Learn the Difference Between Linear Search and Binary Search Today!
Table of Contents

Understanding the difference between linear search and binary search is a lens into how optimized your thinking is as a developer. Especially in a world where milliseconds matter and data is king.
So let’s dive deeper into intuition, patterns, logic, and real-world application. Because once you understand why these two algorithms differ, everything from choosing the right data structure to acing coding interviews becomes far more manageable.
What Is the Difference Between Linear Search and Binary Search?
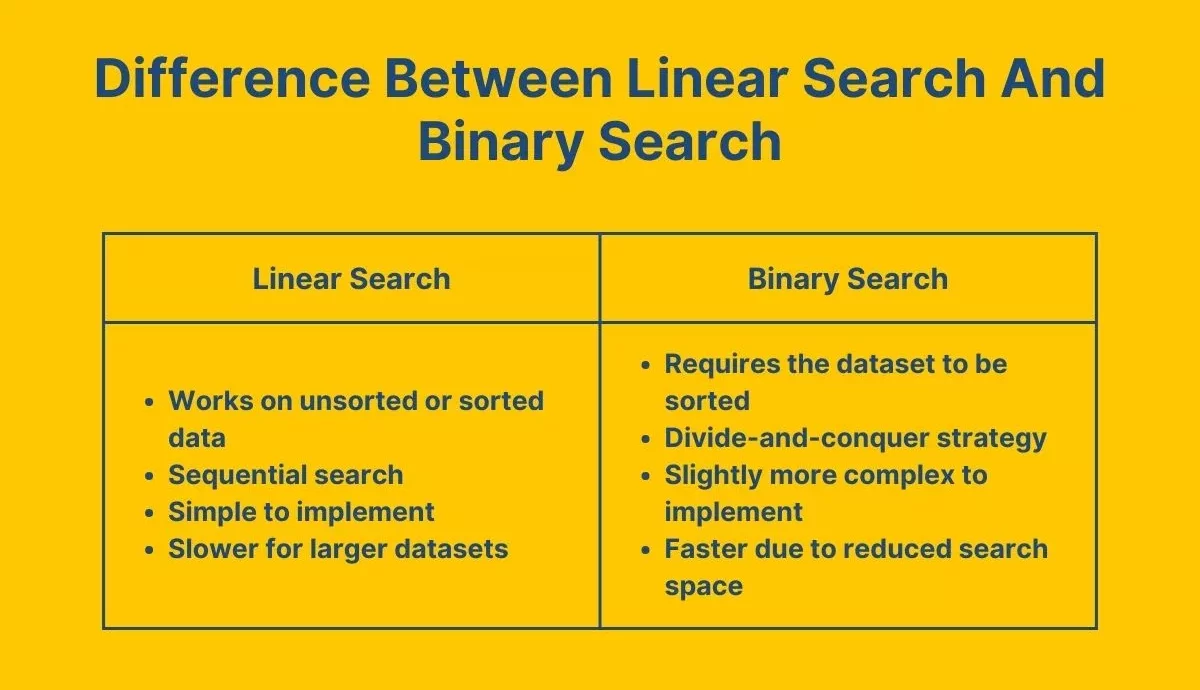
*unstop.com
To understand the difference between linear search and binary search, you have to look beyond what they do and understand how and when they are used.
So, here’s a quick visual reference:
| Feature | Linear Search | Binary Search |
|---|---|---|
| Best Used When | Data is unsorted or small | Data is sorted |
| Approach | Sequential (element by element) | Divide and conquer |
| Time Complexity (Avg/Worst | O(n) / O(n) | O(log n) / O(log n) |
| Data Requirements | No order required | Must be sorted in advance |
| Practical Use Cases | Scanning arrays, small datasets | Searching in databases, sorted files |
So while both fall under the “search” umbrella, the linear vs binary search debate is actually about efficiency, context, and scale.
The Intuition Behind Linear and Binary Search Algorithms
Let’s break down the difference between linear search and binary search in a way you can easily understand:
Linear Search = Door-to-Door Check
In algorithmic terms, linear search operates sequentially. It checks each element one by one from the beginning until it either finds the target value or exhausts the dataset.
- Pros: Simple, reliable when data is unorganized
- Cons: Time-consuming as the data size grows
- When to Use:
- Searching unsorted data
- Small datasets
- Quick checks
- Searching unsorted data
Code logic:
python
def linear_search(arr, target):
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] == target:
return i
return -1
Pretty intuitive. But as your dataset grows from 10 to 10,000, the performance cost adds up, especially if the item is at the end, or not there at all.
Binary Search = Sherlock with a Map
On the other hand, binary search follows a more refined approach, but it only works on sorted data. It strategically narrows down the search space by repeatedly dividing the array in half, comparing the target value with the midpoint. If the value is less than the midpoint, it continues the search in the left half; if greater, it shifts focus to the right half.
- Pros: Super-fast on large, sorted datasets
- Cons: Only works on sorted collections
- When to Use:
- Large sorted lists
- Searching numeric ranges
- Algorithmic problems requiring optimization
- Large sorted lists
Code logic:
python
def binary_search(arr, target):
low = 0
high = len(arr) – 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2
if arr[mid] == target:
return mid
elif arr[mid] < target:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid – 1
return -1
And just like that, a million-row search becomes a 20-step operation. (Yes — log₂(1,000,000) ≈ 20!)
Time Complexity — The Real MVP
If you’re aiming to optimize performance or prep for an interview, this part is crucial. Let’s revisit the time complexity of linear search and binary search. This is where the difference between linear search and binary search has the biggest impact, especially at scale.
| Operation | Linear Search | Binary Search |
|---|---|---|
| Best Case | O(1) (first element) | O(1) (middle match) |
| Average Case | O(n/2) = O(n) | O(log n) |
| Worst Case | O(n) | O(log n) |
In coding rounds or system design, this matters. Say you’re filtering users from a list of 1 million:
- Linear search might take up to 1 million operations.
- Binary search would need only about 20.
So even if the core logic seems simple, the performance delta is staggering at scale.
Real-Life Situations That Make You Choose Linear vs Binary Search
Let’s say you’re building a product filter for an e-commerce site. Here’s how the difference between linear search and binary search plays out:
- If the product list is sorted by price or popularity, binary search is the go-to.
- But if filters are dynamically changing or user-generated, and there’s no guarantee of order, linear search may be more practical.
Similarly, in the backend of an educational platform, student ID lookups across a sorted database are perfect for binary search. But in feedback forms or chat logs with unstructured data, linear search might be the only option.
The bottom line: Context determines the better fit.
Pros and Cons Summary Table
To make the difference between linear search and binary search even clearer, here’s a focused breakdown:
| Criteria | Linear Search | Binary Search |
|---|---|---|
| Data Requirement | No sorting required | Data must be sorted |
| Performance on Large Data | Slower | Much faster |
| Implementation Simplicity | Very simple | Slightly more complex |
| Use Case Flexibility | Works in any dataset | Works only with ordered datasets |
| Time Complexity (Worst) | O(n) | O(log n) |
| Best Use Cases | Small, unsorted datasets | Large, sorted datasets |
| Common Mistake | Using it on large sorted data (inefficient) | Trying it on unsorted data (won’t work) |
When you really understand the difference between linear search and binary search, it becomes second nature to match the method with the problem type.
How the Time Complexity of Linear Search Affects Systems
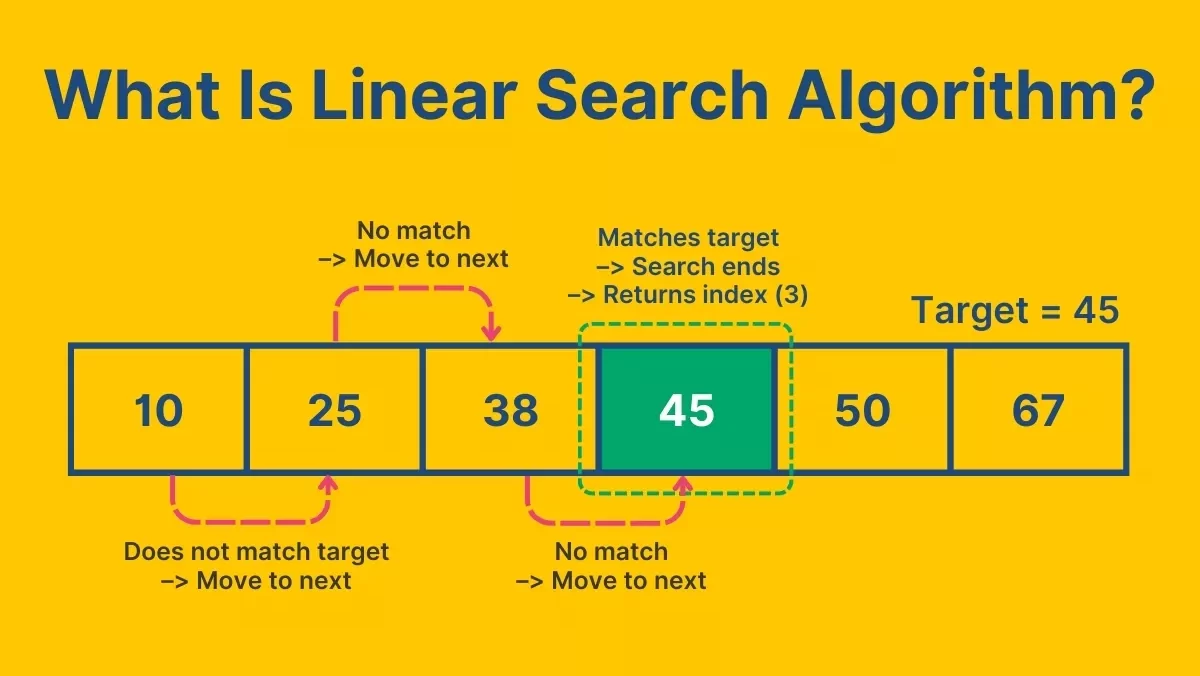
*unstop.com
Let’s go deeper into the time complexity of linear search, which is O(n) in both average and worst-case scenarios. This means that as the dataset grows, the time taken increases linearly.
If you’re processing hundreds or thousands of records once, that’s fine. But in systems that make repeated searches, think search bars, recommendation engines, and log analysis tools, linear search creates a bottleneck.
This is where binary search shines. With a time complexity of O(log n), even massive datasets can be traversed quickly and reliably.
Benchmarking the Time Difference Between Linear and Binary Search
| Dataset Size | Linear Search Time | Binary Search Time |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | Up to 10 steps | ~4 steps |
| 1,000 | Up to 1,000 steps | ~10 steps |
| 100,000 | Up to 100,000 | ~17 steps |
| 1,000,000 | Up to 1 million | ~20 steps |
That’s the real power behind understanding the difference between linear search and binary search.
Developer’s Checklist: When to Use Which
Here’s a simple difference between linear search and binary search decision tree to help make the right choice:
- Is the data sorted?
- Yes → Use binary search
- No → Use linear search
- Yes → Use binary search
- Is the dataset large?
- Yes → Prefer binary search if possible
- No → Linear search is okay
- Yes → Prefer binary search if possible
- Do you need fast lookup performance?
- Yes → Prioritize binary search
- Yes → Prioritize binary search
- Is sorting feasible before search?
- Yes → Consider sorting and then using binary search
- No → Stick with linear
- Yes → Consider sorting and then using binary search
The clarity you gain by knowing this simple difference between linear search and binary search is immense, especially when facing real-world constraints.
Common Interview Scenarios That Test This Knowledge
Interviewers love probing your ability to optimize. Here’s how the difference between linear search and binary search comes up:
Scenario 1: Unsorted Array Lookup
You’re asked to find an element in an unsorted array.
- Best Approach: Linear search
- Common Pitfall: Trying binary search without sorting
Scenario 2: Sorted List of Student Marks
The interviewer gives you a sorted list and asks for the rank of a specific student.
- Best Approach: Binary search
Scenario 3: Rotated Sorted Array
A more advanced question might involve applying binary search logic to a rotated array — testing your grasp of the concept and your adaptability.
In all these, your understanding of the difference between linear search and binary search can make or break your solution.
How Jaro Education Helps Bridge the Learning Gap
Struggling to master key concepts like the difference between linear search and binary search? Jaro Education helps close that gap with industry-relevant, expert-led online programs.
We’re India’s leading edtech platform, offering the best courses in collaboration with top global universities. Our tech-forward curriculum ensures you don’t just learn, you lead.
Ready to upskill with confidence?
Explore technology and IT programs listed on Jaro Education’s platform today and transform your learning, accelerate your career.
Conclusion
While linear search is simple and sequential, binary search is strategic and sorted. Both have their place, but choosing wisely saves time and memory.
Mastering the difference between linear search and binary search can give you a clear edge in technical interviews and real-world development.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between linear search and binary search in terms of speed?
The difference between linear search and binary search is that linear search checks each element, so it’s slower on large datasets, while binary search is much faster with sorted data.
When should I use linear search and binary search in coding?
Use linear search for small or unsorted data; binary search is best when data is already sorted.
What is the time complexity of linear search vs binary search?
The time complexity of linear search is O(n), whereas binary search has a better O(log n) time complexity.
Is binary search always better than linear search?
Not always, binary search requires sorted data. For unsorted lists, linear search is the only option. You need to understand the difference between linear search and binary search to choose the best fit for your requirement.

















