A Beginner’s Guide to Java Exception Handling
Table of Contents

You’ve probably been there.
You’re coding away. Everything compiles fine. The logic feels bulletproof. You run the program — BAM. Something blows up. Maybe it’s a null pointer. Maybe a file isn’t where it’s supposed to be. Or maybe the database just refuses to play nice that day.
Either way, your program crashes. Your manager wants answers. And your users? Well, they just want the app to work.
This — this exact pain—is why Java exception handling exists.
In real-world applications, things break. Not occasionally, often. And no matter how careful you are, you can’t anticipate every possible thing that could go wrong at runtime.
That’s where exception and exception handling in Java come in. It’s not about writing perfect code. It’s about writing code that survives imperfection.
What Exactly Is Java Exception Handling?
At its simplest, Java exception handling is your code’s emergency response system. When something abnormal happens while your program is running, here we’re talking files missing, bad user input, calculation errors – Java throws an exception.
But instead of letting your entire application die right there, Java gives you a chance to catch that exception, do something intelligent about it, and keep the rest of the system running.
You don’t need your shopping cart system to collapse just because someone entered an invalid discount code, right? Exactly. That’s why Java exception handling matters.
Inside Java’s Exception Object: The Core of Error Handling
Here’s the part a lot of new developers gloss over:
An exception in Java isn’t just a message or a random signal—it’s a full-blown object. Every time an exception occurs, Java creates an instance of some class that extends Throwable. That object carries everything you need: the type of problem, the message, the stack trace, and even its cause.
When you use Java exception handling, you’re essentially grabbing that object and deciding what to do with it. Log it? Retry? Inform the user? Abort gracefully? That’s your call.
This is one of the biggest reasons Java is still king in enterprise systems — its exception handling in Java is powerful, consistent, and predictable.
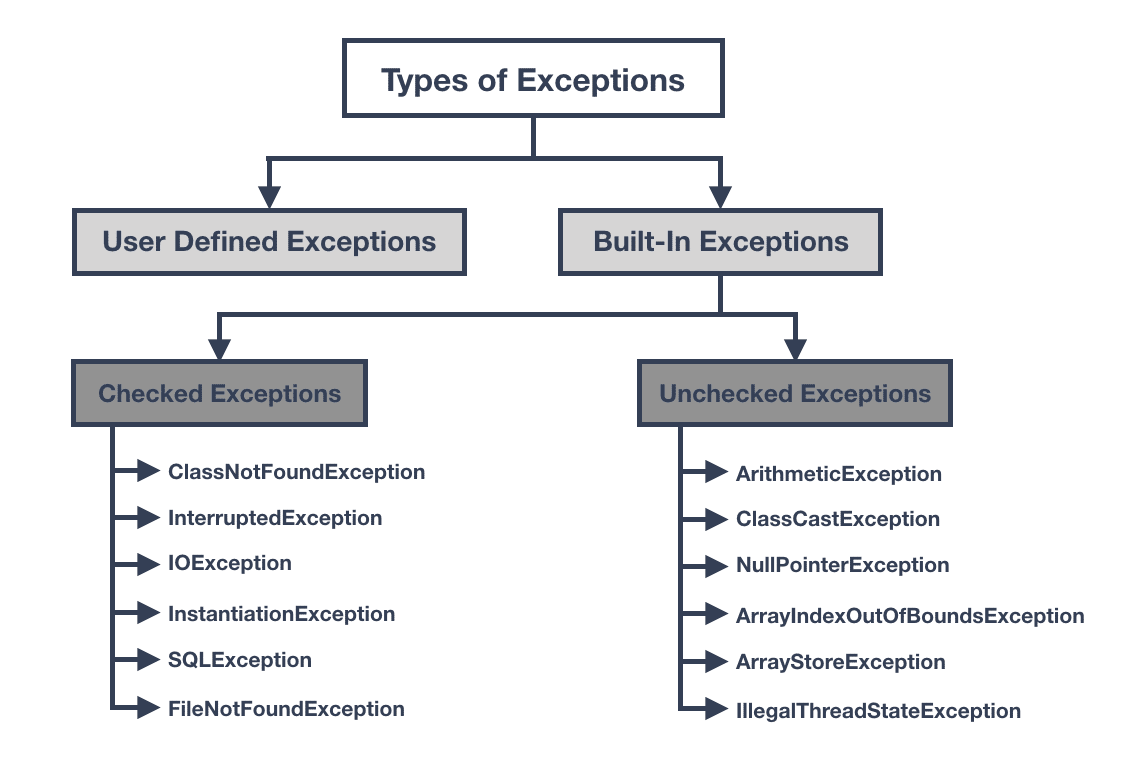
Two Worlds: Checked and Unchecked Exceptions
Let’s get into one of the more debated topics in Java exception handling: checked and unchecked exception types.
*rollbar.com
You’ll hear strong opinions on both sides, but here’s the clean version without the fluff:
Checked Exceptions
- Java forces you to handle them at compile time.
- The compiler literally won’t let you proceed unless you deal with them.
- Example: IOException, SQLException.
Imagine you’re writing code to read a file. Java knows that the file may not exist. So, it makes you write code to handle that possibility, or your code won’t even compile. That’s checked exception behavior.
Unchecked Exceptions
- Handled at runtime (optional handling).
- Compiler won’t stop you if you don’t handle them.
- Example: NullPointerException, ArithmeticException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
These usually represent programming errors, things that could’ve been avoided with better code, but sometimes happen anyway.
| Type | Compiler Forces Handling? | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Checked | Yes | IOException, SQLException |
| Unchecked | No | NullPointerException, ArithmeticException |
Both checked and unchecked have their place in exception and exception handling in Java. Knowing when to expect which makes you a stronger developer.
Types of Exception Handling in Java — The Actual List
Alright, let’s break down some of the most common exception types Java developers deal with:
IOException
- Happens when reading or writing files.
- File not found? No permission? Disk failure? This one handles it.
SQLException
- Database went rogue.
- Query failed, connection lost, bad data type — all roads lead here.
NullPointerException
- Tried to use an object that wasn’t initialized. Classic rookie (and sometimes senior) mistake.
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
- Accessed an invalid index in an array. Happens when loops overshoot.
ClassNotFoundException
- Tried to load a class dynamically that doesn’t exist in the classpath.
Each of these tells a very different story, but they all fall under Java exception handling because your system needs to know what to do when these scenarios hit.
What Happens Behind the Scenes?
You call a method. Inside that method, something goes wrong. Now what?
- Java creates an exception object.
- That object bubbles up the call stack.
- If one of the calling methods has a try-catch block that matches the type of exception, the exception is caught.
- If not, it keeps moving up.
- If no method handles it, Java kills the thread (or the whole app).
That’s exception propagation. This is why proper exception handling in Java requires thinking not just about where an exception might occur, but where you want to handle it.
Why You Need to Take Java Exception Handling Seriously
Here’s a truth bomb: Most real-world production outages aren’t caused by logic errors. They’re caused by unhandled exceptions.
Files missing. APIs failing. Network timeouts. Nulls where you didn’t expect them.
Java exception handling isn’t there to fix your bugs. It’s there to make sure bugs don’t destroy your entire application.
If you want to write backend systems, microservices, or financial apps that stay up and running even under pressure, you need to master exception and exception handling in Java. Period.
Best Java Exception Handling Practices To Swear By
Here’s how to approach Java exception handling in production systems:
- Handle What You Can Fix: If you can take action on an exception — retry, fallback, notify the user — handle it. Don’t catch what you cannot meaningfully resolve.
- Always Log Exceptions: Use structured logs. Include timestamps, exception types, and stack traces. Your future self (and your ops team) will thank you during post-mortem analysis.
- Use Custom Exceptions: When working on large systems, create meaningful custom exceptions that represent real business failures. This makes exception handling in Java far more readable and maintainable.
- Favor Specific Catch Blocks: Always catch the most specific exception you’re prepared to handle.
- Never Swallow Interrupted Exception: When handling multithreading, always respect the thread’s interrupted status — blindly swallowing it can lead to hard-to-detect concurrency bugs.
When NOT to Catch Exceptions
Ironically, one of the most advanced skills in Java exception handling is knowing when not to handle an exception.
For example:
- Security exceptions? Let the framework handle it.
- Programming bugs? Fail immediately; don’t swallow logic errors.
- Interrupted exceptions in threads? Preserve interrupt status.
Blindly catching everything leads to dangerous systems where failures are hidden, not solved.
Monitoring & Observability — The Modern Extension of Exception Handling
In today’s cloud-native world, Java exception handling extends far beyond code:
- Exceptions must be logged (with full stack traces).
- Alerts should be tied to critical exception types.
- Dashboards should monitor error rates in real-time.
We teach our learners to integrate exception handling into monitoring stacks (like ELK, Splunk, Datadog) — because catching an exception is worthless if no one knows it happened.
Exception and exception handling in Java don’t end at the catch block — it feeds your entire system health picture.
The Career Edge You Gain by Mastering This
Professionals who truly understand Java exception handling don’t just fix bugs — they design systems that anticipate failure.
This mindset shift leads directly to:
- Promotions to senior developer or tech lead roles
- Invitations to architecture discussions
- Higher trust from leadership and clients
- Code that survives real-world production load
The Leadership Perspective: How Java Exception Handling Skill Elevates Your Career
Writing code that works is one part. But writing code that survives failure that’s leadership employers highly seek. Here are a few pointers explaining how mastering exception handling in Java sets you apart.
- Your code will be more stable.
- Your systems will scale better.
- Your teams will trust your architecture.
*upgrad.com
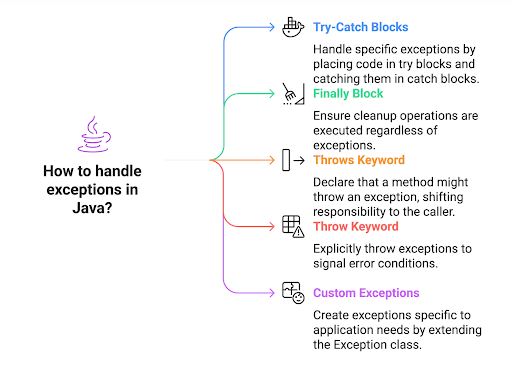
Quick Reference: Java Exception Handling Cheat Sheet
| Concept | What It Means | Quick Pro Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Exception | A condition which disrupts normal code flow | Always read the exception message first, it tells you exactly what went wrong. |
| Checked Exception | Must be handled during compile time | Use try-catch or throws to deal with these proactively. |
| Unchecked Exception | Occurs at runtime, optional to handle | Write defensive code to avoid these wherever possible. |
| Try-catch Block | Catches exceptions and allows custom handling | Keep catch blocks focused—don't catch a generic Exception unless necessary. |
| Finally Block | Executes code whether an exception occurs or not | Great for releasing resources like file streams or database connections. |
| Throw / throws | Used to manually throw exceptions or declare potential exceptions | Always document custom exceptions with clear messages for future maintainability. |
| Custom Exceptions | User-defined exceptions specific to business logic | Use when standard exceptions don’t fully capture your business error cases. |
Pro Insight: Rather than complex logic, a lot of enterprise-grade systems fail because of the negligent handling of exceptions. By mastering these foundations, you can create systems that are adaptable and production-ready.
How Jaro Education Gets You Ready for Java Exception Handling Problems in the Real World
At Jaro Education, we are an accredited online higher education provider in India, renowned for delivering courses that go beyond simple and basic theory to prepare professionals like you for real-world issues. One such program is Manipal University Jaipur’s Master of Computer Applications (MCA) Online Degree Program. This course equips learners with a comprehensive understanding of jobs as database engineers, data scientists, business analysts, and more.
Ready to master Java exception handling and more related essential skills to gain a competitive edge?
Don’t wait, the admissions for the MCA Online Programme are closing soon. Enroll with Jaro Education and take charge of your tech leadership journey today!
Conclusion
To conclude, Java exception handling isn’t the most glamorous part of coding. But it is one of the most valuable, without any questions.
You may not get applause when your system stays online during a failure. But trust us — your clients, your users, and your stakeholders notice. Quiet stability is always loud at scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do developers care so much about Java exception handling?
In real-world coding scenarios, things often go wrong. Incidents like missing files, failed APIs, or server hiccups are quite common. Here, Java exception handling gives you a way to catch these problems early, manage them properly and prevent full-scale crashes that would otherwise break the application.
What’s the deal with checked and unchecked exceptions in Java exception handling?
With Java exception handling, checked exceptions (like IOException) need to be handled before your code even runs. NullPointerException and other unchecked exceptions are not reported until the program is in operation. They are both there to assist in managing various types of hazards in your code.
Should I always catch every exception when doing Java exception handling?
No. Trying to catch every single exception can backfire. Some exceptions, like serious memory errors, should stop the program so you can fix the real issue. Good Java exception handling means knowing which problems to handle and which ones to let fail.
What happens under the hood when Java exception handling kicks in?
When an error occurs, Java exception handling creates an object that holds details of what went wrong. This object moves up the chain of method calls until it finds a block of code prepared to handle it. If nothing catches it, the program may stop or escalate the error.
Why is monitoring tied so closely to Java exception handling these days?
Catching exceptions is insufficient. Modern systems need you to log them, keep an eye out for trends, and configure alerts. Java exception handling becomes a component of your system’s early warning system, allowing your team to react to issues in production before users even see them.
Does mastering Java exception handling really make a difference in my career?
Yes. Developers who handle exceptions well build stronger, more reliable systems. That skill earns trust and often leads to bigger roles in system design, leadership, and critical project ownership.

















