An Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)

Table Of Content
- What Is a Neural Network?
- What Is Convolutional Neural Network and Why Was It Needed?
- Understanding CNN Architecture in a Simple Way
- Why CNNs Are So Powerful
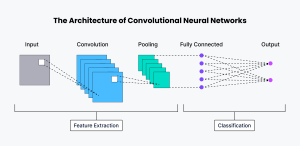
What Is a Neural Network?
*zilliz.com
Before diving into convolutional neural networks, it helps to understand the basic idea of a neural network.
A neural network is inspired by the human brain. Just like our brain has neurons that receive information, process it, and pass it along, artificial neural networks consist of layers of connected nodes. Each layer learns something from the data and forwards that knowledge to the next layer.
Traditional neural networks work well for structured data like numbers or text. But when it comes to images, they struggle. Why? Because images are large, complex, and full of spatial information. Treating every pixel as an independent value simply doesn’t work efficiently.
That’s where convolutional neural networks step in.
What Is Convolutional Neural Network and Why Was It Needed?
A CNN or Convolutional Neural Network is a type of Artificial Neural Network designed specifically for working with image/video data (Visual Data).
For example, if you were to take an image of 100 x 100 pixels and input it into a typical artificial neural network as an image, that would represent 10,000 inputs for just that single image.
Depending upon how many layers the model has, it may have millions of parameters based on the number of neurons and connectable weights connections; thus, it becomes either slow to train or it is very expensive to train, and/or from a high degree of overfitting.
The key feature of CNNs is their ability to process images in a manner similar to how humans visualize their environment, focusing on a small area of an image, rather than looking at the entire image at once. To build recognition of complex shapes and objects from those simple patterns, convolutional neural networks identify simple elements (e.g., edges, corners), then slowly develop into more complicated patterns and complex shapes, objects and features.
Therefore, due to this method of locating patterns, CNNs have become the dominant computational model for training computer vision models.
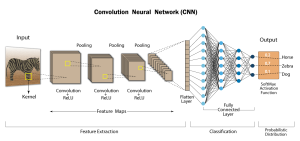
Understanding CNN Architecture in a Simple Way
*analyticsvidhya.com
To get an understanding of how CNNs function, we have to look at the CNN architecture step by step. Each layer of a convolutional neural network has a specific purpose, and when combined, they create a very strong framework for interpreting images.
1. Input Layer
This is where everything begins. The input layer receives the raw image data. This could be a grayscale image with one channel or a color image with three channels (red, green, and blue). Each pixel value becomes part of the input that the network will analyze.
At this stage, the network doesn’t “understand” anything yet, it simply sees numbers.
2. Convolutional Layers
Convolution layers are the most important part of CNN architecture. These layers utilize small filters (often referred to as kernels) that are able to slide across the image. The filter will check the area it passes over for specific patterns. Each filter gets trained on a specific set of features, like edges or curves.
As CNNs progress through the layers and each layer’s filters detect progressively more complex features, eventually the filters begin combining the lower layer features to eventually recognize faces or other objects.
3. Pooling Layers
After the convolution layers have detected the features of the image, the convolutional neural network will frequently employ pooling layers that down-sample the feature maps.
Pooling uses a summary of surrounding pixel values to create a single pixel in the pooled layer. Pooling generally takes one of either the maximum or average value from within the surrounding pixels. By utilizing pooling, the model can achieve the following:
- Create a model that is less computationally expensive.
- Reduce the chances of overfitting.
- Focus on the features that are most relevant.
Pooling also consists of a characteristic known as spatial robustness. Spatial robustness means that the model can recognize an object even if the object is represented in unique positions.
4. Flatten Layer
Once the convolutional and pooling layers finish extracting features, the data needs to be converted into a format suitable for decision-making.
The Flatten layer takes all the learnt features and turns them into a one-dimensional vector. This prepares the data for the final classification stage.
5. Fully Connected Layers
Fully connected layers are the same as traditional neural networks. They take all of the flattened features from an input and learn to recognize how certain combinations of features relate to a target output.
As an example, if a dataset of images of cats has many instances where certain features are commonly seen together, the model would learn to associate those features as indicative of the category “cat”.
6. Output Layer
The output layer produces the final prediction. In classification tasks, this often uses a softmax function to assign probabilities to each possible class.
The class with the highest probability becomes the model’s final answer.
Why CNNs Are So Powerful
The convolutional neural network didn’t become popular by chance. They offer several advantages that make them ideal for image-based tasks.
Automatic Feature Learning
Unlike the older image processing methods, which required manual feature extraction, CNNs learn features through examination of the data set. This results in a more efficient and accurate means of processing images when compared to previous techniques.
Translation Invariance
One major advantage of CNNs is their ability to recognize objects in an image even if the object is in a different position within that image. This ability makes convolutional neural networks far more effective and reliable in real-world applications.
Reduced Computational Complexity
By focusing on local regions and sharing parameters across the image, CNNs use far fewer parameters than traditional neural networks.
CNN in Image Processing: Transforming Visual Data
The role of CNN in image processing goes far beyond classification. CNNs can enhance, modify, and generate images in powerful ways.
Image Enhancement
CNNs are used to improve image quality by removing noise, sharpening details, and enhancing resolution.
Image Segmentation
In medical imaging and satellite analysis, CNNs can divide an image into meaningful regions, helping professionals make accurate decisions.
Style Transfer
CNNs can apply the artistic style of one image to another, blending creativity with technology.
Free Courses
Explore courses related to Data science



Real-World Applications of Convolutional Neural Networks
CNNs are already deeply integrated into modern technology. Here’s how they’re being used across industries.
Image Classification
CNNs possess a high level of accuracy in recognizing objects found within images, for example: animals, cars, various domestic items, etc.
Object Detection
Beyond recognizing objects, CNNs can locate them within an image. This is crucial for surveillance, robotics, and autonomous systems.
Facial Recognition
Many security systems and smartphones will utilize CNNs for identifying and verifying faces very quickly and with a high degree of accuracy.
Medical Imaging
Convolutional neural networks are used to support and assist doctors in identifying tumours, fractures and various diseases through X-rays, MRIs and CT scans.
Self-Driving Cars
CNNs are used to analyse and interpret camera-based data by self-driving cars, in order to identify traffic signs, pedestrians, and provide them with a safe route during travel.
How CNNs Learn Over Time
CNNs improve through a process called training. During training, the model analyzes thousands or millions of images and compares its predictions with correct answers. Each mistake helps the network adjust its internal parameters.
Over time, the model becomes better at recognizing patterns and making accurate predictions. This learning process is what allows CNNs to perform complex tasks with high reliability.
The Bottom Line
Indeed, understanding a convolutional neural network is not just about knowing how it works, it’s about learning where and how to apply it in the real world. If CNNs caught your interest, the good news is that there are clear academic and professional paths to master them.
CNNs are typically taught as part of subjects like Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Computer Vision. You’ll often encounter CNN concepts in undergraduate and postgraduate programs such as B.Tech or M.Tech in Computer Science, Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, or AI & Machine Learning specialisations. Many modern curricula now include hands-on exposure to CNN architecture, image datasets, and real-world problem-solving.
Beyond traditional degrees, online certification programs and executive courses have become a popular choice for working professionals and students who want industry-relevant skills without putting their careers on hold.
Start Your CNN Learning Journey with Jaro Education
If you’re looking for a structured and industry-aligned way to learn convolutional neural networks, Jaro Education can help you take that next step with confidence. Jaro partners with leading universities and institutions to offer online degree programs and professional courses in Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Data Science.
What sets Jaro Education apart is its learner-first approach. You get access to expert-led sessions, real-world projects, academic mentorship, and dedicated career guidance, all designed to help you understand complex concepts like CNN architecture in a practical and application-driven manner. Whether you’re a student building your foundation or a professional upgrading your skills, Jaro Education provides the right ecosystem to grow in the AI domain.
Frequently Asked Questions
A convolutional neural network is primarily used for tasks that involve visual data. This includes image classification, object detection, facial recognition, medical image analysis, and video processing.
Related Courses
Explore our programs
Find a Program made just for YOU
We'll help you find the right fit for your solution. Let's get you connected with the perfect solution.

Is Your Upskilling Effort worth it?

Are Your Skills Meeting Job Demands?

Experience Lifelong Learning and Connect with Like-minded Professionals







