SQL vs NoSQL Databases: Pros, Cons, and Real-World Use Cases

Table Of Content
- What Is SQL?
- Examples of SQL Databases
- Use Cases for SQL Databases
- What Is NoSQL?
What Is SQL?
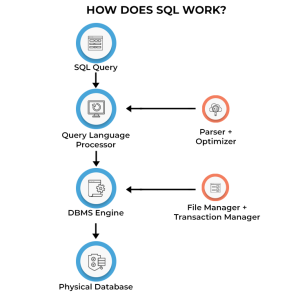 *spiceworks.com
*spiceworks.comSQL (Structured Query Language) is a standard programming language that allows users to work with relational database systems regardless of whether or not you are a technical professional or an end user. SQL allows users to create, access, edit and retrieve information out of relational databases efficiently.
SQL Databases represent stored information in the form of tables, cols & rows. Each relationship between 2 tables in SQL is represented by its primary/unique key (PK) and foreign key (FK). Therefore, data remains consistent between large sets of records that can grow significantly over time due to increased storage costs etc.
One of the main differences between traditional SQL Database Systems and SQL Cloud Database Systems is their ability/capacity to Scale. SQL Database Systems generally have a Vertical Scale Factor. For example, a Server typically has a specific amount of RAM, Storage Space, Intel CPU Speed etc while SQL Cloud Database Systems tend to exhibit Horizontal Scalability Characteristics. For example, online server performance increases as the number of online servers increases.
Key Characteristics of SQL Databases
- It has fixed, predefined schema
- Strong relational integrity
- Table-based data storage
- ACID-compliant transactions
- Best suited for structured data
Examples of SQL Databases
Oracle Data Base
Oracle is typically referred to as the most widely accepted Enterprise-level Relational Database management system because of its high levels of dependability and security. It also manages crucial systems found in finance, public telephone services, and government operations.
MySQL
MySQL is an open source Relational Database Management System for developers who are creating Web based applications because of its easy to use functionalities. It has substantial community support, and can work in conjunction with certain programming languages such as PHP and technologies like modern Web Frameworks.
MariaDB
It is a version of MySQL developed after Oracle acquired the rights to MySQL which provides additional performance benefits as well as the benefit of being governed by a fully open-source Licensing Model.
PostgreSQL
It is also an open-source Relational Database Management System with a robust feature set. PostgreSQL has outstanding indexing capabilities, extensible, and is compliant with the ACID rules of Transaction Processing thus supporting large and complex data bases and workloads.
Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL)
MSSQL is widely used in enterprise environments, especially where Microsoft ecosystems dominate. It supports transaction-heavy applications, reporting systems, and business intelligence tools.
SQLite
SQLite is a lightweight, serverless SQL database embedded directly into applications. It requires zero configuration and is commonly used in mobile apps, browsers, and small-scale systems.
Use Cases for SQL Databases
1. Transactional Applications
Banking systems, payment gateways, and ERP platforms rely on SQL databases because of their strict ACID compliance, ensuring every transaction is accurate and recoverable.
FYI: ACID compliance in databases ensures transactions are processed reliably using four key properties: Atomicity (all or nothing), Consistency (valid state only), Isolation (independent execution), and Durability (permanent save).
2. Reporting and Analytics
SQL databases handle complex queries, joins, aggregations, and reporting extremely well, making them ideal for dashboards and business intelligence systems.
What Is NoSQL?
 *datascientest.com
*datascientest.comMany people believe that NoSQL means no structure or relationships. But the true definition is: NoSQl is a database that stores data in non-tabular forms and allows flexible, dynamic schemas. Since the rise of cloud computing, big data, and IoT applications, NoSQL has gained immense popularity.
Talking from the scalability point of view, NoSQL databases scale horizontally, meaning they distribute data across multiple servers or nodes. This makes them ideal for high-traffic, globally distributed applications.
Common NoSQL Data Models
- Document-based (MongoDB, CouchDB)
- Key-value stores (Redis, DynamoDB)
- Column-family stores (Cassandra, HBase)
- Graph databases (Neo4j)
Use Cases for NoSQL Databases
1. Big Data and Real-Time Analytics
NoSQL databases handle massive volumes of rapidly changing data efficiently, making them suitable for analytics pipelines and streaming platforms.
2. Content Management and Personalization
Applications managing user profiles, preferences, recommendations, and social feeds benefit from NoSQL’s flexible schema design.
Key Differences Between SQL and NoSQL
| Aspects | SQL Database | NoSQL Database |
| Structure | SQL databases are table-based with fixed schemas. | NoSQL databases use documents, key-value pairs, graphs, or column stores with flexible structures. |
| Scalability | When we talk about scalability in SQL vs NoSQL, SQL systems scale vertically | while NoSQL systems scale horizontally across distributed clusters. |
| Language | SQL databases use standardized SQL queries. | NoSQL databases may use JSON-based queries, APIs, or custom query languages. |
| Support And Maturity | SQL has decades of community support and tooling. | NoSQL ecosystems are growing but vary by platform. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of SQL Databases
Advantages of SQL Databases
*turing.com
Strong Data Integrity
SQL databases are designed to ensure that the data entered into them maintains its accuracy through the use of constraints like primary keys, foreign keys, unique indexes, etc. This protection is critical in any application where the accuracy of the data is of utmost importance such as banking, medical records, financial reports.
ACID-Compliant Transactions
ACID compliance is one of the primary benefits of SQL databases. Every transaction is guaranteed to fully and safely complete, even when there are failures in the system. For example: the transfer of money from one bank account to another will either be fully executed or not at all by SQL.
Mature Tools and Ecosystem
SQL databases benefit from a long-standing ecosystem of tools, frameworks, monitoring systems, and integrations. Developers have access to powerful query optimizers, admin dashboards, backup tools, and debugging utilities, making SQL databases easier to manage in production environments.
Standardized Query Language
SQL is based on ANSI standard and ISO standard so all major Databases have a SQL Core Language. It is basically an error-correction free language that does not vary between Database Systems.
Reliable for Structured Data
Structured data represents a well-defined format of stored information. Therefore, in a table format with rows and columns, it is very convenient to insert customer records, invoice records, inventory records, and employee records.
Disadvantages of SQL Databases
Limited Horizontal Scalability
SQL databases offer vertical scalability. Therefore, upgrading server hardware is required to increase performance.
Rigid Schema Design
SQL databases ask for predefined schemas. Whether you’re adding a new row or modifying existing data types, it requires migrations and downtime.
Performance Bottlenecks at Scale
SQL databases may experience performance issues. Heavy joins, large transactions, and locking mechanisms can slow response times if not carefully optimized.
Higher Infrastructure Costs
Enterprise-grade SQL solutions can be expensive due to licensing fees, hardware requirements, and maintenance overhead. Even open-source SQL databases may incur higher operational costs at scale.
Advantages and Disadvantages of NoSQL Databases
Advantages of NoSQL Databases
Flexible Schema
NoSQL databases do not require a fixed schema. Each document or record can have a different structure, allowing developers to adapt quickly as application requirements evolve. This flexibility is ideal for agile development and rapidly changing data models.
Horizontal Scalability
NoSQL systems are built for horizontal scaling. You can add more servers to handle increased traffic or data volume. This makes them highly suitable for cloud-based and distributed applications.
High Performance for Large Workloads
By optimizing data storage for specific access patterns, NoSQL databases deliver fast read and write performance, even under heavy workloads. This is particularly useful for real-time applications like gaming, messaging, and live analytics.
Native Support for Unstructured Data
NoSQL databases handle JSON documents, key-value pairs, graphs, and wide-column data naturally. This makes them perfect for social media data, IoT streams, logs, and multimedia content.
Disadvantages of NoSQL Databases
Consistency Trade-Offs
Many NoSQL systems prioritize availability and partition tolerance over strict consistency. This can lead to eventual consistency, where data may be temporarily out of sync across nodes.
Limited ACID Support in Some Systems
Not all NoSQL databases provide full transactional guarantees. They may not be suitable for applications requiring strict financial or transactional accuracy.
Complex Data Modeling
Unlike SQL, where relationships are handled through joins, NoSQL databases require developers to design data models based on access patterns.
Less Mature Tooling
Although improving rapidly, NoSQL ecosystems may lack the depth of tooling available for SQL databases, especially for advanced reporting, debugging, and analytics.
When to Use SQL and NoSQL (Comparison Table)
| Factor | SQL | NoSQL |
| Data Structure | Best suited for structured, relational data with fixed schemas | Designed for semi-structured or unstructured data with flexible schemas |
| Scalability | Primarily vertical scaling; horizontal scaling is complex | Native horizontal scaling across distributed systems |
| Consistency | Strong consistency with full ACID compliance | Configurable consistency; often eventual consistency |
| Query Complexity | Excellent for complex queries, joins, and aggregations | Optimized for simpler, high-speed queries |
| Best For | Financial systems, ERP, reporting, analytics | Big data, real-time apps, IoT, content platforms |
Why Jaro Education?
Understanding SQL vs NoSQL database architecture is a foundational skill for data professionals, developers, and managers. Jaro Education bridges the gap between theory and real-world application through industry-aligned online programs, hands-on case studies, and expert-led instruction.
Learners gain exposure to real enterprise scenarios, helping them apply database concepts confidently in modern business environments.
Conclusion
If you want to deep dive into databases, take online courses from Jaro Education.
Frequently Asked Questions
SQL uses structured tables with fixed schemas, while NoSQL supports flexible, non-tabular data models.
Yes. Many modern architectures combine SQL for transactions and NoSQL for scalability and analytics.
Related Courses
Explore our programs
Find a Program made just for YOU
We'll help you find the right fit for your solution. Let's get you connected with the perfect solution.

Is Your Upskilling Effort worth it?

Are Your Skills Meeting Job Demands?

Experience Lifelong Learning and Connect with Like-minded Professionals







