
OLTP vs OLAP: Understanding The Differences And Use Cases
Each second, there are millions of digital transactions taking place in the world. From shopping at Amazon to booking an Uber ride, to funding a digital wallet and changing the status on an Instagram profile, these activities are limitless. Thus, there are huge data architectures that take place behind the scenes of these seemingly easy actions. In this, there are two essential systems that make everything possible i.e., OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) and OLAP (Online Analytical Processing).
OLTP is responsible for managing the scheduling of all day-to-day transactions, while OLAP provides businesses with practical means for making more effective decisions based on their data.
And today's organisations are mainly relying on real-time data to gain insight into future trends through prediction models. Thus, it is more essential than ever before to understand how OLTP vs OLAP differ, so that they can effectively leverage both types of systems. In this blog, we will discuss each of these systems in detail and also show examples of how businesses use these systems, helping you grasp real-world OLTP vs OLAP applications.
Table Of Content
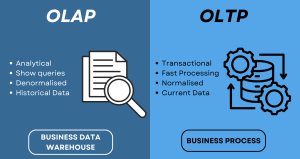
What Is OLTP?
Key Characteristics of OLTP
What Is OLAP?
Key Characteristics of OLAP
OLTP vs OLAP: Key Differences
When to Use OLTP?
Real-time OLTP Use Cases
When to Use OLAP?
Can OLTP and OLAP Work Together?
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
*boardinfinity.com
What Is OLTP?
The majority of operational systems within businesses today, whether they be banks completing cash withdrawals, e-commerce businesses accepting customer credit card payments, or hospitals creating new patient profiles are OLTP.
Key Characteristics of OLTP
1. High Volume of Transactions
OLTP systems have the capability of processing thousands (if not millions) of transactions every second. While individual transactions tend to be small in size, they occur at a greater frequency than in other business operations. Therefore, it is well suited to areas of the industry where there is a constant flow of user activity requiring prompt and continued processing of that activity.
2. Real-Time Process
All operations (e.g. payment, order update, or login) must be accomplished in real-time; therefore, there can be no delays in the capturing of real-time events. If users are presented with delayed information, they will not be satisfied with the level of service and may go to a competitor where they have access to timely and accurate information.
3. Data is Highly Structured
OLTP Databases are organised according to Relational Schemas and must be normalized to prevent redundancies. This organization of data in a highly structured manner promotes data integrity by providing and increasing transaction speed.
4. ACID Compliance
OLTP maintains assurance of transaction reliability through the following attributes:
- Atomicity: A transaction either completes entirely or does not complete at all.
- Consistency: Data is kept valid at all times.
- Isolation: No other transactions can occur that conflict with a Transaction.
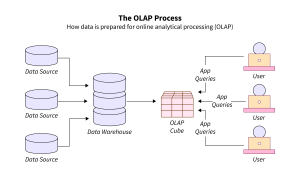
What Is OLAP?
Businesses can benefit from OLAP by gaining insights about trends; analysing performance; forecasting future sales; identifying risk; and making strategic business decisions.
OLTP vs OLAP systems are designed to pull data from multiple sources, including OLTP databases. The OLAP systems combine the extracted data from different sources into one source, and then present the data in a graphical or multidimensional format that is easy for analysts to work with.
Key Characteristics of OLAP
1. Complex Query Support
OLAP handles multi-dimensional queries that involve aggregations, comparisons, and trend analysis.
2. Historical Data Storage
Unlike OLTP, OLAP stores years of data for pattern discovery. Thus, it is easier for organisations to access any year data any time.
3. Multi-Dimensional Analysis
Data can be analysed across multiple dimensions. This helps in generating answers like: “Which cities saw the highest growth in women’s footwear sales in 2024 Q3?“
For example:
- Product category
- Region
- Year
- Customer type
4. Read-Optimised
OLAP is designed for fast reading and analysis, not frequent data updates.
5. Supports Business Intelligence (BI)
OLAP helps business with:
- Dashboards
- Reports
- Data visualizations
- KPIs
- AI/ML analytics
6. Helps in Strategic Decisions
Leaders depend on OLAP insights for planning budgets, marketing campaigns, and sales projections.
OLTP vs OLAP: Key Differences
| Feature | OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) | OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) |
| Full Form | Designed to record and process day-to-day business transactions in real time. | Designed to analyze large datasets and support decision-making with historical insights. |
| Primary Purpose | Ensures smooth execution of operational tasks like payments, orders, and updates. | Helps businesses analyze trends, patterns, and performance for strategic planning. |
| Data Type | Works with real-time, current operational data that reflects immediate activity. | Works with historical, aggregated, and consolidated data collected over months or years. |
| Typical Users | Used by frontline staff—cashiers, bank employees, customer support teams, and customers. | Used by analysts, managers, executives, and data scientists for insights and reporting. |
| Data Structure | Uses highly normalized relational databases to ensure fast updates and minimal redundancy. | Uses de-normalized schemas (Star/Snowflake) to speed up complex analytical queries. |
| Transaction Size | Handles small, quick, atomic transactions affecting a few records. | Handles large, complex analytical operations that scan and aggregate massive datasets. |
| Query Type | Simple, predefined, short queries like checking inventory or updating user details. | Complex, multi-dimensional queries like revenue comparisons, forecasting, or KPI analysis. |
| Performance Goal | Optimized for ultra-fast processing of individual records with low latency. | The difference between OLAP and OLTP Optimized for fast aggregation and computation across millions of rows. |
| Write vs Read | Write-heavy. It helps with continuous inserts, updates, and deletes from many users. | Read-heady, it is primarily used to read and analyse data, with fewer frequent updates. |
| Examples | ATM transactions, POS billing, e-commerce orders, airline bookings, banking operations. | Dashboards, BI reports, forecasting tools, trend analysis, market research systems. |
| Storage | Stores only real-time operational data; older records often archived. | Stores huge volumes of historical data for long-term analysis and predictive modeling. |
| Use Case | The OLAP and OLTP difference in terms of use case is that it is ideal for running and managing daily business operations. | Ideal for strategic decision-making, performance evaluation, and planning. |
*scaler.com
When to Use OLTP?
Real-time processing
For any application that must update its data instantly (payment whether via credit card, web check-in, or an order confirmation), an OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) system is required to provide users with no lag time (or “down time”) in between completing their critical transactions. As such, OLTP has become the foundation for applications that require users to get immediate feedback and allow seamless interaction.
High availability
Many businesses especially in the banking, hospitality and retail industries cannot afford to have downtime. In addition to being able to run 24×7 with little to no interruptions, OLTP supports auto-failover capabilities so customers can continue to engage with their respective businesses, even if the server has issues.
Fast and accurate transactions
For any OLTP system, there can be no duplication, loss or inconsistency of data. The OLTP system follows ACID (Atomic, Consistent, Isolated, Durable) properties to ensure all data is absolutely reliable. In industries such as finance and operations where even one error could lead to significant financial or operational losses, nail biting mistakes are simply not an option.
Daily operations management
If you are using a system for internal and/or external purposes, OLTP is necessary to support your routine operational tasks (order placement, order updates, logging into user accounts and checking inventory). OLTP essentially keeps the heart beating for the everyday operational processes of your business.
Real-time OLTP Use Cases
E-commerce Websites
E-commerce websites rely on real-time data processing to handle thousands of customer actions every second. Every time a user adds a product to the cart, places an order, makes a payment, or updates delivery details, the system must record it instantly and accurately. Fast processing ensures smooth checkouts, correct inventory updates, and a reliable shopping experience without delays or errors.
Banking Apps
Banking apps need secure and instant transaction handling. Actions like money transfers, bill payments, balance updates, and account logins happen continuously. The system ensures each transaction is processed immediately, maintaining data accuracy and preventing duplicate or failed entries. This real-time performance builds customer trust and allows users to manage their finances anytime without interruption.
Ticket Booking Engines
Ticket booking engines handle high traffic, especially during peak hours. When users search for availability, select seats, and complete payments, the system must update seat status instantly. Real-time processing prevents double bookings, confirms reservations immediately, and delivers tickets without delays, ensuring a smooth and stress-free booking experience for users.
*scaler.com
When to Use OLAP?
Data-driven decision making
To support strategic planning, organizations and/or their leaders require an understanding of their company performance as well as their industry performance, Market opportunities, and trends associated with customer behavior. OLAP may be the best way to produce the required performance metrics and reports (dashboards).
Complex analytical queries
OLAP has the ability to quickly run complex queries for analysing aggregate values, ranking, forecasting, and comparing. For example: OLAP can access the millions of rows of an organisation’s data, and get analytical insight in seconds. This is useful when organisations are analysing multidimensional data from multiple departments.
Consolidated historical analytics
For any retailer, the long-term analyses of their sales performance over time, including regional breakdowns by geographical area, are essential to their business model. An OLAP application allows the user to store their historical date information so they can run year-over-year, month-over-month, and trend analysis to identify patterns in their Individual stores and across their Enterprise.
Use cases include:
- Marketing analysis
- Profitability analysis
- Supply chain optimization
- Sales forecasting
- Customer churn prediction
- Financial performance analysis
- Market trend analysis
- Product demand forecasting
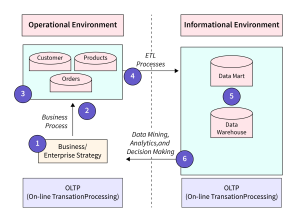
Can OLTP and OLAP Work Together?
1. OLTP Generates Real-Time Data
OLTP is the source of all real-time transaction data including payments, orders and bookings.
2. OLAP Analyzes OLTP Data
OLAP analyzes OLTP data through periodic data movement into:
- Data Warehouses
- Data Lakes
- Business Intelligence Platforms
- With OLAP’s analysis of OLTP data, companies can:
- Enhance Customer Experience
- Streamline Operations
- Forecast Future Demand
- Tailor Marketing Campaigns
- Identify Anomalies/Fraud
3. New Technologies Support Integration of OLTP and OLAP
New technologies such as Snowflake, BigQuery, Databricks, and AWS Redshift offer the ability to easily move data from OLTP to OLAP and perform real-time analytics on OLTP data.
OLTP and OLAP, when used in combination, create a unified ecosystem of data that supports both an organization’s Operations and Strategy.
Conclusion
If you want to have a flourishing career in data, analytics, software engineering, business intelligence, digital transformation, and/or cloud technology, knowing the difference between OLTP vs OLAP is imperative. As AI, automation, and data are becoming increasingly important to the way businesses operate, those who have an understanding of these systems will be the most desirable candidates.
Building your career in technology/data requires upgrading your current skill set, whether at an educational institution or through other means. With a reputation as a globally recognized leader in building strong online education programs with a focus on industry, Jaro Education provides learners with the skills and experience needed for their chosen career.
If you are looking to pursue a career in either Data Analytics or Business Management or work in the IT Systems area of business, Jaro has an outstanding platform to help you launch your career.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, OLTP systems have been designed specifically to handle high-speed processing of numerous small transactions while OLAP systems are focused on conducting complex analytical queries, which take more time to execute.
Commonly used OLAP software includes Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, Qlikview, Snowflake, Amazon Web Services (AWS) Redshift, Google BigQuery, and SAP BW.\

