Skills Every Quantitative Analyst Needs in 2025
Table of Contents

The role of quantitative analyst (also known as a quant) has become more critical due to the data-driven and fast-evolving financial world. Today, they are the analytical backbone of any organization. Blending advanced mathematical models, programming, and data analytics, they make informed decisions to minimize risks and drive profitability.
So, individuals who are looking to make their career as a quantitative analyst must have the essential skills for the role. Additionally, they should consistently upgrade their knowledge with more advanced skills, current trends, and technologies.
This blog will highlight the skills required for this role so that they stay competitive in this changing landscape of quantitative analysis.
*wallstreetmojo.com
Understanding the Quantitative Analyst Job
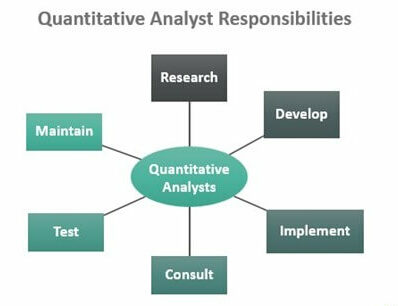
Before jumping into the skill sets, it’s vital to understand what a quantitative analyst actually does. A quant is responsible for solving risk management and complex financial problems by utilizing mathematical models. Their tasks can vary based on the organizational requirements. These may include –
- Developing pricing models for financial instruments
- Creating algorithms for automated trading
- Performing risk assessments and scenario analysis
- Designing and implementing investment strategies
- Conducting back testing of models against historical data
So, a quantitative analyst job is more than just providing financial services. Nowadays, industries like e-commerce, energy, insurance, and healthcare also hire quants for operational optimizations, demand forecasting, and predictive analytics.
Quantitative Analyst Salary Outlook in 2025
A major aspect of becoming a quantitative analyst is a lucrative amount of compensation. The quantitative analyst salary varies based on experience, skills, location, and industry.
- Entry-Level (0–2 years): ₹12–18 lakhs per annum in India / $90,000–$120,000 in the US
- Mid-Level (3–7 years): ₹20–35 lakhs per annum / $130,000–$180,000 in the US
- Senior-Level (8+ years): ₹40 lakhs+ / $200,000+ (often including performance bonuses)
Moreover, many quantitative analyst roles come with bonuses, stock options, and performance incentives.
Core Skills Every Quantitative Analyst Needs in 2025
To be successful in this dynamic field, a quantitative analyst must have mastery over mathematical, technical, and business-related skills. Below is the breakdown of the essential quantitative analyst skills for 2025.
1. Advanced Mathematical and Statistical Knowledge
A quantitative analyst must have a deep knowledge of mathematics and statistics. These are the core concepts of quantitative analysis. Thus, these are the mandatory skills for the professionals.
Key focused areas:
- Probability Theory
- Linear Algebra
- Stochastic Calculus
- Time Series Analysis
- Numerical Methods
These methods are essential for pricing models, optimizing investment strategies, and risk analysis. So, the quants require a strong academic background, such as a master’s or PhD in disciplines like statistics, mathematics, or physics.
2. Programming Proficiency
Spreadsheets were enough for quantitative analysis in the old era. But in 2025, being proficient in spreadsheet operations is not enough; a quantitative analyst also requires programming skills. It is mandatory because most of the quantitative models are developed with code and run on huge datasets. A quant must not only know how to write the code but also how to debug, test, and optimize it for large-scale computations. So, here are the top languages to learn for these professionals –
- Python: The go-to language for data science, machine learning, and general analysis.
- R: Used primarily for statistical modelling.
- C++: Essential for high-frequency trading systems due to its speed.
- SQL: Required for data extraction and manipulation from databases.
3. Data analysis and Data Engineering
Modern quantitative analysis deeply relies on a massive volume of unstructured and structured data. Thus, the professionals must have the ability to clean, handle, and analyze data. That means a quantitative analyst must understand how to make raw data feasible. Also, they should handle datasets from numerous sources and formats, understand data integrity, and prepare data for modelling.
Key tools and concepts:
- Pandas, NumPy, SciPy (Python libraries)
- Jupyter Notebooks
- Apache Spark for big data
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines
- API integration for live data feeds
4. Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI and ML are no longer just buzzwords. These are necessary to thrive in the quantitative analysis field. Many risk management systems and trading strategies are now using ML algorithms for accurate predictions. Thus, every quantitative analyst must have proficiency in predicting customer behaviors, detecting patterns, and assessing credit risk with unprecedented accuracy through ML. Here are some of the popular techniques of ML to perform these tasks.
- Regression Models
- Decision Trees and Random Forests
- Neural Networks
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Reinforcement Learning
5. Financial Knowledge and Market Awareness
Apart from the mathematical and technical skills, a quantitative analyst must have a good grasp of the financial context. Specifically, they should have a good understanding of the market mechanisms for data modelling. Moreover, the knowledge of economic trends and financial instruments helps them develop quality models that are mathematically and financially relevant.
Essential Concepts:
- Derivatives and Options Pricing
- Fixed Income Securities
- Portfolio Optimization
- Risk Management Techniques (VaR, CVaR)
- Macroeconomic Indicators
6. Communication and Visualization Skills
Just developing a brilliant model is not the end of the road. After building the model, it should immediately communicate its value to stakeholders. Thus, quants should have the ability to transform complex quantitative insights into practical business decisions. If a quantitative analyst has this skill, they get more priority than others. That’s why quants work alongside portfolio managers, non-technical executives, and traders to derive valuable business decisions.
Key Skills:
- Report writing and executive summaries
- Data visualization tools (Tableau, Power BI, matplotlib)
- Presenting findings in clear, actionable terms
- Storytelling with data
7. Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
A quantitative analyst works with mathematics, statistics, and data; they are problem solvers at their core. They play a key role in minimizing portfolio risk, identifying arbitrage opportunities, etc. But whatever they are doing, their success rate depends on their analytical thinking and creative model-building. These are the must-have traits when they are working in high-stakes environments like risk desks or trading floors.
So, here are the attributes that fulfil analytical thinking and creative model-building skills –
- Logical reasoning
- Pattern recognition
- Hypothesis testing
- Scenario planning
8. Risk Management Expertise
Risk management has grown drastically, especially after 2020, when the market volatility and regulatory pressure grew. Thus, a quantitative analyst must know the real-world implications of risk apart from the mathematical modelling. Moreover, risk management models serve as the backbone of the decision-making framework in the financial sector. From this point of view, the professional must have a good to expert level of knowledge of risk management.
Key Areas:
- Market Risk
- Credit Risk
- Liquidity Risk
- Operational Risk
- Regulatory compliance (Basel III, IFRS 9)
9. Software and Modeling Tools
Being a quantitative analyst, professionals also have familiarity with the specialized software for simulation, modelling, and analysis. For instance, quants can process large data sets, develop complex financial models, and back-test trading strategies. Through these ways, the tools help to improve productivity. Thus, financial institutions integrate these tools to optimize their day-to-day workflows.
Common Tools:
- MATLAB
- SAS
- Excel (advanced)
- Bloomberg Terminal
- QuantLib
10. Adaptability and Continuous Learning
Now, the financial industry is evolving faster than ever. Whether it’s quantitative analysis, quantum computing, blockchain analytics, or AI, staying up-to-date is crucial. Thus, it’s crucial to stay updated with consistent learning efforts for a quantitative analyst role.
How to stay updated?
- Online courses (Coursera, edX, Udacity)
- Research journals and whitepapers
- Attending fintech and finance conferences
- Participating in online communities like Quant StackExchange
11. Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Analytics
Another valuable skill requirement for a good quantitative analyst is in-depth knowledge of blockchain technology. As decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to gain traction, blockchain skills are becoming increasingly essential. Despite volatility, cryptocurrency markets are increasingly attracting the interest of institutions. Thus, the quants are now expected to analyze trading patterns, evaluate crypto assets, and build models that are accountable for the unique behaviors of a decentralized market.
Key Knowledge Areas:
- Blockchain architecture
- Smart contracts
- Crypto asset pricing models
- On-chain data analysis
Expertise in these areas helps a quantitative analyst to stay ahead in the realm of digital assets on the global market.
12. Cloud Computing and Infrastructure Management
Every day, trillions of data points are generated across the globe. With these data volumes booming, cloud computing becomes indispensable for large-scale financial modelling. Thus, quants utilize and rely on cloud platforms for storing data, deploying analytical models, and running simulations. Here are some popular cloud platforms they rely on:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Knowledge of these platforms enables a quantitative analyst to scale computations efficiently, ensure model availability across distributed teams, and integrate APIs for real-time data.
13. Quantitative Research and Academic Writing
Strong research skills help a quantitative analyst to develop new financial models and validate existing ones. In institutional or academic settings, the quants write detailed research papers, internal documentation, or white papers to justify results or methodologies. This quantitative research skill not only supports decision-making but also fulfils leadership abilities in finance and analytics. For these quants, these skills –
Skill Highlights:
- Literature reviews
- Research design and methodology
- Model validation and hypothesis testing
- Publishing in peer-reviewed journals
14. Regulatory and Compliance Knowledge
Financial regulations are also evolving and becoming more complex in 2025. Specifically, the regulations have become complex due to the increase in algorithmic trading and data privacy laws like GDPR and India’s DPDP Act. Thus, a quantitative analyst must become familiar with this changing landscape of the regulatory and compliance environment. It also helps them to ensure that their models and algorithms are aligned with the legal requirements. As a result, these help them to avoid regulatory penalties and ensure operational integrity.
Important Regulations to Know:
- MiFID II (EU)
- Basel III/IV (Banking)
- SEC Reporting Standards (US)
- Risk-based capital adequacy norms (India)
15. Domain-Specific Expertise
Last but not least, domain knowledge enhances the relevance of quantitative analysts. Domain-specific expertise improves the applicability of models and accuracy. It will help them work in credit risk modelling, insurance modelling, or asset management. Also, by developing customized models for industry-specific requirements, a quantitative analyst becomes more valued in the specialized sectors.
Examples:
- Insurance: Actuarial modelling and claims forecasting
- Healthcare: Patient risk scoring and hospital resource optimization
- Retail: Customer lifetime value modelling and demand forecasting

*pickl.ai
Additional Soft Skills That Add Value
While technical mastery is the foundation, certain soft skills amplify a quant’s effectiveness:
- Team Collaboration: Working with cross-functional teams (IT, compliance, trading)
- Time Management: Meeting tight deadlines on financial reporting and model delivery
- Attention to Detail: Small errors in models can lead to massive financial losses
- Ethical Judgment: Especially important in risk modelling and data privacy contexts
Soft skills ensure that technical expertise is applied responsibly and collaboratively.
Embrace Career Enhancement with Advanced Analytics and Business Intelligence
Want to reshape your career with advanced data analytics? So, delve into the right path with the Professional Certificate Programme in Advanced Analytics & Business Intelligence from IIM Kozhikode. The course provides in-depth exposure to data handling techniques, tools, programming languages, ML, deep learning, and business applications.
Individuals can enroll in the course through the website of Jaro Education. They are the marketing partner of the program and offer numerous supportive educational services for the students. For instance, they offer career enhancement sessions that are conducted by industry experts. These help students build their professional competencies to stay relevant in a changing job market.
Here are a few KPIs of this course –
- 140 hours of learning
- In-campus immersion
- Networking opportunities
- Hands-on live interactive classes
Conclusion
The quantitative analyst role encompasses a dynamic range of skills. It includes mathematics, data science, and more. As industries become increasingly dependent on data-driven decisions, the demand for skilled quantitative analysts has increased. Therefore, individuals seeking to build a career as a quant must possess the right skills and continually enhance their knowledge over time. These habits lead them towards the right opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which programming language should a quant learn in 2025?
Python is the most well-known language for a quant. Additionally, they should learn R for statistics and C++ for speed-critical systems, such as high-frequency trading. Query languages like SQL should be learned for large databases.
What is the major role of a quantitative analyst?
They solve complex data-related problems in finance and other data-driven industries through analytical, coding, risk management, and trading skills.
What industries hire quantitative analysts?
Several industries hire quantitative analysts. These are the tech, finance, e-commerce, healthcare, and energy sectors.
Does an individual need a PhD degree to become a quantitative analyst?
This is not a mandatory requirement. However, individuals having PhDs or master’s degrees in mathematics, physics, or finance are considered the best fit for this role as they have strong coding skills, hands-on experience, and industry knowledge.

















