Top 55 PMP Exam Questions and Answers

Table Of Content
- What Is PMP Certification?
- PMP Certification Test Prep for Beginners: Smart Practice Hacks
- How Can Jaro Education Help You Crack the PMP Exam?
- Conclusion
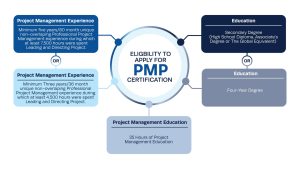
What Is PMP Certification?
The Project Management Professional certification is a globally recognised credential awarded by the Project Management Institute (PMI), a non-profit professional body based in the United States. Individuals with this certification validate that they are ready to apply project management principles, tools, and methodologies across the full project lifecycle.
The PMP exam fee varies depending on PMI membership status. Candidates who are PMI members generally pay a reduced PMP exam fee compared to non-members.
In India, PMP exam fees are charged in US dollars and converted based on prevailing exchange rates at the time of payment. Candidates are advised to review the official PMI website for updated PMP exam fees in India before registration.

*facebook.com
PMP Certification Test Prep for Beginners: Smart Practice Hacks
Beginning your PMP certification path may feel confusing, but practicing the right PMP test questions matters the most. If you’re new to project roles, your attention should be on core project fundamentals to form a solid base.
To guide you in the right direction, below are PMP exam sample questions and answers grouped by topic and experience, giving you a step-by-step preparation roadmap.
*instituteprojectmanagement.com
1. In Which Risk Management Phase Can a Risk Be Found?
- A) Only in the strategy-building step
- B) Only in the delivery step
- C) From the first to the last day of the project
- D) Only when the project ends
Correct Answer for this PMP exam questions: C) From the First to the Last Day of the Project
The process of discovering risk doesn’t end at one stage. Project conditions change, new roadblocks appear and teams must be continuously monitoring for potential risks.
The main milestones in the process to discover and mitigate risks include:
- Planning Stage – Risks you are aware of at that time will be listed in the risk log document
- Delivery Stage – New risks will arise as a function of changes to the project.
- Tracking Stage – Risks can be rechecked and updated regularly.
- Final Stage – Lessons learned will be used to plan for risk management in future projects.
2. A Risk Shows 20% Chance Every Month, Project Runs 5 Months. What Is the Chance It Happens in Month 4?
- A) 20%
- B) 59%
- C) 80%
- D) 67%
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) 59%
The chance of risk not happening in one month is 80% (1 – 0.2). Over 4 months, the chance it never happens becomes:
0.84 = 0.4096
So, the chance it occurs at least once till month 4 is:
1 – 0.4096 = 0.59 or 59%
Learning cumulative probability helps judge risks that build over time.
3. At a Vendor Meet, You Realize One Supplier Is Your Close Buddy. What’s Your Next Move?
- A) Continue if you don’t push the decision
- B) Notify leaders and step away from the contract choice
- C) Pick the cheapest proposal, no matter the connection
- D) Decline your buddy’s proposal to stay safe
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) Notify Leaders and Step Away from the Contract Choice
When selecting suppliers, the moral responsibility of the company is an important factor in order to assure that the selection process is conducted with transparency.
The following five best practices are ideal:
- Be transparent and communicate to all stakeholders that impact the decision process.
- Remove yourself from all levels of the supplier selection process.
- Fairly evaluate suppliers on their performance alone, not other factors.
- Adhere to established PMI and internal moral and ethical guidelines.
By following these steps, supplier selection processes remain objective and fair.
4. What Is the Full Form of RACI?
- A) Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed
- B) Required, Affected, Consulted, Initiated
- C) Registered, Assigned, Checked, Indexed
- D) Responsible, Authorized, Confirmed, Installed
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: A) Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed
RACI is a proven Method to clearly Identify Task Roles.
The Roles for RACI are;
- Responsible – the individual who will complete the job
- Accountable – who owns the final outcome
- Consulted – who provides feedback or advice to the responsible person, and
- Informed – the individuals who are given status updates on the progress of the job.
Simply put, RACI allows teams to stay aligned and make work flow smoothly.
5. A Risk Has 90% Chance, Cost Loss $10,000. What Does $9,000 Mean?
- A) Backup budget fund
- B) Total risk pressure value
- C) Predicted financial risk worth
- D) Risk handling expense
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: C) Predicted Financial Risk Worth
Expected Monetary Value (EMV) calculates the possible money effect. Formula:
EMV = Probability × Impact
EMV = 0.9 × 10,000 = 9,000
Key EMV facts:
- Guides Decisions: Helps check financial risk load.
- Covers Gains & Losses: Positive for chances, negative for threats.
- Improves Budget Plans: Helps assign safety funds wisely.
- EMV supports early financial readiness.
6. Project Has 60% Chance $100,000 Gain, 40% Chance $100,000 Loss. What’s the EMV?
- A) $20,000
- B) $40,000
- C) $60,000
- D) $0
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: A) $20,000
EMV gives a weighted prediction of project results.
EMV = (0.6 × 100,000) + (0.4 × −100,000)
EMV = 60,000 − 40,000 = 20,000
Key EMV facts:
- Smart Risk Choices: Helps pick positive-value work.
- Future Prediction: Helps plan finances better.
- Shows Risk Weight: Helps design safety plans.
- EMV improves investment clarity.
7. Which Description Best Explains a Program?
- A) A group of separate, unrelated work streams
- B) A set of linked projects controlled together
- C) A single massive project
- D) Work only for risk tracking
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) A Set of Linked Projects Controlled Together
Programmes combine projects that serve one common goal.
Core comparison:
| Project | Programme | Portfolio |
| A project is an initiative undertaken for a limited period of time, and the goal is to create a specific output (product/service/result) as a result of this initiative. All projects have a clear beginning and end date, defined objectives and scope. | A programme consists of several projects that relate to each other i.e., they are dependent. Therefore, Programmes will be managed together in a coordinated manner for benefit than if the projects would be managed separately. Programmes have vast scope and duration and create a larger benefit than an individual project. | A portfolio consists of many different Collections of Projects/Programmes that will help an organisation achieve their Long-Term, Strategic Objectives Alignment with their Long-term strategic objective |
8. Deadline Is Close, Only 75% Work Done. A Change Ask Is Raised. What Must It Approve?
- A) More funding support
- B) More time or task rework
- C) Instant sponsor alert
- D) Lowering quality bars
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) More Time or Task Rework
A change will occur in your project when the limitations of the project change.
Smart Steps To Control Delays:
– Check Reality – See If More Time Is Possible
– Rework Tasks-Safely Trimming or Modifying Tasks
– Maintain Open Communication-With Stakeholders
– Check Risk Chain-See How Delays Will Affect Future Tasks To Conduct
– By Establishing an Open Flow of Change Management, Projects Will Not Fall Apart.
9. What Document Comes Out of Monitoring & Control?
- A) Project progress summary sheets
- B) Final sign-off paper
- C) Start agreement doc
- D) Vendor strategy plan
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: A) Project Progress Summary Sheets
The Progress Sheet Provides Leadership With The Next Action In Project Management.
- Typical sections of a Progress Sheet Are:
- Status View – The status of the Job
- Gap View – The differences between the planned work and actual work are evident
- Future View – The projected outcome-is evident
- Risk Notes – The threat & safety related responses- are available
10. On a Control Chart, What Is an Irregular Point?
- A) A point crossing the safe range bar
- B) Any point between the safe bars
- C) A point meeting quality but breaking stability
- D) The center average line point
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: A) A Point Crossing the Safe Range Bar
Control charts track process steadiness. Irregular points crossing bars show process shake-ups.
Key facts include:
- Stability vs. Quality: Bars show stability, specs show quality.
- Unusual Behavior: Irregular points need root checks
- Fix Actions: Cause analysis + fix steps required.
- Finding irregularities early keeps quality safe and stable.
11. What Is the Core Reason for Running Risk Analysis?
- A) Wiping out all risks forever
- B) Finding, judging, and sorting risks
- C) Making sure nothing goes wrong
- D) Preventing budget slips
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) Finding, Judging, and Sorting Risks
Risk analysis helps teams to manage risk effectively, not avoid it. The core part of risk analysis includes:
- Risk Spotting: Finding threats early.
- Risk Judging: Checking size and chances.
- Risk Sorting: Solving big threats first.
- Safety Plans: Creating fixed paths early.
- Smart risk control keeps delivery steady.
12. Which Trait Best Matches Qualitative Risk Analysis?
- A) Giving the risks’ exact figures
- B) Marking chance and pressure levels
- C) Running random outcome models
- D) Finding financial risk worth
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) Marking Chance and Pressure Levels
Qualitative risk checks are judgment-based, no figures needed.
Key traits include:
- Judgment Based: Uses expert inputs.
- Matrix Sorting: Big, medium, small risk tags.
- Fast Process: Quick sorting for next steps.
- No Math: No EMV or random outcome models.
This step always comes before math-based checks.
13. What Is the Best Way to Control a Big Threat That Rarely Happens?
- A) Delete it completely
- B) Shift it using contracts or coverage
- C) Let it be and track silently
- D) Keep extra budget ready
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) Shift It Using Contracts or Coverage
Typically, large threats, even when infrequent, can still cause significant damage. Consequently, it would be wise to remove risk from yourself and assign it to others.
Common methods of moving risk include:
- Insurance Coverage: Financial protection through insurance policies.
- Vendor Contracts: Contracts transferring responsibility from product/service provider to customer.
- Specialist Providers: Use of specialists for products/services with inherent risk.
- Recourse Provisions: Provision in contracts which provide for recovery in case of loss.
14. Which Tool Is Most Used for Math-Based Risk Checks?
- A) SWOT method
- B) Probability outcome modeling
- C) Cause–effect map
- D) Stakeholder influence chart
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) Probability Outcome Modeling
Monte Carlo simulations have become one of the industry’s leading methods for quantifying financial risk.
Monte Carlo simulation provides:
- Multiple Scenarios
- Risk Assessment based on data
- Identification of areas of potential risk: Budget and Schedule
- Data to make informed decisions based on accurate projections
15. When Can a Contingency Fund Be Used?
- A) For logged risks with ready response plans
- B) For unknown risks with no ready answers
- C) For inflation cost shifts
- D) As a team reward
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: A) For Logged Risks with Ready Response Plans
A contingency fund provides an opportunity for the protection of a project from the known risks.
Contingency funds cover:
- Documented Risk
- Funds added to the project’s Cost Baseline
- Funds that need formal approval for use
- Are not a form of back-up fund – Back ups cover unknown risks
16. Which Statement Best Matches Remaining Risk?
- A) The risk left after safety plans run
- B) The risk found after the project ends
- C) A risk found mid delivery
- D) A risk fully deleted
Correct Answer: A) The Risk Left After Safety Plans Run
Remaining risks are those which still stay after taking all the precautionary measures. For example: even after you install a security system in your house, there is always a risk of theft. Thus, the core traits of remaining risks are:
Hard to Delete: Some risks are tough to delete and they never go.
Logged Plan: if there is any extra control steps added to the process
17. What Is the Key Gap Between a Risk Check and a Risk Refresh?
- A) A check tests response success, a refresh finds fresh risks
- B) A check happens only at end, a refresh always runs
- C) A check is for leaders, a refresh is for teams
- D) A check is extra, refresh is always needed
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: A) A Check Tests Response Success, a Refresh Finds Fresh Risks
The key gap between a risk check and a risk refresh is their scope and frequency: a risk check is a quick, often ad-hoc review of known risks or specific indicators, while a risk refresh is a comprehensive, periodic re-evaluation of the entire risk landscape.
18. What Is a Risk breakdown structure (RBS)?
- A) Project output map
- B) Risk type grouping ladder
- C) Risk timeline flow
- D) Risk money summary
Correct Answer: B) Risk Type Grouping Ladder
In project management, the risk breakdown structure or RBS is a graph or flowchart representation that helps to describe and identify multiple risks in any given project. It provides a hierarchical representation of risks, beginning with the ones that are the most serious and most likely to occur, moving to the least serious and least likely to happen. The result is an easy-to-read map of potential project risks.
19. Which Risk Response Strategy Works Best for Opportunities That Can Boost Project Value?
- A) Mitigation
- B) Exploitation
- C) Acceptance
- D) Avoidance
Correct Answer: B) Exploitation
Exploitation is a forward-looking approach used to fully capitalize on positive risks and unlock maximum gains.
Key aspects include:
- Drives Higher Impact: Helps secure the best possible advantage from an opportunity.
- Action-Based Strategy: Requires deliberate steps instead of passive observation.
- Strengthens Project Edge: Can improve outcomes like speed, cost efficiency, or quality.
- Example: Allocating your most skilled team members to a high-value opportunity to guarantee success.
20. What Is the Main Purpose of a Decision Tree Analysis in Project Risk Planning?
- A) To build timeline charts for project execution
- B) To compare multiple risk outcomes and choose the best path
- C) To replace team accountability assignments
- D) To remove risk documentation work
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) To Compare Multiple Risk Outcomes and Choose the Best Path
Decision Tree Analysis, helps teams map different risk scenarios and evaluate the impact of each decision branch clearly. For example: Using a decision tree to decide whether to outsource development or keep it in-house based on cost and delivery risks.
Key benefits include:
- Scenario Mapping: Breaks risks into decision paths and possible results.
- Outcome Comparison: Helps pick the most value-driven or least harmful option.
- ‘Smart Decision Support: Uses structured logic instead of assumptions.
21. What Does the Project Charter Primarily Authorize?
- A) Procurement execution
- B) Stakeholder communication plan
- C) Project initiation and the project manager’s authority
- D) Risk mitigation budget
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: C) Project Initiation and the Project Manager’s Authority
The project charter, often created using platforms like LucidSpark PM Studio, formally launches a project and defines the project manager’s role.
Key highlights include:
- Official Project Approval: Confirms project start.
- Authority Definition: Grants power to manage resources and decisions.
- Goal Alignment: Documents business needs and outcomes.
Example: A charter approves a new ERP rollout and assigns leadership control to the PM.
22. Which Leadership Style Focuses on Inspiring and Motivating the Team?
- A) Directive
- B) Laissez-faire
- C) Transformational
- D) Transactional
Correct Answer: C) Transformational
Transformational leadership builds energy, creativity, and ownership in teams. This kind of leader helps their followers become innovative by providing opportunities to think creatively about how to solve problems for themselves and for the organisation.
For example, when a project manager encourages developers to go above and beyond what is required by the project requirements, the developer feels that their efforts are appreciated by the PM.
23. What Is the First Step in Developing a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)?
- A) Estimating costs
- B) Identifying deliverables
- C) Assigning team roles
- D) Scheduling tasks
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) Identifying Deliverables
WBS creation starts with breaking the projects into multiple key outcomes. The key points are:
- Deliverable-Led Breakdown: Focuses on what must be delivered.
- Hierarchical Structuring: Divides into smaller work packages
- Clarity Boost: Helps avoid confusion later.
For example: A website project starts WBS by listing UI, backend, and hosting as deliverables.
24. What Does CPI > 1 Signify in Earned Value Management?
- A) Over budget
- B) Under budget
- C) Behind schedule
- D) Scope change
Correct Answer: B) Under Budget
CPI is a measure of cost performance. If your CPI is greater than 1, you’re resulting in a gain in cost performance.
The additional value you are gaining from each dollar spent is greater than what you spent so far. For example, if the CPI for this project is 1.2, you have gained 20% more in cost efficiency as compared to the original estimation.
25. What Is a Key Goal of Sprint Retrospective in Agile?
- A) Assigning new risks
- B) Improving team process and future sprint outcomes
- C) Approving budgets
- D) Updating project charter
Correct Answer: B) Improving Team Process and Future Sprint Outcomes
Sprint retros focus on lessons and improvements.
Key points:
- Fixing Process = better delivery;
- Co-ordinating Team = open feedback;
- Being Prepared for Future Sprints = improving future performer capabilities.
For example, the team identifies and resolves bottlenecks to streamline the process.
26. Which Contract Type Places the Highest Cost Risk on the Buyer?
- A) Fixed-price
- B) Cost-plus
- C) Time & Material
- D) Lump sum
Correct Answer: B) Cost-Plus
A Cost-Plus Agreement reimburses the Seller, thereby transferring any financial risk to the Buyer. The Buyer is responsible for any cost overruns. The Seller continues to be compensated on a profit basis.
For example: the Buyer pays for the actual cost of development and a Fee.
27. What Does Scope Creep Most Commonly Result From?
- A) Approved change requests
- B) Uncontrolled or undocumented changes
- C) Risk register updates
- D) Vendor delays
Correct Answer: B) Uncontrolled or Undocumented Changes
Scope creep grows when changes bypass the process.
- Delays Delivery: when there is more work than planned.
Raises Cost: more work means more resources consumed, which ultimately raises cost. - Project Delay: The deadline shifts unintentionally
For Example: without considering time, budget, resources, there are extra features added in the project without anyone approval.
28. What Is the Key Role of a PMO?
- A) Run all project tasks
- B) Provide governance, standards, and support
- C) Hire project teams
- D) Approve all procurement
Correct Answer: B) Provide Governance, Standards, and Support
A PMO is mainly responsible to ensure projects run in a smooth manner. Their duties are:
- Setting processes and templates
- Maintain project delivery standards
- Taking project updates and training team
<h3>29. What Does Risk Transference Mean?
- A) Removing risk
- B) Shifting risk to another party
- C) Accepting risk
- D) Reducing impact internally
Correct Answer: B) Shifting Risk to Another Party
Transference means shifting the financial and operational impact of risks to third parties
Key points:
- Ownership moves to vendor/insurance.
- The project stays protected.
Example: Taking insurance for legal risk.
30. What Is the Main Benefit of a Stakeholder Engagement Assessment Matrix?
- A) Calculates budget
- B) Shows stakeholder interest vs influence
- C) Assigns risks
- D) Creates schedule
Correct Answer: B) Shows Stakeholder Interest vs Influence
This matrix maps stakeholder power and interest.
Key benefits:
- Priority Mapping: Helps decide engagement approach.
- Clear Influence View: Avoids mismanagement.
- Engagement Planning: Helps customize communication.
Example: CFO strong influence → managed closely.
31. What Does EMV Help Project Managers Quantify?
- A) Team size
- B) Financial exposure of risk events
- C) Sprint velocity
- D) Stakeholder expectations
Correct Answer: B) Financial Exposure of Risk Events
The expected monetary value will measure how much a risk will cost you if it is incurred.
Key aspects are:
- Supports risk ranking by potential money impact
- Guides budget buffering in establishing reserves
Example: A potential impact of ₹5L with a probability of occurring 30% would have a potential EMV of ₹1.5L.
32. Which Technique Helps Gain Consensus Without Face-to-Face Discussion?
- A) Brainstorming
- B) Interviews
- C) Delphi Technique
- D) SWOT
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: C) Delphi Technique
In the Delphi Technique, experts can achieve consensus on an extremely important risk through anonymous questionnaires.
Key Points:
- No Dominance Bias: it minimises peer pressure influence.
- Multiple levels: Reduces risk views or estimates.
For example, experts rank risks anonymously.
33. What Is the Primary Focus of Schedule Management?
- A) Reducing risk
- B) On-time delivery of project outcomes
- C) Team hiring
- D) Contract selection
Correct Answer: B) On-Time Delivery of Project Outcomes
The Schedule Management Plan will help monitor for delays and measure the progress of a project against the established project schedule.
Key Focus Areas:
- Scheduling Activities
- Controlling Delays
Example: Weekly tracking of milestones.
- 3 What Is a Risk Register Used For?</h3>
- A) Track project scope
- B) Log risks, priority, owners, and response plans
- C) Approve contracts
- D) Design sprints
Correct Answer: B) Log Risks, Priority, Owners, and Response Plans
When a Risk Register is created, all risks will have the following key elements for continued monitoring:
- Priority Ratings
- Response Tags
Example: Risk created for supplier delay, response plan for the risk.
35. What Is the Best Response to a Risk That Cannot Be Avoided or Mitigated?
- A) Transfer
- B) Accept
- C) Escalate always
- D) Ignore
Correct Answer: B) Accept
Acceptance is feasible when no other response is available or there is no ability for a team to respond.
Key Facts:
- The team must continue to monitor it;
- the team will not create a new response for it (the initial response).
Example: Minor unavoidable compliance effort.
36. What Does an SPI < 1 Indicate?
- A) Under budget
- B) Behind schedule
- C) No risks exist
- D) Scope approved
Correct Answer: B) Behind Schedule
SPI = EV / PV, schedule efficiency metric.
Meaning:
Less progress than planned so far.
Example: SPI 0.8 means 20% delay in progress.
37. Which Method Best Helps Identify the Root Cause of a Defect?
- A) Control chart
- B) Ishikawa diagram
- C) Sprint planning
- D) Budget forecast
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) Ishikawa Diagram
Ishikawa diagram is also known as fishbone, used for cause analysis.
Key points:
- Groups Causes: Process, people, tools, etc.
- Finds Weak Spots: Helps corrective planning.
Example: Finds reason for repeated UI bugs.
38. What Is the Main Goal of Project Integration Management?
- A) Work in silos
- B) Align all moving parts and decision flows
- C) Only manage budget
- D) Only manage risks
Correct Answer: B) Align All Moving Parts and Decision Flows
Integration helps to keep project pieces synced.
Key benefits of project integration management are:
- Increased accountability from team members
- Integration management means reviewing all project teams and analysing where efficiency can be improved.
Example: Syncing agile + vendor delivery plan.
39. What Is a Key Input to Risk Response Planning?
- A) Project charter
- B) Risk register
- C) Vendor hiring sheet
- D) Sprint retro
Correct Answer: B) Risk Register
Risk register feeds response planning. It means that in a project, a team designs responses based on logged risks.
40. What Does a Fixed-Price Contract Protect the Buyer From?
- A) Scope clarity
- B) Cost overruns
- C) Team motivation
- D) Sprint delays
Correct Answer: B) Cost Overruns
A fixed-price contract is a type of agreement where the total cost of a project is agreed upon upfront, regardless of changes in circumstance or scope.
Example: Lump sum software delivery contract.
41. What Is a Milestone?
- A) Smallest WBS unit
- B) A key checkpoint or project progress marker
- C) Budget buffer
- D) Risk type
Correct Answer: B) A Key Checkpoint or Project Progress Marker
Milestones are significant markers that show all important accomplishments, pivotal events, or the completion of key deliverables within a project’s timeline. For a project manager, it is crucial to understand milestones and how to use them to track performance.
Example: Beta release sign-off date.
42. What Is Risk Prioritization Based On?
- A) Emotion
- B) Probability × Impact
- C) Team size
- D) Vendor role
Correct Answer: B) Probability × Impact
Risks may be infinite, but our time and budget are not. Risk prioritization is the technique to analyse potential risk and deciding the order in which their mitigation deserves your time and attention.
Example: High prob + high impact → top rank.
43. Which Risk Response Enhances Opportunity Probability?
- A) Mitigate
- B) Exploit/Enhance
- C) Transfer
- D) Avoid
Correct Answer: B) Exploit/Enhance
Exploit
When there’s a positive risk or opportunity you need to exploit, you require to add more tasks or change the management plan to take benefit.
Enhance
This strategy helps to nurture potential opportunities and maximise its upside for the project. It is ideal when the risk has benefits and the cost and efforts to enhance the risk are justified.
Example: Invest extra budget to win market edge.
44. What Is a Hybrid Project?
- A) Only agile
- B) A mix of predictive + agile delivery
- C) No risk project
- D) Only charter-based
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) A Mix of Predictive + Agile Delivery
Hybrid project management is a technique that blends principles and practices from both traditional project management methodologies, such as waterfall, and agile project management methodologies. Being a flexible and adaptive approach, this method aims to use the strength of various other methodologies that suit the specific project requirement.
For example: Agile dev + fixed compliance scope.
45. What Is a Change Request?
- A) Charter rewrite
- B) Formal proposal to modify scope, schedule, cost, or quality
- C) Risk deletion
- D) Team reshuffle
Correct Answer: B) Formal Proposal to Modify Scope, Schedule, Cost, or Quality
In project management, a change request is a kind of formal proposal for a change to products or systems. These change requests come from clients or stakeholders who want to add any other features or change existing product design.
Example: Feature addition via approval flow.
46. Which Tool Is Great for Real-Time Team Collaboration?
- A) Excel only
- B) Miro/Risk boards
- C) Contracts
- D) Charter doc
Correct Answer: B) Miro/Risk Boards
Example: Team maps risks visually.
47. What Does Risk Escalation Mean?
- A) Transfer
- B) Sending risk to higher authority for decision or action
- C) Removing risk
- D) Ignoring risk
Correct Answer: B) Sending Risk to Higher Authority
Example: CFO approval needed for cost threat.
48. What Is a Project Baseline?
- A) Final delivery
- B) Approved snapshot of scope, schedule, and cost for tracking
- C) Risk list
- D) Team size
Correct Answer: B) Approved Snapshot of Scope, Schedule & Cost
Example: Original plan used for variance checks.
49. What Is Risk Mitigation?
- A) Shift risk
- B) Reduce probability or impact using internal action
- C) Delete risk register
- D) Escalate always
Correct Answer: B) Reduce Probability or Impact
Example: Add backup developer to avoid delay.
50. What Is Velocity in Agile?
- A) Cost metric
- B) Work completed in a sprint cycle
- C) Charter type
- D) Risk score
Correct Answer for these PMP exam questions: B) Work Completed in a Sprint Cycle
Example: 40 story points delivered.
51. What Is the Main Goal of Quality Planning?
- A) Find stakeholders
- B) Set standards to ensure correct and acceptable delivery
- C) Write contracts
- D) Log risks
Correct Answer: B) Set Standards for Correct Delivery
Example: Define testing, UI, and performance bars.
52. What Is a Threat?
- A) Positive risk
- B) A negative uncertain event
- C) Work package
- D) KPI
Correct Answer: B) Negative Uncertain Event
Example: Delay, defect, or cost spike.
53. What Is an Opportunity?
- A) Negative risk
- B) Positive uncertain event that can increase value
- C) KPI
- D) Contract
Correct Answer: B) Positive Uncertain Event
Example: Early delivery bonus possibility.
54. What Is the Best Way to Avoid Team Conflict?
- A) Ignore
- B) Clear roles + communication + integration alignment
- C) Transfer
- D) Only budget
Correct Answer: B) Clear Roles + Communication + Integration Alignment
Example: RACI chart + daily sync.
55. What Does a Risk Audit Do?
- A) Deletes risks
- B) Checks if risk processes are being followed properly
- C) Approves scope
- D) Checks velocity
Correct Answer: B) Checks if Risk Processes Are Followed
Example: Auditing risk ownership logs.

*instituteprojectmanagement.com
Free Courses
Explore courses related to Data science




How Can Jaro Education Help You Crack the PMP Exam?
Getting a PMP certification takes focus, consistency, and a solid study plan. To make your preparation stronger, Jaro Education’s online courses give you step-by-step guidance and real-world learning, created by experienced industry mentors.
What you get with Jaro Education:
- Easy-to-follow lessons that cover the full PMP syllabus
- Live sessions and expert support to clear doubts quickly
- Practice questions and case-based learning to improve accuracy
- Smart tips to help you plan your study time better
- Career guidance to help you grow after certification
- We also offer job-focused management programs that build project leadership skills along with PMP prep.
Want the right direction? Book your free, 1-on-1 career counseling session today and kick-start your PMP journey with confidence.
For more information, check the official website.
Conclusion
The above-mentioned PMP exam questions and answers give you a clear idea of real exam patterns and help you understand risk, conflict, and decision-making concepts easily. With the right study plan and guided practice, you can improve accuracy and confidence. Jaro Education’s expert-led courses and counseling support can make your PMP preparation smarter and more effective.
Frequently Asked Questions
PMI sometimes checks (audits) applications at random to confirm that the details you shared are correct. If your application gets selected, you’ll need to upload proof of your project work experience and your training certificates. After PMI reviews and accepts your documents, you can go ahead and book your exam slot.
Related Courses
Explore our programs
Find a Program made just for YOU
We'll help you find the right fit for your solution. Let's get you connected with the perfect solution.

Is Your Upskilling Effort worth it?

Are Your Skills Meeting Job Demands?

Experience Lifelong Learning and Connect with Like-minded Professionals







