Object-Oriented Programming
C++ introduces classes and objects, making code modular, maintainable, and reusable. This feature is one of the key differences between C and C++.
2. Function Overloading and Operator Overloading
C++ allows multiple functions with the same name but different parameters, which increases flexibility. Operators like ‘+’ or ‘-‘ can also be redefined for custom objects.
3. Inheritance
C++ supports inheritance, allowing new classes to inherit properties and behaviors from existing ones. This is an important concept in both C and C++ programming.
4. Polymorphism
With virtual functions, C++ enables the same function name to behave differently depending on the object that calls it.
5. Templates
Templates in C++ support generic programming, allowing developers to create flexible code that works with different data types.
6. Standard Template Library (STL)
STL offers pre-built data structures, such as vectors, stacks, and maps, along with algorithms, saving development time and boosting performance.
These features make C++ a powerful language for developing various applications, from operating systems to video games and enterprise software.
*Collidu
Difference between C and C++: Explained
Now that we’ve explored both languages, let’s look at the difference between C and C++ in a clear comparison format.
Programming Paradigm:
- C is a procedural language — it emphasizes functions and step-by-step procedures.
- C++ is an object-oriented language — it emphasizes objects, data encapsulation, and modularity.
Approach:
- C adopts a top-down approach (problem divided into smaller tasks).
- C++ adopts a bottom-up approach (objects created and then combined to solve problems).
Data Security:
- C lacks more data security since it does not support encapsulation.
- C++ ensures improved data protection through classes, access specifiers, and encapsulation.
Code Reusability:
- In C, reusability is restricted to functions.
- In C++, reusability is extended using inheritance and polymorphism.
Function and Operator Overloading:
- Not supported in C.
- Completely supported in C++, allowing flexibility.
Memory Management:
- C employs manual memory handling (malloc() and free()).
- C++ has constructors/destructors and employs new and delete operators for improved memory management.
Namespaces:
- C does not support namespaces.
- C++ employs namespaces to prevent name clashes in big projects.
Exception Handling:
- C uses error codes or return values for error handling.
- C++ employs exception handling with try, catch, and throw.
- C++ supports built-in exception handling using try, catch, and throw.
Input/Output Handling:
- C employs printf() and scanf() for I/O statements.
- C++ employs stream-based I/O using cin and cout.
Standard Library:
- C’s standard library has a focus on rudimentary I/O, string manipulation, and mathematical functions.
- C++ supports the Standard Template Library (STL) with powerful data structures and algorithms.
Compatibility:
- C is the root language; C++ is a superset of it.
- C++ is backwards-compatible with a majority of C programs.
Applications:
- C is primarily applied in system-level programming, compilers, and embedded systems.
- C++ is extensively used for application-level software such as games, GUIs, and large applications.
The above points describe the primary difference between C and C++, highlighting that C++ enhances C’s strengths by incorporating advanced-level programming features.
C and C++ Programming in Modern Development
Although newer languages such as Python, Java, and Go have become popular, C and C++ programming are still the foundation of most contemporary systems.
- Operating Systems: Both C and C++ are heavily utilized in constructing operating systems such as Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- Embedded Systems: The low-level access of C makes it perfect for microcontroller and firmware programming.
- Game Development: C++ reigns supreme here because of its performance, object-oriented nature, and libraries such as Unreal Engine.
- Database Systems: Numerous databases, including MySQL and Oracle are implemented in C/C++.
- High-Performance Applications: Financial trading platforms, 3D modeling applications, and scientific simulations depend on C++ for their speed and efficiency.
Practically, learning C and C++ makes it possible to know how the software interacts with the hardware and enables programmers to create solid, effective programs.
Advantages of Learning C and C++ Programming
Gaining knowledge of these two foundational programming languages provides programmers with a competitive advantage. Here’s why:
Strong Fundamentals: C introduces you to the underlying principles of memory management, data structures, and algorithms.
Versatility: C++ broadens these fundamentals into object-oriented and generic programming.
Performance: Both C and C++ provide unparalleled speed and efficiency.
Industry Relevance: Numerous industries still rely on C vs C++ codebases, ranging from aerospace to finance.
Career Opportunities: Developers proficient in these languages are in high demand for system, embedded, and game development roles.
Understanding the difference between C and C++ helps beginners transition smoothly from procedural to object-oriented thinking.
When to Use C vs C++
Choosing between C and C++ programming depends on your project needs.
Use C when:
- You’re working on system-level software (e.g., operating systems, kernels).
- You need maximum control over hardware.
- You require minimal abstraction and direct memory access.
Use C++ when:
- You’re developing applications that require modularity and reusability.
- You need advanced data handling, classes, and inheritance.
- You’re working on complex software like games or GUIs.
Both languages complement each other rather than compete. Many modern developers use C for core system modules and C++ for application-level logic.
Grow Your Career with Jaro Education
Grow your career to the next level with Jaro Education, the name that is synonymous with excellence and innovation in the edtech space. Jaro provides one-on-one career guidance to assist learners in making the correct decision based on their goals. With a diverse portfolio of technical and management programs specially crafted in association with premier institutions like IITs and IIMs, Jaro equips students with industry-relevant skills and internationally accepted credentials. As a proven education provider with over a decade’s presence, Jaro Education enables students and working professionals to attain academic accomplishment and fast-track their careers.
Conclusion
Recognizing the distinctions between C and C++ is vital for any developer who is serious about understanding the core fundamentals of software development.
Where C is designed with speed and low-level system access in mind, C++ introduces modern programming considerations like OOP, templates, and exception handling. Combined, C and C++ form an incredibly powerful design pattern for developers who want both control and flexibility with their programming languages.
Whether you’re a student, professional software engineer, or simply a technology enthusiast, learning C versus C++ gives you a fantastic foundation for understanding how computers actually work—and how to make them work for you!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between C and C++?
The prime difference between C and C++ is that while C is a procedural programming language, C++ is object-oriented. In C vs C++, C is all about functions and logic step by step, while C++ is about classes, objects, and reusable code structures.
What can C++ do that C can't?
C++ can do object-oriented programming, which cannot be done by C. This implies that in C and C++ programming, C++ supports concepts such as inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation — allowing more modular and scalable software development.
Why is C++ faster than C?
While both are effective, C vs C++ demonstrates how C++ may be faster in some cases by virtue of more efficient memory handling, inline functions, and optimized object management. The difference between C and C++ is whether C++ balances performance with high-level abstractions for more optimization.
Which is easier, C or C++?
For beginners, C is easier as it’s more straightforward and procedural. Still, C and C++ programming both lay strong foundations — C++ introduces additional complexity with OOP concepts, but it’s more flexible once you understand the difference between C and C++.


















